Abstract
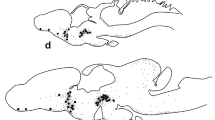
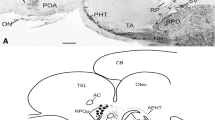
The distribution of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-like immunoreactivity and its colocalization with neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like substances were investigated in the optic lobe and peduncle complex of the octopus (Octopus vulgaris) using immunohistochemical techniques. In the optic lobe cortex, CRF-immunoreactive (CRF-IR) and NPY-immunonegative varicose fibers were observed in the plexiform layer. In the medulla, CRF-IR somata were seen in the cell islands, and CRF-IR varicose fibers were observed in the neuropil. About half of the CRF-IR structures in the medulla showed NPY-like immunoreactivity. In the peduncle lobe, no CRF-IR somata but abundant CRF-IR varicose fibers were observed, and about half of them showed NPY-like immunoreactivity. In the olfactory lobe, CRF-IR somata and abundant CRF-IR varicose fibers were observed. Almost all the CRF-IR somata located in the posterior olfactory lobule showed NPY-like immunoreactivity, whereas those seen in the median olfactory lobule were immunonegative for NPY. About half of the CRF-IR fibers in the anterior lobule neuropil were immunopositive for NPY, but those in the median and posterior lobule neuropils were immunonegative for NPY. In the optic gland, almost all the CRF-IR varicose fibers were immunoreactive for NPY. Western blot analysis of the optic lobe and peduncle complex indicated that anti-CRF antiserum labeled approximate 16.4- and 14.6-kDa bands and that anti-NPY antiserum labeled an approximate 16.2-kDa band. CRF-IR and NPY-immunoreactive neurons in the optic lobe may participate in the modulation of visual information and those in the optic gland may be involved in the regulation of endocrine function.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audsley N, Goldsworthy GJ, Coast GM (1997) Quantification of Locusta diuretic hormone in the central nervous system and corpora cardiaca: influence of age and feeding status, and mechanism of release. Regul Pept 69:25–32
Boadle MC (1969) Observation on a histaminase of invertebrate origin: a contribution to the study of cephalopod amine oxidases. Comp Biochem Physiol 30:611–620
Chen Y, Veenstra JA, Hagedorn H, Davis NT (1994) Leucokinin and diuretic hormone immunoreactivity of neurons in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, and co-localization of this immunoreactivity in lateral neurosecretory cells of abdominal ganglia. Cell Tissue Res 278:493–507
Cornwell CJ, Messenger JB, Williamson R (1993) Distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the octopus brain. Brain Res 621:353–357
Cory HT, Rose SPR (1969) Glucose and amino acid metabolism in octopus optic and vertical lobes in vitro. J Neurochem 16:979–988
Cummings S, Elde R, Ells J, Lindall A (1983) Corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity is widely distributed within the central nervous system of the rat: an immunohistochemical study. J Neurosci 3:1355–1368
Donaldson CJ, Sutton SW, Perrin MH, Corrigan AZ, Lewis KA, Rivier JE, Vaughan JM, Vale WW (1996) Cloning and characterization of human urocortin. Endocrinology 137:2167–2170
Di Cosmo A, Di Cristo C (1998) Neuropeptidergic control of the optic gland of Octopus vulgaris: FMRFamide and GnRH immunoreactivity. J Comp Neurol 398:1–12
Emery SB, Ma MC, Wong WKR, Tips A, De Loof A (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of a diuretic peptide Manduca diuresin (MasDPII) in the brain and suboesophageal ganglion of the tobacco hawkmoth Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 27:137–152
Flood JF, Hernandez EN, Morley JE (1987) Modulation of memory processing by neuropeptide Y. Brain Res 421:280–290
Flood JF, Baker ML, Hernandez EN, Morley JE (1989) Modulation of memory processing by neuropeptide Y varies with brain injection site. Brain Res 503:73–82
Florey E, Winesdorfer J (1968) Cholinergic nerve ending in octopus brain. J Neurochem 15:169–177
Gambacciani M, Yen SSC, Rasmussen DD (1986) GnRH release from the mediobasal hypothalamus: in vitro inhibition by corticotropin-releasing factor. Neuroendocrinology 43:533–536
González GC, Martinez-Padrón M, Ko D, Lukowiak K, Lederis K, Kobayashi H (1991) Urotensin I-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of Aplysia californica. Peptides 12:787–793
González GC, Martinez-Padrón M, Lederis K, Lukowiak K (1992) Distribution and coexistence of urotensin I and urotensin II peptides in the cerebral ganglia of Aplysia californica. Peptides 13:695–703
Ichikawa T, McMaster D, Lederis K (1982) Isolation and amino acid sequence of urotensin I, a vasoactive and ACTH-releasing neuropeptide, from the carp (Cyprinus carpio) urophysis. Peptides 3:859–867
Juorio AV (1971) Catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in nervous tissue of cephalopods. J Physiol 216:213–226
Kataoka H, Troetschler RG, Li JP, Kramer SJ, Carney RL, Schooley DA (1989) Isolation and identification of a diuretic hormone from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:2976–2980
Kito-Yamashita T, Haga C, Hirai K, Uemura T, Kondo H, Kosaka K (1990) Localization of serotonin immunoreactivity in cephalopod visual system. Brain Res 521:81–88
Kleinschuster SJ, Morris JE (1972) Glutamine synthetase, an enzyme characteristic of vertebrate systems in invertebrate tissues. Experientia 28:1157–1158
Koob GF, Bloom FE (1985) Corticotropin-releasing factor and behavior. Fed Proc 44:259–263
Kowall NW, Beal MF (1988) Cortical somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, and NADPH diaphorase neurons: normal anatomy and alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 23:105–114
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lederis K, Letter A, McMaster D, Moore G, Schlesinger D (1982) Complete amino acid sequence of urotensin I, a hypotensive and corticotropin-releasing neuropeptide from Catostomus. Science 218:162–164
Lehnert H, Schulz C, Dieterich K (1998) Physiological and neurochemical aspects of corticotrophin-releasing factor actions in the brain: the role of the locus coeruleus. Neurochem Res 23:1039–1052
Liang KC, Lee EHY (1988) Intra-amygdala injections of corticotropin releasing factor facilitate inhibitory avoidance learning and reduce exploratory behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 96:232–236
MacLusky NJ, Naftolin F, Leranth C (1988) Immunocytochemical evidence for direct synaptic connections between corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-containing neurons in the preoptic area of the rat. Brain Res 439:391–395
Matus AI (1973) Histochemical localization of biogenic monoamines in the cephalic ganglia of Octopus vulgaris. Tissue Cell 5:591–601
Messenger JB (1967) The peduncle lobe: a visuo-motor center in Octopus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 167:225–251
Montecucchi PC, Anastasi A, de Castiglione R, Erspamer V (1980) Isolation and amino acid composition of sauvagine. An active polypeptide from methanol extracts of the skin of the South American frog Phyllomedusa sauvagei. Int J Pept Protein Res 16:191–199
Nikolarakis KE, Almeida OFX, Herz A (1986) Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) inhibits gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) release from superfused rat hypothalami in vitro. Brain Res 377:388–390
Osakada F, Ishii Y, Ichikawa T, Lederis K, Ohashi S, Shiraki M, Munekata E (1984) Synthesis of carp urotensin I. In: Munekata E (ed) Peptide chemistry 1983. Protein Research Foundation, Osaka, pp 267–272
Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (1991) Physiology and pharmacology of corticotropin-releasing factor. Pharmacol Rev 43:425–473
Patel M, Chung JS, Kay I, Mallet AI, Gibbon CR, Thompson KSJ, Bacon JP, Coast GM (1994) Localization of Locusta-DP in locust CNS and hemolymph satisfies initial hormonal criteria. Peptides 15:591–602
Powers RE, Walker LC, De Souza EB, Vale WW, Struble RG, Whitehouse PJ, Price DL (1987) Immunohistochemical study of neurons containing corticotropin-releasing factor in Alzheimer's disease. Synapse 1:405–410
Rivier CL, Plotsky PM (1986) Mediation by corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) of adrenohypophysial hormone secretion. Ann Rev Physiol 48:475–494
Saidel WN (1982) Connections of the octopus optic lobe: an HRP study. J Comp Neurol 206:346–358
Sithigorngul P, Stretton AOW, Cowden C (1990) Neuropeptide diversity in Ascaris: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 294:362–376
Spiess J, Rivier J, Rivier C, Vale W (1981) Primary structure of corticotropin-releasing factor from ovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78:6517–6521
Suzuki H, Yamamoto T (2002) Centrifugal neurons of the octopus optic lobe cortex are immunopositive for calcitonin gene-related peptide. Neurosci Lett 324:21–24
Suzuki H, Yamamoto T, Inenaga M, Uemura H (2000) Galanin-immunoreactive neuronal system and colocalization with serotonin in the optic lobe and peduncle complex of the octopus (Octopus vulgaris). Brain Res 865:168–176
Suzuki H, Yamamoto T, Nakagawa M, Uemura H (2002) Neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neuronal system and colocalization with FMRFamide in the optic lobe and peduncle complex of the octopus (Octopus vulgaris). Cell Tissue Res 307:255–264
Tamarelle M, Coast GM, Veenstra JA (2000) Ovary maturing parsin and diuretic hormone are produced by the same neuroendocrine cells in the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. Peptides 21:737–739
Tansey EM (1980) Aminergic fluorescence in the cephalopod brain. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 291:127–145
Te Brugge VA, Miksys SM, Coast GM, Schooley DA, Orchard I (1999) The distribution of a CRF-like diuretic peptide in the blood-feeding bug Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Biol 202:2017–2027
Tellam DJ, Perone MJ, Dunn IC, Radovick S, Brennand J, Rivier JE, Castro MG, Lovejoy DA (1998) Direct regulation of GnRH transcription by CRF-like peptides in an immortalized neuronal cell line. Neuroreport 9:3135–3140
Vale W, Spiess J, Rivier C, Rivier J (1981) Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and β-endorphin. Science 213:1394–1397
Vaughan J, Donaldson C, Bittencourt J, Perrin MH, Lewis K, Sutton S, Chan R, Turnbull AV, Lovejoy D, Rivier C, Rivier J, Sawchenko PE, Vale W (1995) Urocortin, a mammalian neuropeptide related to fish urotensin I and to corticotropin-releasing factor. Nature 378:287–292
Veenstra JA, Hagedorn HH (1991) Identification of neuroendocrine cells producing a diuretic hormone in the tobacco hornworm moth, Manduca sexta. Cell Tissue Res 266:359–364
Verhaert P, Marivoet S, Vandesande F, De Loof A (1984) Localization of CRF immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of three vertebrate and one insect species. Cell Tissue Res 238:49–53
Wells MJ, Wells J (1959) Hormonal control of sexual maturity in Octopus. J Exp Biol 36:1–33
Wells MJ, Wells J (1969) Pituitary analogue in the octopus. Nature 222:293–294
Young JZ (1962) The optic lobes of Octopus vulgaris. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 245:19–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, H., Muraoka, T. & Yamamoto, T. Localization of corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive nervous tissue and colocalization with neuropeptide Y-like substance in the optic lobe and peduncle complex of the octopus (Octopus vulgaris). Cell Tissue Res 313, 129–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0734-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0734-0