Abstract
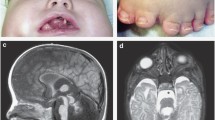
We report on a large family in which a novel X-linked recessive mental retardation (XLMR) syndrome comprising macrocephaly and ciliary dysfunction co-segregates with a frameshift mutation in the OFD1 gene. Mutations of OFD1 have been associated with oral–facial–digital type 1 syndrome (OFD1S) that is characterized by X-chromosomal dominant inheritance and lethality in males. In contrast, the carrier females of our family were clinically inconspicuous, and the affected males suffered from severe mental retardation, recurrent respiratory tract infections and macrocephaly. All but one of the affected males died from respiratory problems in infancy; and impaired ciliary motility was confirmed in the index patient by high-speed video microscopy examination of nasal epithelium. This family broadens the phenotypic spectrum of OFD1 mutations in an unexpected way and sheds light on the complexity of the underlying disease mechanisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RC, Zoghbi HY, Moseley AB, Rosenblatt HM, Belmont JW (1992) Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet 51: 1229–1239
Avidor-Reiss T, Maer AM, Koundakjian E, Polyanovsky A, Keil T, Subramaniam S, Zuker CS (2004) Decoding cilia function: defining specialized genes required for compartmentalized cilia biogenesis. Cell 117: 527–539
Brzustowicz LM, Farrell S, Khan MB, Weksberg R (1999) Mapping of a new SGBS locus to chromosome Xp22 in a family with a severe form of Simpson-Golabi–Behmel syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 65: 779–783
de Conciliis L, Marchitiello A, Wapenaar MC, Borsani G, Giglio S, Mariani M, Consalez GG, Zuffardi O, Franco B, Ballabio A, Banfi S (1998) Characterization of Cxorf5 (71–7A), a novel human cDNA mapping to Xp22 and encoding a protein containing coiled-coil alpha-helical domains. Genomics 51: 243–250
Eley L, Yates LM, Goodship JA (2005) Cilia and disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15: 308–314
Ferrante MI, Giorgio G, Feather SA, Bulfone A, Wright V, Ghiani M, Selicorni A, Gammaro L, Scolari F, Woolf AS, Sylvie O, Bernard L, Malcolm S, Winter R, Ballabio A, Franco B (2001) Identification of the gene for oral–facial–digital type I syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 68: 569–576
Ferrante MI, Zullo A, Barra A, Bimonte S, Messaddeq N, Studer M, Dolle P, Franco B (2005) Oral–facial–digital type I protein is required for primary cilia formation and left-right axis specification. Nat Genet 38(1):112–117
Fliegauf M, Olbrich H, Horvath J, Wildhaber JH, Zariwala MA, Kennedy M, Knowles MR, Omran H (2005) Mislocalization of DNAH5 and DNAH9 in respiratory cells from patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171: 1343–1349
Fuchs JL, Schwark HD (2004) Neuronal primary cilia: a review. Cell Biol Int 28: 111–118
Gerdes JM, Katsanis N (2005) Microtubule transport defects in neurological and ciliary disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 62: 1556–1570
Herbst DS, Miller JR (1980) Nonspecific X-linked mental retardation II: the frequency in British Columbia. Am J Med Genet 7: 461–469
Hildebrandt F, Otto E (2005) Cilia and centrosomes: a unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat Rev Genet 6: 928–940
Hirokawa N, Takemura R (2004) Molecular motors in neuronal development, intracellular transport and diseases. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14: 564–573
Khanna H, Hurd TW, Lillo C, Shu X, Parapuram SK, He S, Akimoto M, Wright AF, Margolis B, Williams DS, Swaroop A (2005) RPGR-ORF15, which is mutated in retinitis pigmentosa, associates with SMC1, SMC3, and microtubule transport proteins. J Biol Chem 280: 33580–33587
Kulaga HM, Leitch CC, Eichers ER, Badano JL, Lesemann A, Hoskins BE, Lupski JR, Beales PL, Reed RR, Katsanis N (2004) Loss of BBS proteins causes anosmia in humans and defects in olfactory cilia structure and function in the mouse. Nat Genet 36: 994–998
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM (1984) Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet 36: 460–465
Li JB, Gerdes JM, Haycraft CJ, Fan Y, Teslovich TM, May-Simera H, Li H, Blacque OE, Li L, Leitch CC, Lewis RA, Green JS, Parfrey PS, Leroux MR, Davidson WS, Beales PL, Guay-Woodford LM, Yoder BK, Stormo GD, Katsanis N, Dutcher SK (2004) Comparative genomics identifies a flagellar and basal body proteome that includes the BBS5 human disease gene. Cell 117: 541–552
Odent S, Le Marec B, Toutain A, David A, Vigneron J, Treguier C, Jouan H, Milon J, Fryns JP, Verloes A (1998) Central nervous system malformations and early end-stage renal disease in oro-facio-digital syndrome type I: a review. Am J Med Genet 75: 389–394
Rakkolainen A, Ala-Mello S, Kristo P, Orpana A, Jarvela I (2002) Four novel mutations in the OFD1 (Cxorf5) gene in Finnish patients with oral–facial–digital syndrome 1. J Med Genet 39: 292–296
Romio L, Fry AM, Winyard PJ, Malcolm S, Woolf AS, Feather SA (2004) OFD1 is a centrosomal/basal body protein expressed during mesenchymal-epithelial transition in human nephrogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 2556–2568
Ropers HH, Hamel BC (2005) X-linked mental retardation. Nat Rev Genet 6: 46–57
Sambrook J MT, Fritsch EF (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sisson JH, Stoner JA, Ammons BA, Wyatt TA (2003) All-digital image capture and whole-field analysis of ciliary beat frequency. J Microsc 211: 103–111
Thauvin-Robinet C, Cossee M, Cormier-Daire V, Van Maldergem L, Toutain A, Alembik Y, Bieth E, Layet V, Parent P, David A, Goldenberg A, Mortier G, Heron D, Sagot P, Bouvier AM, Huet F, Cusin V, Donzel A, Devys D, Teyssier JR, Faivre L (2006) Clinical, molecular, and genotype-phenotype correlation studies from 25 cases of oral–facial–digital syndrome type 1: a French and Belgian collaborative study. J Med Genet 43: 54–61
Van’s Gravesande KS, Omran H (2005) Primary ciliary dyskinesia: clinical presentation, diagnosis and genetics. Ann Med 37: 439–449
Whitlon DS (2004) Cochlear development: hair cells don their wigs and get wired. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12: 449–454
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients and their families for their participation in the studies. This work was supported by the EU (grant no. QLRT-2001-01810) and by a ‘Partner Group’ grant from the Max Planck Society (to H.H.R and A.L.-B.). H.O. and M.F. were supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG Om 6/2; SFB592).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budny, B., Chen, W., Omran, H. et al. A novel X-linked recessive mental retardation syndrome comprising macrocephaly and ciliary dysfunction is allelic to oral–facial–digital type I syndrome . Hum Genet 120, 171–178 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0210-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0210-5