Abstract
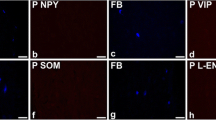
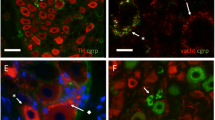
The afferent output from the bladder is important for triggering micturition. This study identifies different types of afferent nerve and explores the connections of their collateral fibres on intramural ganglia and potential ganglionic targets. The experiments were performed on tissues from male guinea-pigs (n=16). Fibres positive for choline acetyl transferase (ChAT+) were found to originate close to the urothelium, to transit the sub-urothelial interstitial cell layer and to pass into the lamina propria. A different population of fibres, immunopositive for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), capsaicin receptors or neurofilament protein (NF), were seen to intertwine with the ChAT+ fibres in the lamina propria. The ChAT+ fibres did not express NF. Ganglia with ChAT+ and NF+ neurones were found in the lamina propria and muscle. ChAT+ fibres, with pronounced terminal varicosities, were present on the nerve cell bodies. Two types were noted: NF+ terminals and those with little or no NF (NF−) suggesting that their origins were the ChAT+ afferent collaterals and the adjacent ganglia. Fibres containing CGRP or substance P were seen on the ganglionic cells. α1B adrenergic receptors were also found on the neurones indicative of adrenergic synapses. Thus, the ganglia had multiple inputs. Different types of ChAT+ nerves were seen in the muscle: NF+ and NF−. The ChAT+/NF+ nerves may represent a ganglionic output to the muscle. This complex neuronal network may therefore represent the elements generating and modulating bladder sensations. The role of such a scheme in bladder pathology and the therapeutic sites of action of anticholinergic and sympathomimetic drugs are discussed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, Kerrebroeck P van, Victor A, Wein A, Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society (2002) The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society.Neurourol Urodyn 21:167–178
Andersson K-E (2002) Bladder activation: afferent mechanisms. Urology 59:43–50
Andersson KE, Arner A (2004) Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 84:935–986
Birder LA, Apodaca G, De Groat WC, Kanai AJ (1998) Adrenergic- and capsaicin-evoked nitric oxide release from urothelium and afferent nerves in urinary bladder. Am J Physiol 275:F226–F229
Birder LA, Kanai AJ, De Groat WC, Kiss S, Nealen ML, Burke NE, Dineley KE, Watkins S, Reynolds IJ, Caterina MJ (2001) Vanilloid receptor expression suggests a sensory role for urinary bladder epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13396–13401
Birder LA, Nealen ML, Kiss S, De Groat WC, Caterina MJ, Wang E, Apodaca G, Kanai AJ (2002) Beta-adrenoceptor agonists stimulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase in rat urinary bladder urothelial cells. J Neurosci 22:8063–8070
Coolsaet BL, Van Duyl WA, Van Os-Bossagh P, De Bakker HV (1993) New concepts in relation to urge and detrusor activity. Neurourol Urodyn 12:463–471
Davidson RA, McCloskey KD (2005) Morphology and localization of interstitial cells in the guinea pig bladder: structural relationships with smooth muscle and neurons. J Urol 173:1385–1390
De Groat WC (2004) The urothelium in overactive bladder: passive bystander or active participant. Urology 64:7–11
De Vente J, Hopkins DA, Markerink-van Ittersum M, Emson PC, Schmidt HHHW, Steinbusch HWM (1998) Distribution of nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide-receptive, cyclic GMP producing structures in the rat brain. Neuroscience 87:207–241
Dixon JS, Gilpin SA, Gilpin CJ, Gosling JA (1983) Intra-mural ganglia of the human urinary bladder. Br J Urol 55:195–198
Drake MJ, Mills IW, Gillespie JI (2001) Model of peripheral autonomous modules and a myovesical plexus in normal and overactive bladder function. Lancet 358:401–403
Drake MJ, Gardner BP, Brading AF (2003) Innervation of the detrusor muscle bundle in neurogenic detrusor overactivity.BJU Int 91:702–710
Ferguson DR, Kennedy I, Burton TJ (1997) ATP is released from rabbit urinary bladder epithelial cells by hydrostatic pressure changes—a possible sensory mechanism? J Physiol 505:503–511
Furness JB, Kunze WAA, Bertrand PP, Clerc N, Bornstein JC (1998) Intrinsic primary afferent neurones in the intestine. Prog Neurobiol 64:1–18
Furness JB, Jones C, Nurgali K, Clerc N (2004) Intrinsic primary afferent neurones and nerve circuits within the intestine. Prog Neurobiol 72:143–164
Gabella G (1990) Intramural neurones in the urinary bladder of the guinea pig. Cell Tissue Res 261:231–237
Gabella G, Davis C (1998) Distribution of affernt axons in the bladder of rats. J Neurocytol 27:141–155
Gibbins IL, Jobling P, Morris JL (2003) Functional organization of peripheral vasomotor pathways. Acta Physiol Scand 177:237–245
Gilpin CJ, Dixon JS, Gilpin SA, Gosling JA (1983) The fine structure of autonomic neurones in the wall of the human urinary bladder. J Anat 137:705–713
Gillespie JI (2004a) The autonomous bladder: a view of the origin of bladder overactivity. BJU Int 93:478–483
Gillespie JI (2004b) Modulation of autonomous contractile activity in the isolated bladder of the GP. BJU Int 93:393–400
Gillespie JI (2004c) Noradrenaline inhibits autonomous activity in the isolated guinea pig bladder. BJU Int 93:401–409
Gillespie JI (2005a) Inhibitory actions of calcitonin gene related peptide and capsaicin: evidence for local axonal reflexes in the bladder wall. BJU Int 95:149–156
Gillespie JI (2005b) A developing view of the origins of urgency: the importnce of animal models. BJU Int 96:22–28
Gillespie JI, Harvey IJ, Drake MJ (2003) Agonist and nerve induced phasic activity in the isolated whole bladder of the guinea pig: evidence for two types of bladder activity. Exp Physiol 88:343–357
Gillespie JI, Markerink-van Ittersum M, De Vente J (2005) Interstitial cells and cholinergic signalling in the outer muscle layers of the guinea-pig bladder. BJU Int 97:379–385
Gjone R (1965) Peripheral autonomic influence on the motility of the urinary bladder in the cat. I. Rhythmic contractions. Acta Physiol Scand 65:370–377
Gosling JA (1986) The distribution of noradrenergic nerves in the human lower urinary tract. Clin Sci 70(Suppl 14):3s–6s
Gosling JA, Dixon JS (1974) Sensory nerves in the mammalian urinary tract. An evaluation using light and electron microscopy. J Anat 117:133–144
Hardwick JC, Mawe GM, Parsons RL (1995) Evidence for afferent fibre innervation of parasympathetic neurones of the guinea pig cardiac ganglion. J Auton Nerv Syst 53:166–174
Hashitani H, Yanai Y, Suzuki H (2004) Role of interstitial cells and gap junctions in the transmission of spontaneous Ca2+ signals in detrusor smooth muscles of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol (Lond) 559:567–581
Iggo A (1955) Tension receptors in the stomach and urinary bladder. J Physiol (Lond) 128:593–607
Kirby RS, Fowler CJ, Gosling JA, Bannister R (1985) Bladder dysfunction in distal autonomic neuropathy of acute onset. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 448:762–767
Lagou M, Drake MJ, Gillespie JI (2005) Volume-induced effects on the isolated bladder: a possible local reflex. BJU Int 94:1356–1365
Maggi CA, Meli A (1988) The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol 19:1–43
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Geppetti P, Patacchini R, Frilli S, Astolfi M, Fusco B, Meli A (1988) Simultaneous release of substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-like immunoreactivity from isolated muscle of the guinea pig urinary bladder. Neurosci Lett 87:163–167
Mazzia C, Clerc N (1997) Ultrastructural relationships of spinal primary afferent fibres with neuronal and non-neuronal cells in the myenteric plexus of the cat oesophago-gastric junction. Neuroscience 80:925–937
McCloskey KD, Gurney AM (2002) kit-positive cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol 168:832–836
Morrison J (1999) The activation of bladder wall afferent nerves. Exp Physiol 84:131–136
Persson K, Igawa Y, Mattiasson A, Andersson KE (1992) Effects of inhibition of the L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the rat lower urinary tract in vivo and in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 107:178–184
Pirker ME, Montedonico S, Rolle U, Austvoll H, Puri P (2005) Regional differences in nitrergic neuronal density in the developing porcine urinary bladder. Pediatr Surg Int 21:161–168
Rong W, Spyer KM, Burnstock G (2002) Activation and sensitisation of low and high threshold afferent fibres mediated by P2X receptors in the mouse urinary bladder. J Physiol (Lond) 541:591–600
Sann H, McCarthy PW, Mader M, Schemann M (1995a) Choline acetyltransferase-like immunoreactivity in small diameter neurones of the rat dorsal root ganglion. Neurosci Lett 198:17–20
Sann H, McCarthy PW, Schemann M, Jurzak M, Poethke R, Pierau FK (1995b) Choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive neurones in a prevertebral sympathetic ganglion, the inferior mesenteric ganglion. J Auton Nerv Syst 54:195–205
Schrodl F, Tines R, Brehmer A, Neuhuber WL (2001) Intrinsic choroidal neurones in the duck eye receive sympathetic input: anatomical evidence for adrenergic modulation of nitergic functions in the choroid. Cell Tissue Res 304:175–184
Schrodl F, Schweigert M, Brehmer A, Neuhuber WL (2003) Intrinsic neurones in the duck choroid are contacted by CGRP-immunoreactive nerve fibres: evidence for a local pre-central reflex arc in the eye. Exp Eye Res 72:137–146
Sherrington CS (1892) Notes on the arrangement of some motor fibres in the lumbo-sacral plexus. J Physiol (Lond) 13:621–772
Smet PJ, Edyvane KA, Jonavicius J, Marshall VR (1996) Neuropeptides and neurotransmittersynthesizing enzymes in intrinsic neurons of the human urinary bladder. J Neurocytol 25:112–124
Vaughan CW, Satchell PM (1995) Urine storage mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 46:215–237
Yoshida M, Miyamae K, Iwashita H, Otani M, Inadome A (2004) Management of detrusor dysfunction in the elderly: changes in acetylcholine and adenosine triphosphate release during aging. Urology 63-sup1:17–23
Zhou Y, Ling EA (1998) Co-localization of nitric oxide synthase and some neurotransmitters in the intramural ganglia of the guinea pig urinary bladder. J Comp Neurol 394:496–505
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We gratefully acknowledge the support of Pfizer. This work was supported by a grant from the Detrol Research Programme.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillespie, J.I., Markerink-van Ittersum, M. & de Vente, J. Sensory collaterals, intramural ganglia and motor nerves in the guinea-pig bladder: evidence for intramural neural circuits. Cell Tissue Res 325, 33–45 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0166-8