Abstract
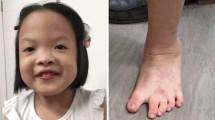
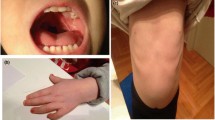
Complex chromosome rearrangements (CCRs) are extremely rare but often associated with mental retardation, congenital anomalies, or recurrent spontaneous abortions. We report a de novo apparently balanced CCR involving chromosomes 3 and 12 and a two-way translocation between chromosomes 11 and 21 in a woman with mild intellectual disability, obesity, coarse facies, and apparent synophrys without other distinctive dysmorphia or congenital anomalies. Molecular analysis of breakpoints using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with region-specific BAC clones revealed a more complex character for the CCR. The rearrangement is a result of nine breaks and involves reciprocal translocation of terminal chromosome fragments 3p24.1→pter and 12q23.1→qter, insertion of four fragments of the long arm of chromosome 12: q14.1→q21?, q21?→q22, q22→q23.1, and q23.1→q23.1 and a region 3p22.3→p24.1 into chromosome 3q26.31. In addition, we detected a ∼0.5-Mb submicroscopic deletion at 3q26.31. The deletion involves the chromosome region that has been previously associated with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) in which a novel gene NAALADL2 has been mapped recently. Other potential genes responsible for intellectual deficiency disrupted as a result of patient’s chromosomal rearrangement map at 12q14.1 (TAFA2), 12q23.1 (METAP2), and 11p14.1 (BDNF).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astbury C, Christ LA, Aughton DJ, Cassidy SB, Kumar A, Eichler EE, Schwartz S (2004) Detection of deletions in de novo “balanced” chromosome rearrangements: further evidence for their role in phenotypic abnormalities. Genet Med 6:81–89
Batanian JR, Eswara MS (1998) De novo apparently balanced complex chromosome rearrangement (CCR) involving chromosomes 4, 18 and 21 in girl with mental retardation: report and review. Am J Med Genet 78:44–51
Battisti C, Bonaglia MC, Giglio S, Anichini C, Pucci L, Dotti MT, Zuffardi O, Federico A (2003) De novo double translocation 3;13 and 4;8;18 in a patient with mental retardation and skeletal abnormalities. Am J Med Genet 117A:207–211
Belloni E, Muenke M, Roessler E, Traverso G, Siegel-Bartelt J, Frumkin A, Mitchell HF, Donis-Keller H, Helms C, Hing AV, Heng HHQ, Koop B, Martindale D, Rommens JM, Tsul LC, Scherer SW (1996) Identification of Sonic hedgehog as a candidate gene responsible for holoprosencephaly. Nat Genet 14:353–356
Bodrug SE, Roberson JR, Weiss L, Ray PN, Worton RG, Van Dyke DL (1990) Prenatal identification of a girl with a t(X;4)(p21;q35) translocation: molecular characterisation, paternal origin, and association with muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet 27:426–432
Borck G, Redon R, Sanlaville D, Rio M, Prieur M, Lyonnet S, Vekemans M, Carter NP, Munnich A, Colleaux L, Cormier-Daire V (2004) NIPBL mutations and genetic heterogeneity in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. J Med Genet 41:el128
Borg I, Squire M, Menzel C, Stout K, Morgan D, Willatt L, O’Brien PCM, Ferguson-Smith MA, Ropers HH, Tommerup N, Kalscheuer VM, Sargan DR (2002) A cryptic deletion of 2q35 including part of the PAX3 gene detected by breakpoint mapping in a child with autism and a de novo 2;8 translocation. J Med Genet 39:391–399
Bugge M, Bruun-Petersen G, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Friedrich U, Hansen J, Jensen G, Jensen PKA, Kristoffersson U, Lundsteen C, Niebuhr E, Rasmussen KR, Rasmussen K, Tommerup N (2000) Disease associated balanced chromosome rearrangements: a resource for large scale genotype-phenotype delineation in man. J Med Genet 37:858–865
Collins FS (1992) Positional cloning: let’s not call it reverse anymore. Nat Genet 1:3–6
David D, Cardoso J, Marques B, Marques R, Silva ED, Santos H, Boavida MG (2003) Molecular characterization of a familial translocation implicates disruption of HDAC9 and possible position effect on TGFβ 2 in the pathogenesis of Peters’ anomaly. Genomics 81:489–503
Doble A (1999) The role of excitotoxicity in neurodegenerative disease: implications for therapy. Pharmacol Ther 81:163–221
Endris V, Wogatzky B, Leimer U, Bartsch D, Zatyka M, Latif F, Maher ER, Tariverdian G, Kirsch S, Karch D, Rappold GA (2002) The novel Rho-GTPase activating gene MEGAP/srGAP3 has a putative role in severe mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:11754–11759
Faas BHW, de Vries BBA, van Es-van Gaal J, Merkx G, Draaisma JMT, Smeets DFCM (2002) A new case of dup (3q) syndrome due to a pure duplication of 3qter. Clin Genet 62:315–320
Fantes J, Redeker B, Breen M, Boyle S, Brown J, Fletcher J, Jones S, Bickmore W, Fukushima Y, Mannens M, Danes S, Van Heyningen V, Hanson I (1995) Aniridia-associated cytogenetic rearrangements suggest that a position effect may cause the mutant phenotype. Hum Mol Genet 4:415–422
Flinta C, Persson B, Jornvall H, von Heijne G (1986) Sequence determinants of cytosolic N-terminal protein processing. Eur J Biochem 154:193–196
Gribble SM, Prigmore E, Burford DC, Porter KM, Bee Ling Ng, Douglas EJ, Fiegler H, Carr P, Kalaitzopoulos D, Clegg S, Sandstrom R, Temple IK, Youings SA, Thomas NS, Dennis NR, Jacobs PA, Crolla JA, Carter NP (2005) The complex nature of constitutional de novo apparently balanced translocations in patients presenting with abnormal phenotypes. J Med Genet 42:8–16
Guillemot F, Auffray C, Devignes MD (1999) Detailed transcript map of a 810-kb region at 11p14 involving identification of 10 novel human 3′ exons. Eur J Hum Genet 7:487–495
Hearn T, Renforth GL, Spalluto C, Hanley NA, Piper K, Brickwood S, White C, Connolly V, Taylor JFN, Russell-Eggitt I, Bonneau D, Walker M, Wilson DI (2002) Mutation of ALMS1, a large gene with a tandem repeat encoding 47 amino acids, causes Alström syndrome. Nat Genet 31:79–83
Higgins JJ, Pucilowska J, Lombardi RQ, Rooney JP (2004) Candidate genes for recessive non-syndromic mental retardation on chromosome 3p (MRT2A). Clin Genet 65:496–500
Houge G, Liehr T, Schoumans J, Ness GO, Solland K, Starke H, Claussen U, Strømme P, Akre B, Vermeulen S (2003) Ten years follow up of a boy with a complex chromosomal rearrangement: going from a >5 to 15-breakpoint CCR. Am J Med Genet 118A:235–240
Ireland M, English C, Cross I, Houlsby WT, Burn J (1991) A de novo translocation t(3;17)(q26.3;q23.1) in a child with Cornelia de Lange syndrome. J Med Genet 28:639–640
Kausch K, Haaf T, Köhler J, Schmid M (1988) Complex chromosomal rearrangement in a woman with multiple miscarriages. Am J Med Genet 31:415–420
Kirchhoff M, Rose H, Lundsteen C (2001) High resolution comparative genomic hybridization in clinical cytogenetics. J Med Genet 38:740–744
Klann E, Antion MD, Banko JL, Hou L (2004) Synaptic plasticity and translation initiation. Learn Mem 11:365–372
Kleczkowska A, Fryns JP, Van den Berghe H (1982) Complex chromosomal rearrangement (CCR) and their genetic consequences. J Genet Hum 30:199–214
Kleinjan DA, van Heyningen V (2005) Long-range control of gene expression: emerging mechanisms and disruption in disease. Am J Hum Genet 76:8–32
Kousseff BG, Papenhausen P, Essig Y-P, Torres MP (1993) Complex chromosomal rearrangement with ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum. J Med Genet 30:167–170
Krantz ID, Tonkin E, Smith M, Devoto M, Bottani A, Simpson C, Hofreiter M, Abraham V, Jukofsky L, Conti BP, Strachan T, Jackson L (2001) Exclusion of linkage to the CDL1 gene region on chromosome 3q26.3 in some familial cases of Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Am J Med Genet 101:120–129
Krantz ID, McCallum J, DeScipio C, Kaur M, Gillis LA, Yaeger D, Jukofsky L, Wasserman N, Bottani A, Morris CA, Nowaczyk MJ, Toriello H, Bamshad MJ, Carey JC, Rappaport E, Kawauchi S, Lander AD, Calof AL, Li HH, Devoto M, Jackson LG (2004) Cornelia de Lange syndrome is caused by mutations in NIPBL, the human homolog of Drosophila melanogaster Nipped-B. Nat Genet 36:631–635
Kumar A, Becker LA, Depinet TW, Haren JM, Kurtz CL, Robin NH, Cassidy SB, Wolff DJ, Schwartz S (1998) Molecular characterization and delineation of subtle deletions in de novo “balanced” chromosomal rearrangements. Hum Genet 103:173–178
Megonigal MD, Rappaport EF, Jones DH, Williams TM, Lovett BD, Kelly KM, Lerou PH, Moulton T, Budarf ML, Felix CA (1998) t(11;22)(q23;q11.2) in acute myeloid leukemia of infant twins fuses MLL with hCD Crel, a cell division cycle gene in the genomic region of deletion in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:6413–6418
Midro AT, Panasiuk B, Tümer Z, Stankiewicz P, Silahtaroglu A, Lupski JR, Zemanova Z, Stasiewicz-Jarocka B, Hubert E, Tarasów E, Famulski W, Zadrożna-Tołwińska B, Wasilewska E, Kirchhoff M, Kalscheuer V, Michalova K, Tommerup N (2004) Interstitial deletion 9q22.32-q33.2 associated with additional familial translocation t(9;17)(q34.11;p11.2) in a patient with Gorlin–Goltz syndrome and features of Nail–Patella syndrome. Am J Med Genet 124A:179–191
Patsalis PC, Evangelidou P, Charalambous S, Sismani C (2004) Fluorescence in situ hybridization characterization of apparently balanced translocation reveals cryptic complex chromosomal rearrangements with unexpected level of complexity. Eur J Hum Genet 12:647–653
Pichon B, Vankerckhove S, Bourrouillou G, Duprez L, Abramowicz MJ (2004) A translocation breakpoint disrupts the ASPM gene in a patient with primary microcephaly. Eur J Hum Genet 12:419–421
Robinson MB, Blakely RD, Couto R, Coyle JT (1987) Hydrolysis of the brain dipeptide N-acetyl-l-aspartyl-l-glutamate. Identification and characterization of a novel N-acetylated alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase activity from rat brain. J Biol Chem 262:14498–14506
Sodhi MS, Sanders-Bush E (2004) Serotonin and brain development. Int Rev Neurobiol 59:111–174
Tom Tang Y, Emtage P, Funk WD, Hu T, Arterburn M, Park EE, Rupp F (2004) TAFA: a novel secreted family with conserved cysteine residues and restricted expression in the brain. Genomics 83:727–734
Tommerup N (1993) Mendelian cytogenetics. Chromosome rearrangements associated with Mendelian disorders. J Med Genet 30:713–727
Tonkin ET, Wang T-J, Lisgo S, Bamshad MJ, Strachan T (2004b) NIPBL, encoding a homolog of fungal Scc2-type sister chromatid cohesion proteins and fly Nipped-B, is mutated in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Nat Genet 36:636–641
Tonkin ET, Smith M, Eichhorn P, Jones S, Imamwerdi B, Lindsay S, Jackson M, Wang T-J, Ireland M, Burn J, Krantz ID, Carr P, Strachan T (2004a) A giant novel gene undergoing extensive alternative splicing is severed by a Cornelia de Lange-associated translocation breakpoint at 3q26.3. Hum Genet 115:139–148
Vermeulen S, Menten B, Van Roy N, Van Limbergen H, De Paepe A, Mortier G, Speleman F (2004) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of complex chromosomal rearrangements in patients with mental retardation and congenital malformations: delineation of 7q21.11 breakpoints. Am J Med Genet 124A:10–18
Wagner T, Wirth J, Meyer J, Zabel B, Held M, Zimmer J, Pasantes J, Bricarelli FD, Keutel J, Hustert E, Wolf U, Tommerup N, Schempp W, Schere G (1994) Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SKY-related gene SOX9. Cell 79:1111–1120
Warburton D (1991) De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 49:995–1013
Weise A, Rittinger O, Starke H, Ziegler M, Claussen U, Liehr T (2003) De novo 9-break-event in one chromosome 21 combined with a microdeletion in 21q22.11 in a mentally retarded boy with short stature. Cytogenet Genome Res 103:14–16
Wirth J, Nothwang H-G, S van der Maarel, Menzel C, Borck G, Lopez-Pajares I, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Tommerup N, Bugge M, Ropers H-H, Haaf T (1999) Systematic characterisation of disease associated balanced chromosome rearrangements by FISH: cytogenetically and genetically anchored YACs identify microdeletions and candidate regions for mental retardation genes. J Med Genet 36:271–278
Zhu G, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Wirth J, Passarge E, Bartsch O (2001) Girl with phenotypic abnormalities and de novo, apparently balanced translocation 46,XX,t(5;10)(q35.2q11.2). Am J Med Genet 98:317–319
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute for providing BAC clones. This research was financed by the Polish Ministry of Scientific Research and Information Technology—Grant PBZ/KBN no. 042/P05/2001, the National Institute of Child Health and Development (PO1 HD39420), and the Baylor College of Medicine Mental Retardation Research Center (HD24064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0089-6
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borg, K., Stankiewicz, P., Bocian, E. et al. Molecular analysis of a constitutional complex genome rearrangement with 11 breakpoints involving chromosomes 3, 11, 12, and 21 and a ∼0.5-Mb submicroscopic deletion in a patient with mild mental retardation. Hum Genet 118, 267–275 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0021-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0021-0