Abstract
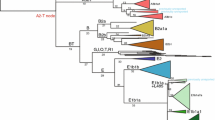
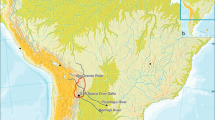
Diffusion of Tibeto-Burman populations across the Tibetan Plateau led to the largest human community in a high-altitude environment and has long been a focus of research on high-altitude adaptation, archeology, genetics, and linguistics. However, much uncertainty remains regarding the origin, diversification, and expansion of Tibeto-Burman populations. In this study, we analyzed a 7.0M bp region of 285 Y-chromosome sequences, including 81 newly reported ones, from male samples from Tibeto-Burman populations and other related Eastern Asian populations. We identified several paternal lineages specific to Tibeto-Burman populations, and most of these lineages emerged between 6000 and 2500 years ago. A phylogenetic tree and lineage dating both support the hypothesis that the establishment of Tibeto-Burman ancestral groups was triggered by Neolithic expansions from the middle Yellow River Basin and admixtures with local populations on the Tibetan Plateau who survived the Paleolithic Age. Furthermore, according to the geographical distributions of the haplogroups, we propose that there are two Neolithic expansion origins for all modern Tibeto-Burman populations. Our research provides a clear scenario about the sources, admixture process and later diffusion process of the ancestor population of all Tibeto-Burman populations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
An ZM (1992) The bronze age in eastern parts of Central Asia. In: Dani AH, Masson VM (eds) History of civilizations of Central Asia. vol. 1. Unesco, Paris, pp 319–336
Chen FH, Dong GH, Zhang DJ, Liu XY, Jia X, An CB, Ma MM, Xie YW, Barton L, Ren XY, Zhao ZJ, Wu XH, Jones MK (2015) Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600 B.P. Science 347:248–250
Dong YL, Yang ZL, Shi H, Gao L, Lu J, Cheng BW, Li KY, Zan RG, Xiao CJ (2004) Principal component analysis of Y-chromosome haplotype distribution in 18 ethnic groups in Yunnan Province (in Chinese). J Genet Genom 31:1030–1036
Hallast P, Batini C, Zadik D, Maisano Delser P, Wetton JH, Arroyo-Pardo E, Cavalleri GL, de Knijff P, Destro Bisol G, Dupuy BM, Eriksen HA, Jorde LB, King TE, Larmuseau MH, Lopez de Munain A, Lopez-Parra AM, Loutradis A, Milasin J, Novelletto A, Pamjav H, Sajantila A, Schempp W, Sears M, Tolun A, Tyler-Smith C, Van Geystelen A, Watkins S, Winney B, Jobling MA (2015) The Y-chromosome tree bursts into leaf: 13,000 high-confidence SNPs covering the majority of known clades. Mol Biol Evol 32:661–673
Heller R, Chikhi L, Siegismund HR (2013) The confounding effect of population structure on Bayesian skyline plot inferences of demographic history. PLoS One 8:e62992
Jeong C, Ozga AT, Witonsky DB, Malmstrom H, Edlund H, Hofman CA, Hagan RW, Jakobsson M, Lewis CM, Aldenderfer MS, Di Rienzo A, Warinner C (2016) Long-term genetic stability and a high-altitude East Asian origin for the peoples of the high valleys of the Himalayan arc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:7485–7490
Karmin M, Saag L, Vicente M, Wilson Sayres MA, Jarve M, Talas UG, Rootsi S, Ilumae AM, Magi R, Mitt M, Pagani L, Puurand T, Faltyskova Z, Clemente F, Cardona A, Metspalu E, Sahakyan H, Yunusbayev B, Hudjashov G, DeGiorgio M, Loogvali EL, Eichstaedt C, Eelmets M, Chaubey G, Tambets K, Litvinov S, Mormina M, Xue Y, Ayub Q, Zoraqi G, Korneliussen TS, Akhatova F, Lachance J, Tishkoff S, Momynaliev K, Ricaut FX, Kusuma P, Razafindrazaka H, Pierron D, Cox MP, Sultana GN, Willerslev R, Muller C, Westaway M, Lambert D, Skaro V, Kovacevic L, Turdikulova S, Dalimova D, Khusainova R, Trofimova N, Akhmetova V, Khidiyatova I, Lichman DV, Isakova J, Pocheshkhova E, Sabitov Z, Barashkov NA, Nymadawa P, Mihailov E, Seng JW, Evseeva I, Migliano AB, Abdullah S, Andriadze G, Primorac D, Atramentova L, Utevska O, Yepiskoposyan L, Marjanovic D, Kushniarevich A, Behar DM, Gilissen C, Vissers L, Veltman JA, Balanovska E, Derenko M, Malyarchuk B, Metspalu A, Fedorova S, Eriksson A, Manica A, Mendez FL, Karafet TM, Veeramah KR, Bradman N, Hammer MF, Osipova LP, Balanovsky O, Khusnutdinova EK, Johnsen K, Remm M, Thomas MG, Tyler-Smith C, Underhill PA, Willerslev E, Nielsen R, Metspalu M, Villems R, Kivisild T (2015) A recent bottleneck of Y chromosome diversity coincides with a global change in culture. Genome Res 25:459–466
Liu F, Zhang Y, Feng Z, Hou G, Zhou Q, Zhang H (2010) The impacts of climate change on the Neolithic cultures of Gansu-Qinghai region during the late Holocene Megathermal. J Geogr Sci 20:417–430
Lu D, Lou H, Yuan K, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang C, Lu Y, Yang X, Deng L, Zhou Y, Feng Q, Hu Y, Ding Q, Yang Y, Li S, Jin L, Guan Y, Su B, Kang L, Xu S (2016) Ancestral origins and genetic history of Tibetan highlanders. Am J Hum Genet 99:580–594
Ma M, Dong G, Jia X, Wang H, Cui Y, Chen F (2016) Dietary shift after 3600 cal yr BP and its influencing factors in northwestern China: evidence from stable isotopes. Quatern Sci Rev 145:57–70
Mallick S, Li H, Lipson M, Mathieson I, Gymrek M, Racimo F, Zhao M, Chennagiri N, Nordenfelt S, Tandon A, Skoglund P, Lazaridis I, Sankararaman S, Fu Q, Rohland N, Renaud G, Erlich Y, Willems T, Gallo C, Spence JP, Song YS, Poletti G, Balloux F, van Driem G, de Knijff P, Romero IG, Jha AR, Behar DM, Bravi CM, Capelli C, Hervig T, Moreno-Estrada A, Posukh OL, Balanovska E, Balanovsky O, Karachanak-Yankova S, Sahakyan H, Toncheva D, Yepiskoposyan L, Tyler-Smith C, Xue Y, Abdullah MS, Ruiz-Linares A, Beall CM, Di Rienzo A, Jeong C, Starikovskaya EB, Metspalu E, Parik J, Villems R, Henn BM, Hodoglugil U, Mahley R, Sajantila A, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Wee JT, Khusainova R, Khusnutdinova E, Litvinov S, Ayodo G, Comas D, Hammer MF, Kivisild T, Klitz W, Winkler CA, Labuda D, Bamshad M, Jorde LB, Tishkoff SA, Watkins WS, Metspalu M, Dryomov S, Sukernik R, Singh L, Thangaraj K, Paabo S, Kelso J, Patterson N, Reich D (2016) The simons genome diversity project: 300 genomes from 142 diverse populations. Nature 538:201–206
Peng MS, He JD, Fan L, Liu J, Adeola AC, Wu SF, Murphy RW, Yao YG, Zhang YP (2014) Retrieving Y chromosomal haplogroup trees using GWAS data. Eur J Hum Genet 22:1046–1050
Qi X, Cui C, Peng Y, Zhang X, Yang Z, Zhong H, Zhang H, Xiang K, Cao X, Wang Y, Wu T, Chen H, Shi H, Su B (2013) Genetic evidence of paleolithic colonization and neolithic expansion of modern humans on the tibetan plateau. Mol Biol Evol 30:1761–1778
Rhode D, Madsen DB, Jeffrey Brantingham P, Dargye T (2007) Yaks, yak dung, and prehistoric human habitation of the Tibetan Plateau. In: Developments in quaternary sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 205–224
Sagart L (2008) The expansion of Setaria farmers in East Asia: a linguistic and archaeological model. In: Sanchez-Mazas A, Blench R, Ross MD, Peiros I, Lin M (eds) Past human migrations in East Asia: matching archaeology, linguistics and genetics. Routledge, London, pp 133–157
Shi H, Dong YL, Wen B, Xiao CJ, Underhill PA, Shen PD, Chakraborty R, Jin L, Su B (2005) Y-chromosome evidence of southern origin of the East Asian-specific haplogroup O3-M122. Am J Hum Genet 77:408–419
Shi H, Zhong H, Peng Y, Dong YL, Qi XB, Zhang F, Liu LF, Tan SJ, Ma RZ, Xiao CJ, Wells RS, Jin L, Su B (2008) Y chromosome evidence of earliest modern human settlement in East Asia and multiple origins of Tibetan and Japanese populations. BMC Biol 6:45
Simons GF, Fennig CD (2017) Ethnologue: languages of the world, 20 edn. SIL International, In., Dallas
Su B, Xiao C, Deka R, Seielstad MT, Kangwanpong D, Xiao J, Lu D, Underhill P, Cavalli-Sforza L, Chakraborty R, Jin L (2000) Y chromosome haplotypes reveal prehistorical migrations to the Himalayas. Hum Genet 107:582–590
Van Driem G (1999) Neolithic correlates of ancient Tibeto–Burman migrations. In: Blench R, Spriggs M (eds) Archaeology and language II: archaeological data and linguistic hypotheses. Routledge, London, pp 67–102
Wang CC, Wang LX, Shrestha R, Zhang M, Huang XY, Hu K, Jin L, Li H (2014) Genetic structure of Qiangic populations residing in the western Sichuan corridor. PLoS One 9:e103772
Yao HB, Tang S, Yao X, Yeh HY, Zhang W, Xie Z, Du Q, Ma L, Wei S, Gong X, Zhang Z, Li Q, Xu B, Zhang HQ, Chen G, Wang CC (2017) The genetic admixture in Tibetan-Yi Corridor. Am J Phys Anthropol 164:522–532
Zhang C, Lu Y, Feng Q, Wang X, Lou H, Liu J, Ning Z, Yuan K, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Deng L, Liu L, Yang Y, Li S, Ma L, Zhang Z, Jin L, Su B, Kang L, Xu S (2017) Differentiated demographic histories and local adaptations between Sherpas and Tibetans. Genome Biol 18:115
Acknowledgements
We thank all donors for providing DNA samples. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91731303 to S.X. and H.L., 31222030 and 31671297 to H.L., 31401060 to Y.S., 31271338 to L.J., 31501011 to Y.L., 31525014‚ 31771388‚ and 31711530221 to S.X.), MOE Scientific Research Project (113022A to H.L.), Shanghai Shuguang Project (14SG05 to H.L.), Ministry of Science and Technology of China (MOST) (2016YFC0900300 to H.L.). S.X. also acknowledges financial support from the Strategic Priority Research Program (XDB13040100) and Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-SYS009) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader (16XD1404700), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (2017SHZDZX01)‚ and the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0906403). L.H.W. was supported by Future Scientists Project of China Scholarship Council. C.C.W was supported by the Nanqiang Outstanding Young Talents Program of Xiamen University. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LXW, YL, CZ, and LHW carried out the molecular genetic studies and drafted the manuscript. YL, CZ, SHX, SY, and SM collected the samples. YL, CZ, and SY participated in the experiments. YZH, CCW, SQW, SM, and LJ participated in the statistical analysis. SHX and HL designed the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
438_2018_1461_MOESM3_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 3 Table S2. Age and posterior support estimates for each numbered clade on the phylogenetic tree in Figure S1 (XLSX 41 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LX., Lu, Y., Zhang, C. et al. Reconstruction of Y-chromosome phylogeny reveals two neolithic expansions of Tibeto-Burman populations. Mol Genet Genomics 293, 1293–1300 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1461-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1461-2