Abstract
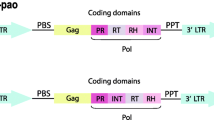
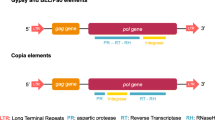
Crustacean species have not been examined in great detail for their transposable elements content. Here we focus on galatheid crabs, which are one of the most diverse and widespread taxonomic groups of Decapoda. Ty1/copia retrotransposons are a diverse and taxonomically dispersed group. Using degenerate primers, we isolated several DNA fragments that show homology with Ty1/copia retroelements reverse transcriptase gene. We named the corresponding elements from which they originated GalEa1 to GalEa3 and analyzed one of them further by isolating various clones containing segments of GalEa1. This is the first LTR retrotransposon described in crustacean genome. Nucleotide sequencing of the clones revealed that GalEa1 has LTRs (124 bp) and that the internal sequence (4,421 bp) includes a single large ORF containing gag and pol regions. Further screening identified highly related elements in six of the nine galatheid species studied. By performing BLAST searches on genome databases, we could also identify GalEa-like elements in some fishes and Urochordata genomes. These elements define a new clade of Ty1/copia retrotransposons that differs from all other Ty1/copia elements and that seems to be restricted to aquatic species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba K (1988) Chirostylidae and Galatheidae Crustaceans (Decapoda: Anomura) of the Albatross Philippine Expedition, 1907–1910. Res Crust 2:1–203
Britten RJ, McCormack TJ, Mears TL, Davidson EH (1995) Gypsy/Ty3-class retrotransposons integrated in the DNA of herring, tunicate and echinoderms. J Mol Evol 40:13–24
Bui Q-T, Delaurière L, Casse N, Nicolas V, Laulier M, Chénais B (2007) Molecular characterization and phylogenetic position of a new mariner-like element in the coastal crab, Pachygrapsus marmoratus. Gene 396:248–256
Burke WD, Malik HS, Jones JP, Eickbush TH (1999) The domain structure and retrotransposition mechanism of R2 elements are conserved throughout arthropods. Mol Biol Evol 12(4):502–511
Capy P, Bazin C, Higuet D, Langin T (1997) Dynamics and evolution of transposable elements. R. G. Landes Company, Austin, TX
Casse N, Pradier E, Loiseau C, Bigot Y, Laulier M (2000) Mariner, a mobile DNA transposon in the genomes of several hydrothermal invertebrates. InterRidge News 9:15–17
Casse N, Bui QT, Nicolas V, Renault S, Bigot Y, Laulier M (2006) Species sympatry and horizontal transfers of Mariner transposons in marine crustacean genomes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 40(2):609–619
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17(4):540–552
Devic M, Albert S, Delseny M, Roscoe TJ (1997) Efficient PCR walking on plant genomic DNA. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:331–339
Fedoroff N (2000) Transposons and genome evolution in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(13):7002–7007
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Finnegan DJ (1989) Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet 5(4):103–107
Flavell AJ, Dunbar E, Anderson R, Pearce SR, Hartley R, Kumar A (1992) Ty1-copia group retrotransposons are ubiquitous and heterogeneous in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res 20(14):3639–3644
Gonzalez P, Lessios HA (1999) Evolution of sea urchin retroviral-like (SURL) elements: evidence from 40 echinoid species. Mol Biol Evol 16(7):938–952
Gregory TR (2007) Animal genome size database. http://www.genomesize.com. Cited Jan 2007
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52(5):696–704
Greenwood AD, Leib-Mösch C, Seifarth W (2005) Abyss1: a novel L2-like non-LTR retroelement of the snakelocks nemone (Anemonia sulcata). Cytogenet Genome Res 110:553–558
Halaimia-Toumi N, Casse N, Demattei MV, Renault S, Pradier E, Bigot Y, Laulier M (2004) The GC-rich transposon Bytmar1 from the deep-sea hydrothermal crab, Bythograea thermydron, may encode three transposase isoforms from a single ORF. J Mol Evol 59(6):747–760
Hiller A, Holger K, Almon M, Werding B (2006) The Petrolisthes galathinus complex: species boundaries based on color pattern, morphology and molecules, and evolutionary interrelationships between this complex and other Porcellanidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Anomura). Mol Phylogenet Evol 33(2):259–279
Ishaq M, Wolf B, Ritter C (1990) Large-scale isolation of plasmid DNA using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Biotechniques 9(1):19–24
Jordan IK, Rogozin IB, Glazko GV, Koonin EV (2003) Origin of a substantial fraction of human regulatory sequences from transposable elements. Trends Genet 19(2):68–72
Jurka J (1998) Repeats in genomic DNA: mining and meaning. Curr Opin Struct Biol 8(3):333–337
Kazazian HH Jr (2004) Mobile elements: drivers of genome evolution. Science 12:1626–1632
Kidwell MG, Lisch D (1997) Transposable elements as sources of variation in animals and plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(15):7704–7711
Kidwell MG (2002) Transposable elements and the evolution of genome size in eukaryotes. Genetica 115:49–63
Kvamme BJ, Kongshaug H, Nilsen F (2005) Organisation of trypsin genes in the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis, Crustacea, copepoda) genome. Gene 352:63–74
Li WH, Gu Z, Wang H, Nekrutenko A (2001) Evolutionary analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:847–849
Lovsin N, Gubensek F, Kordi D (2001) Evolutionary dynamics in a novel L2 clade of non-LTR retrotransposons in Deuterostomia. Mol Biol Evol 18:2213–2224
McClure MA (1991) Evolution of retroposons by acquisition or deletion of retrovirus-like genes. Mol Biol Evol 8(6):835–856
Machordom A, Macpherson E (2004) Rapid radiation and cryptic speciation in squat lobsters of the genus Munida (Crustacea, Decapoda) and related genera in the South West Pacific: molecular and morphological evidence. Mol Phylogenet Evol 33(2):259–279
Malik HS, Burke WD, Eickbush TH (1999) Modular evolution of the integrase domain in the Ty3/Gypsy class of LTR retrotransposons. J Virol 73(6):5186–5190
Malik HS, Eickbush TH (2001) TH Phylogenetic analysis of ribonuclease H domains suggests a late, chimerical origin of LTR retrotransposable elements and retroviruses. Genome Res 11(7):1187–1197
Misra S, Crosby MA, Mungall CJ et al (26 co-authors) (2002) Annotation of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatic genome: a systematic review. Genome Biol 3(12):1–22
Nylander JAA (2004) MrAIC.pl. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University
Ochman H, Ajioka JW, Garza D, Hartl DL (1990) Inverse polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnology (NY) 8:759–760
Palumbi SR, Benzie J (1991) Large mitochondrial DNA differences between morphologically similar Penaeid shrimp. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 1(1):27–34
Penton EH, Sullender BW, Crease TJ (2002) Pokey, a new DNA transposon in Daphnia (cladocera: crustacea). J Mol Evol 55(6):664–673
Petrov DA, Sangster TA, Johnston JS, Hartl DL, Shaw KL (2000) Evidence for DNA loss as a determinant of genome size. Science 287:1060–1062
Poulter RT, Goodwin TJ (2005) DIRS-1 and the other tyrosine recombinase retrotransposons. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:575–588
Rambaut A, Drummond A (2005) Tracer version 1.2.1. Computer program distributed by the authors. Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, UK
Robertson HM (1997) Multiple mariner transposons in flatworms and hydras are elated to those of insects. J Hered 88:195–201
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Van de Lagemaat LN, Landry JR, Mager DL, Medstrand P (2003) Transposable elements in mammals promote regulatory variation and diversification of genes with specialized functions. Trends Genet 19:530–536
Volff JN, Schartl M (2000) Multiple lineages of the non-LTR retrotransposon Rex1 with varying success in invading fish genomes. Mol Biol Evol 17:1673–1684
Volff JN, Hornung H, Schartl M (2001a) Fish retotransposons to the Penelope element of Drosophila virilis define a new group of retrotransposable elements. Mol Genet Genomics 265:711–720
Volff JN, Körting C, Meyr A, Schartl M (2001b) Evolution and discontinuous distribution of Rex3 retrotransposons in fish. Mol Biol Evol 18(3):427–431
Volff JN, Bouneau L, Ozouf-Costaz C, Fischer C (2003) Diversity of retrotransposable elements in compact pufferfish genome. Trends Genet 19:674–678
Waugh R, McLean K, Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A, Thomas BBT, Powell W (1997) Genetic distribution of Bare-1-like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (S-SAP). Mol Gen Genet 253:687–694
Xiong Y, Eickbush TH (1990) Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J 9(10):3353–3362
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Claude Bazin, Clémentine Vitte, Guillaume Achaz, and Philippe Lopez for helpful comments on manuscript and Malcom Eden for English revision. We also thank Enrique MacPherson for biological and phylogenetical informations on squat lobsters species, and Marie-Catherine Boisselier, Michel Descombes, Guillaume Lecointre, and Bertrand Richer de Forges for providing biological material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.-A. Grandbastien.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terrat, Y., Bonnivard, E. & Higuet, D. GalEa retrotransposons from galatheid squat lobsters (Decapoda, Anomura) define a new clade of Ty1/copia-like elements restricted to aquatic species. Mol Genet Genomics 279, 63–73 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0295-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0295-0