Abstract
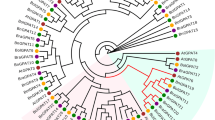
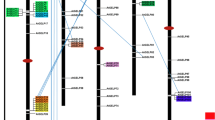
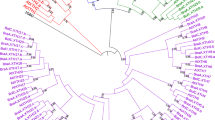
GDSL esterase/lipase proteins (GELPs), a very large subfamily of lipolytic enzymes, have been identified in microbes and many plants, but only a few have been characterized with respect to their roles in growth, development, and stress responses. In Brassica crops, as in many other species, genome-wide systematic analysis and functional studies of these genes are still lacking. As a first step to study their function in B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (Chinese cabbage), we comprehensively identified all GELP genes in the genome. We found a total of 121 Brassica rapa GDSL esterase/lipase protein genes (BrGELPs), forming three clades in the phylogenetic analysis (two major and one minor), with an asymmetrical chromosomal distribution. Most BrGELPs possess four strictly conserved residues (Ser-Gly-Asn-His) in four separate conserved regions, along with short conserved and clade-specific blocks, suggesting functional diversification of these proteins. Detailed expression profiling revealed that BrGELPs were expressed in various tissues, including floral organs, implying that BrGELPs play diverse roles in various tissues and during development. Ten percent of BrGELPs were specifically expressed in fertile buds, rather than male-sterile buds, implying their involvement in pollen development. Analyses of EXL6 (extracellular lipase 6) expression and its co-expressed genes in both B. rapa and Arabidopsis, as well as knockdown of this gene in Arabidopsis, revealed that this gene plays an important role in pollen development in both species. The data described in this study will facilitate future investigations of other BrGELP functions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agee AE, Surpin M, Sohn EJ, Girke T, Rosado A, Kram BW et al (2010) MODIFIED VACUOLE PHENOTYPE1 is an Arabidopsis myrosinase-associated protein involved in endomembrane protein trafficking. Plant Physiol 152:120–132
Akoh CC, Lee GC, Liaw YC, Huang TH, Shaw JF (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43:534–552
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L et al (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208
Brick DJ, Brumlik MJ, Buckley JT, Cao JX, Davies PC, Misra S et al (1995) A new family of lipolytic plant enzymes with members in rice, arabidopsis and maize. FEBS Lett 377:475–480
Cheng F, Wu J, Fang L, Sun S, Liu B, Lin K et al (2012) Biased gene fractionation and dominant gene expression among the subgenomes of Brassica rapa. PLoS One 7:e36442
Chepyshko H, Lai CP, Huang LM, Liu JH, Shaw JF (2012) Multifunctionality and diversity of GDSL esterase/lipase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica) genome: new insights from bioinformatics analysis. BMC Genom 13:309
Devisetty UK, Covington MF, Tat AV, Lekkala S, Maloof JN (2014) Polymorphism identification and improved genome annotation of Brassica rapa through deep RNA sequencing. G3 4:2065–2078
Dong X, Feng H, Xu M, Lee J, Kim YK, Lim YP et al (2013a) Comprehensive analysis of genic male sterility-related genes in Brassica rapa using a newly developed Br 300K oligomeric chip. PLoS One 8:e72178
Dong X, Kim WK, Lim YP, Kim YK, Hur Y (2013b) Ogura-CMS in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) causes delayed expression of many nuclear genes. Plant Sci 199–200:7–17
Du Z, Zhou X, Ling Y, Zhang Z, Su Z (2010) agriGO: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W64–W70
Duan W, Song X, Liu T, Huang Z, Ren J, Hou X et al (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Brassica rapa (Chinese cabbage). Mol Genet Genomics 290:239–255
Edlund AF, Swanson R, Preuss D (2004) Pollen and stigma structure and function: the role of diversity in pollination. Plant Cell 16:S84–S97
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR (2011) HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W29–W37
Hong JK, Choi HW, Hwang IS, Kim DS, Kim NH, Choi DS et al (2008) Function of a novel GDSL-type pepper lipase gene, CaGLIP1, in disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 227:539–558
Jiang Y, Chen R, Dong J, Xu Z, Gao X (2012) Analysis of GDSL lipase (GLIP) family genes in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Omics 5(4):351–358
Kim KJ, Lim JH, Kim MJ, Kim T, Chung HM, Paek KH (2008) GDSL-lipase1(CaGL1) contributes to wound stress resistance by modulation of CaPR-4 expression in hot pepper. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:693–698
Koonin EV (2005) Orthologs, paralogs, and evolutionary genomics. Annu Rev Genet 39:309–338
Krishnamurthy P, Hong JK, Kim JA, Jeong MJ, Lee YH, Lee SI (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals Brassica rapa-specific evolutionary dynamics upon whole genome triplication. Mol Genet Genomics 290:521–530
Kwon SJ, Jin HC, Lee S, Nam MH, Chung JH, Kwon SI et al (2009) GDSL lipase-like 1 regulates systemic resistance associated with ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 58:235–245
Lee DS, Kim BK, Kwon SJ, Jin HC, Park OK (2009) Arabidopsis GDSL lipase 2 plays a role in pathogen defense via negative regulation of auxin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:1038–1042
Leščić Ašler I, Ivić N, Kovačić F, Schell S, Knorr J, Krauss U et al (2010) Probing enzyme promiscuity of SGNH hydrolases. Chembiochem 11:2158–2167
Li J, Gao G, Zhang T, Wu X (2013) The putative phytocyanin genes in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.): genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 288:1–20
Li J, Gao G, Xu K, Chen B, Yan G, Li F et al (2014) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the putative non-specific lipid transfer proteins in Brassica rapa L. PLoS One 9:e84556
Ling H (2008) Sequence analysis of GDSL lipase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Pak J Biol Sci 11:763–767
Ling H, Zhao J, Zuo K, Qiu C, Yao H, Qin J et al (2006) Isolation and expression analysis of a GDSL-like lipase gene from Brassica napus L. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:297–303
Mayfield JA, Preuss D (2000) Preuss, Rapid initiation of Arabidopsis pollination requires the oleosin-domain protein GRP17. Nat Cell Biol 2:128–130
Mayfield JA, Fiebig A, Johnstone SE, Preuss D (2001) Gene families from the Arabidopsis thaliana pollen coat proteome. Science 292:2482–2485
Mølgaard A, Kauppinen S, Larsen S (2000) Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Structure 8:373–383
O’Brien KP, Remm M, Sonnhammer EL (2005) Inparanoid: a comprehensive database of eukaryotic orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D476–D480
Oh IS, Park AR, Bae MS, Kwon SJ, Kim YS, Lee JE, Kang NY, Lee S, Cheong H, Park OK (2005) Secretome analysis reveals an Arabidopsis lipase involved in defense against Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Cell 17:2832–2847
Peterson R, Slovin JP, Chen C (2010) A simplified method for differential staining of aborted and non-aborted pollen grains. Int J Plant Biol 1:e13
Quilichini TD, Douglas CJ, Samuels AL (2014) New views of tapetum ultrastructure and pollen exine development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Ann Bot 114:1189–1201
Song X, Li Y, Hou X (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genom 14:573
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tan X, Yan S, Tan R, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Chen J (2014) Characterization and expression of a GDSL-like lipase gene from Brassica napus in Nicotiana benthamiana. Protein J 33:18–23
Thamilarasan SK, Park JI, Jung HJ, Nou IS (2014) Genome-wide analysis of the distribution of AP2/ERF transcription factors reveals duplication and CBFs genes elucidate their potential function in Brassica oleracea. BMC Genom 15:422
Toufighi K, Brady SM, Austin R, Ly E, Provart NJ (2005) The Botany Array Resource: e-Northerns, Expression Angling, and promoter analyses. Plant J 43:153–163
Updegraff EP, Zhao F, Preuss D (2009) The extracellular lipase EXL4 is required for efficient hydration of Arabidopsis pollen. Sex Plant Reprod 22:197–204
Upton C, Buckley JT (1995) A new family of lipolytic enzymes? Trends Biochem Sci 20:178–179
Volokita M, Rosilio-Brami T, Rivkin N, Zik M (2011) Combining comparative sequence and genomic data to ascertain phylogenetic relationships and explore the evolution of the large GDSL-lipase family in land-plants. Mol Biol Evol 28:551–565
Wang X, Wang H, Wang J, Sun R, Wu J, Liu S et al (2011) The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat Genet 43:1035–1039
Winter D, Vinegar B, Nahal H, Ammar R, Wilson GV, Provart NJ (2007) An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS One 2:e718
Xu J, Ding Z, Vizcay-Barrenan G, Shi J, Liang W, Yuan Z et al (2014) ABORTED MICROSPORES acts as a mater regulator of pollen wall formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:1544–1556
Zhang Z, Ober JA, Kliebenstein DJ (2006) The gene controlling the quantitative trait locus EPITHIOSPECIFIER MODIFIER1 alters glucosinolate hydrolysis and insect resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:1524–1536
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by research grants from Golden Seed Project (Center for Horticultural Seed Development, nos. 213003-04-3-CG100 and 213003-04-3-SB230), Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA), Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (MOF), and Rural Development Administration (RDA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dong X declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yi H declares that he has no conflict of interest. Han C-T declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nou I-S declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hur Y declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
438_2015_1123_MOESM1_ESM.rar
Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of the Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa) GELP candidate genes, its pseudoenzymes and genes coding for muti-domain proteins. Supplementary Table 2. Characteristics of the Arabidopsis GELP candidate genes, its pseudoenzymes and genes coding for muti-domain proteins. Supplementary Table 3. Conserved motifs identified in the BrGELP proteins. Supplementary Table 4. Orthologous GELP genes in B. rapa and Arabidopsis. Supplementary Table 5. List of genes co-expressed with BrEXL6, with the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) threshold value set at 0.85. ESTs co-expressed with all BrEXL6 probes, Brapa_ESTC003525, Brapa_ESTC000535 and Brapa_ESTC010981, were included. Supplementary Table 6. List of genes co-expressed with AtEXL6, with the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) threshold value set at 0.85. Supplementary Fig. 1 Gene structures of the BrGELPs and BrGELP pseudoenzymes. Exon/intron structures of 121 genes and 29 pseudoenzymes are presented. Green boxes represent exon regions, and solid lines indicate intron regions. Supplementary Fig. 2 Multiple sequence alignment of BrGELP and AtGELP genes. Supplementary Fig. 3 Phylogenetic relationships among the BrGELP and AtGELP gene families. Multiple protein sequence alignment was performed using ClustalW implemented in MEGA6. For this tree, the initial tree were generated by implementing NJ/BioNJ method, and tree improvement was achieved by Nearest-Neighbor-Interchange (NNI) and branch support analysis by 1000 replicates bootstrap. Different clades and branches (subclades) are indicated by the colors of the background and branch lines, respectively. Supplementary Fig. 4 Heat map representation and hierarchical clustering of BrGELP genes (A) and its pseudoenzymes (B) across root, stem, and leaf. Heat maps were generated from RPKM values (Cheng et al. 2012) using the MeV software. NA, no available data. Supplementary Fig. 5 A, Whole anthers of wild-type and AtEXL6-transgenic plants stained with modified Alexander solution (Peterson et al. 2010). Bar, 40 μm. B, Overall plant morphology of the AtEXL6-antisense and -sense transgenic lines. Bar, 50 mm. (RAR 64997 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X., Yi, H., Han, CT. et al. GDSL esterase/lipase genes in Brassica rapa L.: genome-wide identification and expression analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 291, 531–542 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1123-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1123-6