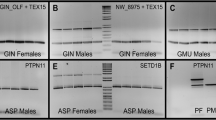
Abstract
Sex determination in the endemic Australian lizard Bassiana duperreyi (Scincidae) is influenced by sex chromosomes and incubation temperature, challenging the traditional dichotomy in reptilian sex determination. Analysis of those interactions requires sex chromosome markers to identify temperature-induced sex reversal. Here, we report the isolation of Y chromosome DNA sequence from B. duperreyi using amplified fragment length polymorphism PCR, the conversion of that sequence to a single-locus assay, and its combination with a single-copy nuclear gene (C-mos) to form a duplex PCR test for chromosomal sex. The accuracy of the assay was tested on an independent panel of individuals with known phenotypic sex. When used on offspring from field nests, our test identified the likely occurrence of a low rate of natural sex reversal in this species. This work represents the first report of Y chromosome sequence from a reptile and one of the few reptile sex tests.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bull JJ (1980) Sex determination in reptiles. Q Rev Biol 55:3–21
Bull JJ, Vogt RC (1979) Temperature-dependent sex determination in turtles. Science 206:186–1188
Burger J, Zappalorti RT (1988) Effects of incubation temperatures on sex ratios in pine snakes: differential vulnerability of males and females. Am Nat 132:492–505
Conover DO (2004) Temperature-dependent sex determination in fishes. In: Valuenzuela N, Lance VA (eds) Temperature-dependent sex determination in vertebrates. Smithsonian Institute, Washington, pp 11–20
Conover DO, Kynard BE (1981) Environmental sex determination: interaction of temperature and genotype in a fish. Science 213:577–579
Cooper SJB, Bull CM, Gardner MG (1997) Characterisation of microsatellite loci from the social monogamous lizard Tiliqua rugosa using a PCR-based isolation technique. Mol Ecol 6:793–795
Devlin RH, Nagahama Y (2002) Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 208:191–364
Donnellan SC (1985) The evolution of sex chromosomes in scincid lizards. PhD thesis. Macquarie University, Sydney
Donnellan SC (1991) Chromosomes of Australian lygosomine skinks (Lacertilia, Scincidae) II. The genus Lampropholis. Genetica 83:223–234
Ezaz T, Harvey SC et al (2004) Isolation and physical mapping of sex-linked AFLP markers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Mar Biotech 6:435–445
Ezaz T, Stiglec R, Veyrunes F, Graves JAM (2006) Relationships between vertebrate ZW and XY sex chromosome systems. Curr Biol 16:736–743
Felip A, Young WP et al (2005) An AFLP-based approach for the identification of sex-linked markers in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 247:35–43
Graves JAM (2006) Sex chromosome specialization and degeneration in mammals. Cell 124:901–912
Graves JAM, Shetty S (2001) Sex from W to Z: evolution of vertebrate sex chromosomes and sex determining genes. J Exp Zool 290:449–462
Griffiths R (2000) Sex identification using DNA markers. In: Baker AJ (ed) Molecular methods in ecology. Blackwell, London, pp 295–322
Griffiths R, Orr KJ (1999) The use of amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) in the isolation of sex-specific markers. Mol Ecol 8:671–674
Griffiths R, Orr KJ, Adam A, Barber I (2000) DNA sex identification in the three-spined stickleback. J Fish Biol 57:1331–1334
Halverson J, Spelman LH (2002) Sex determination. In: Murphy JB, Ciofi C, de la Panouse C, Walsh T (eds) Biology and conservation of Komodo dragons. Smithsonian Institute, Washington, pp 165–177
Hardy GM (1979) The karyotypes of two scincid lizards, and their bearing on relationships in genus Leiolopisma and relatives (Scincidae: Lygosominae). N Z J Zool 6:609–612
Harlow PS (1996) A harmless technique for sexing hatchling lizards. Herp Rev 27:71–72
Hutchinson MN, Donnellan SC (1992) Taxonomy and geographic variation in the Australian lizards of the genus Pseudemoia (Scincidae: Lygosominae). J Nat Hist 26:215–264
Janzen FJ, Paukstis GL (1991) Environmental sex determination in reptiles: ecology, evolution, and experimental design. Q Rev Biol 66:149–179
Lebel-Hardenack S, Hauser E, Law TF, Schmid J, Grant SR (2002) Mapping of sex determination loci on the white campion (Silene latifolia) Y chromosome using amplified fragment length polymorphism. Genetics 160:717–725
Matsubara K, Tarui H, Toriba M, Yamada K, Nishida-Umehara C, Agata K, Matsuda Y (2006) Evidence for different origin of sex chromosomes in snakes, birds, and mammals and step-wise differentiation of snake sex chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18190–18195
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting-out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Nanda I, Zend-Ajusch E et al (2000) Conserved synteny between the chicken Z sex chromosome and human chromosome 9 includes the male regulatory gene DMRT1: a comparative (re)view on avian sex determination. Cytogenet Cell Genet 89:67–78
Ohno S (1967) Sex chromosomes and sex-linked genes. Springer, Heidelberg
Olmo E (1986) Animal cytogenetics 4, chordata 3, A. reptilia. Gebruder Borntraeger, Stuttgart
Peil A, Flachowsky H, Schumann E, Weber WE (2003) Sex-linked AFLP markers indicate a pseudoautosomal region in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:102–109
Quinn AE, Georges A, Sarre SD, Guarino F, Ezaz T, Graves JAM (2007) Temperature sex reversal implies sex gene dosage in a reptile. Science 316:411
Radder RS, Ali S, Shine R (2007) Offspring sex is not related to maternal allocation of yolk steroids in the lizard Bassiana duperreyi (Scincidae). Physiol Biochem Zool 80:220–227
Radder RS, Quinn AE, Georges A, Sarre SD, Shine R (2008) Genetic evidence for co-occurrence of chromosomal and thermal sex-determining systems in a lizard. Biol Lett 4:176–178
Reamon-Büttner SM, Schondelmaier J, Jung C (1998) AFLP markers tightly linked to the sex locus in Asparagus officinalis L. Mol Breed 4:91–98
Saint KM, Austin CC, Donnellan SC, Hutchinson MN (1998) C-mos, a nuclear marker useful for squamate phylogenetic analysis. Mol Phylogenet Evol 10:259–263
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Sarre SD, Georges A, Quinn AE (2004) The ends of a continuum: genetic and temperature-dependent sex determination in reptiles. BioEssays 26:639–645
Shine R, Elphick MJ, Donnellan SC (2002) Co-occurrence of multiple, supposedly incompatible modes of sex determination in a lizard population. Ecol Lett 5:486–489
Solari AJ (1994) Sex chromosomes and sex determination in vertebrates. CRC, Boca Raton
Stiglec R, Ezaz T, Graves JAM (2007) A new look at the evolution of avian sex chromosomes. Cytogenet Genome Res 117:103–109
Stow AJ, Sunnucks P, Briscoe DA, Gardner MG (2001) The impact of habitat fragmentation on dispersal of Cunningham’s skink (Egernia cunninghami): evidence from allelic and genotypic analyses of microsatellites. Mol Ecol 10:867–878
Valenzuela N, Lance VA (eds) (2004) Temperature-dependent sex determination in vertebrates. Smithsonian Institute, Washington
Valenzuela N, Adams DC, Janzen FJ (2003) Pattern does not equal process: exactly when is sex environmentally determined? Am Nat 161:676–683
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Homes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Acknowledgments
We thank Melanie Elphick and Jacqui Richardson for laboratory assistance, and the Australian Research Council (DP0346850 to SDS and AG, DP0449935 to JM Graves, SDS and AG, and FF561365 to RS) for funding. We are deeply indebted to our late colleague Raju Radder who died unexpectedly at the age of 34 before this manuscript was finalized.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Becker.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quinn, A.E., Radder, R.S., Sarre, S.D. et al. Isolation and development of a molecular sex marker for Bassiana duperreyi, a lizard with XX/XY sex chromosomes and temperature-induced sex reversal. Mol Genet Genomics 281, 665–672 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-009-0437-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-009-0437-7