Abstract
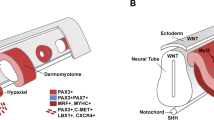
To investigate the role of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in the differentiation process of skeletal muscle, we analyzed the in vivo expression of BMP2 and BMP4, of BMP receptors (BMPR) IA, IB, and II, and of activin receptors (ActR) IA, II, and IIB in mouse tongue muscle between embryonic day 11 (E11) and E17. The mRNA expression levels for BMP2 were 5-fold to 11-fold greater than those for BMP4 between E13 and E17 (P < 0.05-0.01). Expression of the BMP2, BMPRIB, ActRIA, ActRII, and ActRIIB proteins was first observed at E13. Expression of BMP2 and BMPRIB was detected in the whole area of the differentiating muscle tissues identified by immunostaining for fast myosin heavy chain (fMHC), but that of ActRIA, ActRII, and ActRIIB was detected only in the peripheral area of the differentiating muscle tissues. In the E15 tongue, all of the BMPs, BMPRs, and ActRs studied herein were expressed in the whole area of the differentiating muscle tissues identified by immunostaining for fMHC. These results suggest that BMPs play a role in the differentiation of tongue muscle tissues at E15 but have little or no effect at E13.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano O, Yamane A, Shimada M, Koshimizu U, Nakamura T, Iseki S (2002) Hepatocyte growth factor is essential for migration of myogenic cells and promotes their proliferation during the early periods of tongue morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Dev Dyn 223:169–179
Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, Daubas P, Hadchouel J, Meilhac S, Montarras D, Rocancourt D, Relaix F (2003) The formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb. J Anat 202:59–68
Chalaux E, Lopez-Rovira T, Rosa JL, Bartrons R, Ventura F (1998) JunB is involved in the inhibition of myogenic differentiation by bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Biol Chem 273:537–543
Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 22:233–241
Cobourne MT, Sharpe PT (2003) Tooth and jaw: molecular mechanisms of patterning in the first branchial arch. Arch Oral Biol 48:1–14
Cossu G, Borello U (1999) Wnt signaling and the activation of myogenesis in mammals. EMBO J 18:6867–6872
Dietrich S, Schubert FR, Healy C, Sharpe PT, Lumsden A (1998) Specification of the hypaxial musculature. Development 125:2235–2249
Duprez DM, Coltey M, Amthor H, Brickell PM, Tickle C (1996) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) inhibits muscle development and promotes cartilage formation in chick limb bud cultures. Dev Biol 174:448–452
Feng JQ, Harris MA, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Feng M, Mundy GR, Harris SE (1994) Structure and sequence of mouse bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene (BMP-2): comparison of the structures and promoter regions of BMP-2 and BMP-4 genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1218:221–224
Feng JQ, Chen D, Cooney AJ, Tsai MJ, Harris MA, Tsai SY, Feng M, Mundy GR, Harris SE (1995) The mouse bone morphogenetic protein-4 gene. Analysis of promoter utilization in fetal rat calvarial osteoblasts and regulation by COUP-TFI orphan receptor. J Biol Chem 270:28364–28373
Florini JR, Ewton DZ, Coolican SA (1996) Growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system in myogenesis. Endocr Rev 17:481–517
Gersbach CA, Byers BA, Pavlath GK, Garcia AJ (2004) Runx2/Cbfa1 stimulates transdifferentiation of primary skeletal myoblasts into a mineralizing osteoblastic phenotype. Exp Cell Res 300:406–417
Katagiri T, Yamaguchi A, Komaki M, Abe E, Takahashi N, Ikeda T, Rosen V, Wozney JM, Fujisawa-Sehara A, Suda T (1994) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 converts the differentiation pathway of C2C12 myoblasts into the osteoblast lineage. J Cell Biol 127:1755–1766
Katagiri T, Akiyama S, Namiki M, Komaki M, Yamaguchi A, Rosen V, Wozney JM, Fujisawa-Sehara A, Suda T (1997) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 inhibits terminal differentiation of myogenic cells by suppressing the transcriptional activity of MyoD and myogenin. Exp Cell Res 230:342–351
Kaufman MH (1992) The atlas of mouse development. Academic Press, San Diego
Linker C, Lesbros C, Stark MR, Marcelle C (2003) Intrinsic signals regulate the initial steps of myogenesis in vertebrates. Development 130:4797–4807
Massague J, Chen YG (2000) Controlling TGF-β signaling. Genes Dev 14:627–644
Miyazono K, Maeda S, Imamura T (2005) BMP receptor signaling: transcriptional targets, regulation of signals, and signaling cross-talk. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:251–263
Nagata J, Yamane A (2004) Progress of cell proliferation in striated muscle tissues during development of the mouse tongue. J Dent Res 83:926–929
Nie X, Luukko K, Kettunen P (2006) BMP signalling in craniofacial development. Int J Dev Biol 50:511–521
Nishimura R, Hata K, Harris SE, Ikeda F, Yoneda T (2002) Core-binding factor α1 (Cbfa1) induces osteoblastic differentiation of C2C12 cells without interactions with Smad1 and Smad5. Bone 31:303–312
Noden DM (1983) The embryonic origins of avian cephalic and cervical muscles and associated connective tissues. Am J Anat 168:257–276
Ohnuki Y, Saeki Y, Yamane A, Yanagisawa K (2000) Quantitative changes in the mRNA for contractile proteins and metabolic enzymes in masseter muscle of bite-opened rats. Arch Oral Biol 45:1025–1032
Reshef R, Maroto M, Lassar AB (1998) Regulation of dorsal somitic cell fates: BMPs and Noggin control the timing and pattern of myogenic regulator expression. Genes Dev 12:290–303
Tajbakhsh S (2003) Stem cells to tissue: molecular, cellular and anatomical heterogeneity in skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13:413–422
Tzahor E, Kempf H, Mootoosamy RC, Poon AC, Abzhanov A, Tabin CJ, Dietrich S, Lassar AB (2003) Antagonists of Wnt and BMP signaling promote the formation of vertebrate head muscle. Genes Dev 17:3087–3099
Urist MR (1965) Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science 150:893–899
Wan M, Cao X (2005) BMP signaling in skeletal development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328:651–657
Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, Hewick RM, Wang EA (1988) Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science 242:1528–1534
Yamane A (2005) Embryonic and postnatal development of masticatory and tongue muscles. Cell Tissue Res 322:183–189
Yamane A, Mayo ML, Shuler C (2000a) The expression of insulin-like growth factor-I, II and their cognate receptor 1 and 2 during mouse tongue embryonic and neonatal development. Zool Sci 17:935–945
Yamane A, Mayo M, Shuler C, Crowe D, Ohnuki Y, Dalrymple K, Saeki Y (2000b) Expression of myogenic regulatory factors during the development of mouse tongue striated muscle. Arch Oral Biol 45:71–78
Yamane A, Urushiyama T, Diekwisch TGH (2002) Roles of insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the differentiation of mouse tongue myoblasts. Int J Dev Biol 46:807–816
Yamane A, Amano O, Slavkin HC (2003) Insulin-like growth factors, hepatocyte growth factor and transforming growth factor-α in mouse tongue myogenesis. Dev Growth Differ 45:1–6
Yamane A, Amano O, Urushiyama T, Nagata J, Akutsu S, Fukui T, Diekwisch TGH (2004) Exogenous hepatocyte growth factor inhibits myoblast differentiation by inducing myf5 expression and suppressing myoD expression in an organ culture system of embryonic mouse tongue. Eur J Oral Sci 112:177–181
Zhao J, Araki N, Nishimoto SK (1995) Quantitation of matrix Gla protein mRNA by competitive polymerase chain reaction using glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as an internal control. Gene 155:159–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported in part by grants-in-aid for funding scientific research (no. 16591871 to A.Y.) from the Bio-ventures and High-Technology Research Center of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan and by the Science Research Promotion Fund from the Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suga, T., Fukui, T., Shinohara, A. et al. BMP2, BMP4, and their receptors are expressed in the differentiating muscle tissues of mouse embryonic tongue. Cell Tissue Res 329, 103–117 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0416-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0416-4