Abstract
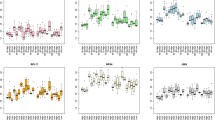
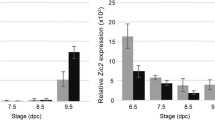
RT-qPCR is a commonly used method for evaluating gene expression; however, its accuracy and reliability are dependent upon the choice of appropriate reference gene(s), and there is limited information available on suitable reference gene(s) that can be used in mouse testis at different stages. In this study, using the RT-qPCR method, we investigated the expression variations of six reference genes representing different functional classes (Actb, Gapdh, Ppia, Tbp, Rps29, Hprt1) in mice testis during embryonic and postnatal development. The expression stabilities of putative reference genes were evaluated using five algorithms: geNorm, NormFinder, Bestkeeper, the comparative delta C t method and integrated tool RefFinder. Analysis of the results showed that Ppia, Gapdh and Actb were identified as the most stable genes and the geometric mean of Ppia, Gapdh and Actb constitutes an appropriate normalization factor for gene expression studies. The mRNA expression of AT1 as a test gene of interest varied depending upon which of the reference gene(s) was used as an internal control(s). This study suggested that Ppia, Gapdh and Actb are suitable reference genes among the six genes used for RT-qPCR normalization and provide crucial information for transcriptional analyses in future studies of gene expression in the developing mouse testis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64(15):5245–5250
Bas A, Forsberg G, Hammarström S, Hammarström ML (2004) Utility of the Housekeeping genes 18 s rRNA, beta-actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate -dehydrogenase for normalization in real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of gene expression in human T-lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol 59(6):566–573
Boda E, Pini A, Hoxha E, Parolisi R, Tempia F (2009) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR studies in mouse brain. J Mol Neurosci 37(3):238–253
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622
Chalmel F, Lardenois A, Georg I, Barrionuevo F, Demougin P, Jégou B, Scherer G, Primig M (2013) Genome-wide identification of Sox8-, and Sox9-dependent genes during early post-natal testis development in the mouse. Andrology 1(2):281–292
Chechi K, Gelinas Y, Mathieu P, Deshaies Y, Richard D (2012) Validation of reference genes for the relative quantification of gene expression in human epicardial adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 7(4):e32265
Cicinnati VR, Shen Q, Sotiropoulos GC, Radtke A, Gerken G, Beckebaum S (2008) Validation of putative reference genes for gene expression studies in human hepatocellular carcinoma using real-time quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Cancer 8:350
Czechowski T, Stitt M, Altmann T, Udvardi MK, Scheible WR (2005) Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139(1):5–17
Dheda K, Huggett JF, Chang JS, Kim LU, Bustin SA, Johnson MA, Rook GA, Zumla A (2005) The implications of using an inappropriate reference gene for real-time reverse transcription PCR data normalization. Anal Biochem 344(1):141–143
Faccioli P, Ciceri GP, Provero P, Stanca AM, Morcia C, Terzi V (2007) A combined strategy of “in silico” transcriptome analysis and web search engine optimization allows an agile identification of reference genes suitable for normalization in gene expression studies. Plant Mol Biol 63(5):679–688
Feng L, Yu Q, Li X, Ning X, Wang J, Zou J, Zhang L, Wang S, Hu J, Hu X, Bao Z (2013) Identification of reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis in Yesso Scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. PLoS ONE 8(9):e75609
Fletcher DA, Mullins RD (2010) Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton. Nature 463(7280):485–492
Gebeh AK, Marczylo EL, Amoako AA, Willets JM, Konje JC (2012) Variation in stability of endogenous reference genes in fallopian tubes and endometrium from healthy and ectopic pregnant women. Int J Mol Sci 13(3):2810–2826
Glare EM, Divjak M, Bailey MJ, Walters EH (2002) Beta-actin and GAPDH housekeeping gene expression in asthmatic airways is variable and not suitable for normalising mRNA levels. Thorax 57(9):765–770
Gu YR, Li MZ, Zhang K, Chen L, Jiang AA, Wang JY, Li XW (2011) Evaluation of endogenous control genes for gene expression studies across multiple tissues and in the specific sets of fat- and muscle-type samples of the pig. J Anim Breed Genet 128(4):319–325
Hong SY, Seo PJ, Yang MS, Xiang F, Park CM (2008) Exploring valid reference genes for gene expression studies in Brachypodium distachyon by real-time PCR. BMC Plant Biol 8:112
Kanehara H, Song K, Hirai K, Ueda H, Shiota N, Azuma H, Katsuoka Y, Miyazaki H, Miyazaki M (1998) Involvement of angiotensin II receptor subtypes during testicular development in rats. Int J Androl 21(4):186–195
Kuijk EW, du Puy L, van Tol HT, Haagsman HP, Colenbrander B, Roelen BA (2007) Validation Of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies in porcine oocytes and preimplantation embryos. BMC Dev Biol 7:58
Leung PS, Sernia C (2003) The renin-angiotensin system and male reproduction: new functions for old hormones. J Mol Endocrinol 30(3):263–270
Migrenne S, Moreau E, Pakarinen P, Dierich A, Merlet J, Habert R, Racine C (2012) Mouse testis development and function are differently regulated by follicle-stimulating hormone receptors signaling during fetal and prepubertal life. PLoS ONE 7(12):e53257
Miles DC, Wakeling SI, Stringer JM, van den Bergen JA, Wilhelm D, Sinclair AH, Western PS (2013) Signaling through the TGF beta-activin receptors ALK4/5/7 regulates Testis formation and male germ cell development. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54606
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006) Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc 1(3):1559–1582
Paolacci AR, Tanzarella OA, Porceddu E, Ciaffi M (2009) Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR normalization in wheat. BMC Mol Biol 10:11
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper–Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26(6):509–515
Phillips BT, Gassei K, Orwig KE (2010) Spermatogonial stem cell regulation and spermatogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365(1546):1663–1678
Pombo-Suarez M, Calaza M, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gonzalez A (2008) Reference genes for normalization of gene expression studies in human osteoarthritic articular cartilage. BMC Mol Biol 9:17
Selvey S, Thompson EW, Matthaei K, Lea RA, Irving MG, Griffiths LR (2001) Beta-actin-an unsuitable internal control for RT-PCR. Mol Cell Probes 15(5):307–311
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:33
Stephens AS, Stephens SR, Morrison NA (2011) Internal control genes for quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis in mouse osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages. BMC Res Notes 4:410
Tricarico C, Pinzani P, Bianchi S, Paglierani M, Distante V, Pazzagli M, Bustin SA, Orlando C (2002) Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction: normalization to rRNA or single housekeeping genes is inappropriate for human tissue biopsies. Anal Biochem 309(2):293–300
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(7):research0034.1–research0034.11
Wan H, Zhao Z, Qian C, Sui Y, Malik AA, Chen J (2010) Selection of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in cucumber. Anal Biochem 399(2):257–261
Wong ML, Medrano JF (2005) Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. Biotechniques 39(1):75–85
Zhang Y, Chen D, Smith MA, Zhang B, Pan X (2012) Selection of reliable reference genes in Caenorhabditis elegans for analysis of nanotoxicity. PLoS ONE 7(3):e31849
Acknowledgments
This research project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81160263), the Scientific Research Fund of Guangxi Education Department (Grant No. 200103YB025) and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Program (Grant No. 2010GXNSFA013162). We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Z.-K. Gong and S.-J. Wang contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, ZK., Wang, SJ., Huang, YQ. et al. Identification and validation of suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in mouse testis development. Mol Genet Genomics 289, 1157–1169 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0877-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0877-6