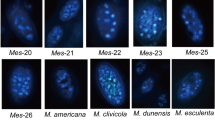
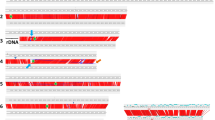
Abstract
Multigene families are features of most eukaryotic genomes, which evolve through a variety of mechanisms. This study describes the structure, expression, and evolution of a novel family in the oomycete Phytophthora. In the heterothallic species P. infestans, M96 is expressed specifically during sexual sporogenesis, and encodes a low-complexity extracellular protein that may be a component of oospore walls. Intriguingly, M96 exists in P. infestans as 22 relatively homogeneous loci tandemly repeated at a single site, which is partitioned by inversions and retroelements into subclusters exhibiting semi-independent evolution. M96 relatives were detected in other heterothallic and homothallic oomycetes including species closely (P. mirabilis, P. phaseoli) or distantly (P. ramorum, P. sojae) related to P. infestans. Those M96 relatives also exhibit oosporogenesis-specific expression and are arrayed multigene families. Nucleotide changes and repeat expansion diversify M96 in each species, however, paralogues are more related than orthologues. Concerted evolution through gene conversion and not strong purifying selection appears to be the major contributor to intraspecific homogenization. Divergence and concerted evolution was also detected between isolates of P. infestans. The divergence of M96 proteins between P. infestans, P. ramorum, and P. sojae exceeds that of typical proteins, reflecting trends in reproductive proteins from other kingdoms.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alibardi L, Spisni E, Toni M (2003) Presence of putative histidine-rich proteins in the amphibian epidermis. J Exp Zool 297A:105–117
Armbrust EV et al (2004) The genome of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana: ecology, evolution, and metabolism. Science 306:79–86
Baldauf SL, Roger AJ, Wenk-Siefert I, Doolittle WF (2000) A kingdom-level phylogeny of eukaryotes based on combined protein data. Science 290:972–977
Bartnicki-Garcia S, Wang MC (1983) Biochemical aspects of morphogenesis in Phytophthora. In: Erwin DC, Bartnicki-Garcia S, Tsao PH (eds) Phytophthora, its biology, taxonomy, ecology, and pathology. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 121–137
Bettencourt BR, Feder ME (2002) Rapid concerted evolution via gene conversion at the Drosophila hsp70 genes. J Mol Evol 54:569–586
Borts RH, Haber JE (1989) Length and distribution of meiotic gene conversion tracts and crossovers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 123:69–80
Cassab GI (1998) Plant cell wall proteins. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:281–309
Casselton LA, Olesnicky NS (1998) Molecular genetics of mating recognition in basidiomycete fungi. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:55–70
Chamnanpunt J, Shan W-x, Tyler Brett M (2001) High frequency mitotic gene conversion in genetic hybrids of the oomycete Phytophthora sojae. Proc Natl Acad Sci.USA 98:14530–14535
Chen LL, Rekosh DM, Loverde PT (1992) Schistosoma mansoni p48 eggshell protein gene characterization developmentally regulated expression and comparison to the p14 eggshell protein gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol 52:39–52
Chen W, Jinks-Robertson S (1998) Mismatch repair proteins regulate heteroduplex formation during mitotic recombination in yeast. Mol Cell Biol 18:6525–6537
Cooke DEL, Drenth A, Duncan JM, Wagels G, Brasier CM (2000) A molecular phylogeny of Phytophthora and related oomycetes. Fungal Genet Biol 30:17–32
Cornels H, Ichinose Y, Barz W (2000) Characterization of cDNAs encoding two glycine-rich proteins in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): accumulation in response to fungal infection and other stress factors. Plant Sci 154:83–88
Cvitanich C, Judelson HS (2003) A gene expressed during sexual and asexual sporulation in Phytophthora infestans is a member of the Puf family of translational regulators. Eukaryot Cell 2:465–473
Elder JF Jr, Turner BJ (1995) Concerted evolution of repetitive DNA sequences in eukaryotes. Quart Rev Biol 70:297–320
Ellis J, Dodds P, Pryor T (2000) Structure, function and evolution of plant disease resistance genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:278–284
Fabritius A-L, Cvitanich C, Judelson HS (2002) Stage-specific gene expression during sexual development in Phytophthora infestans. Mol Microbiol 45:1057–1066
Fabritius AL, Judelson HS (2003) A mating-induced protein of Phytophthora infestans is a member of a family of elicitors with divergent structures and stage-specific patterns of expression. Mol Plant-Microbe Inter 16:926–935
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Fernandez-Pavia SP, Grunwald NJ, Diaz-Valasis M, Cadena-Hinojosa M, Fry WE (2004) Soilborne oospores of Phytophthora infestans in central Mexico survive winter fallow and infect potato plants in the field. Plant Dis 88:29–33
Ferris PJ, Pavlovic C, Fabry S, Goodenough UW (1997) Rapid evolution of sex-related genes in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8634–8639
Fiebig A, Kimport R, Preuss D (2004) Comparisons of pollen coat genes across Brassicaceae species reveal rapid evolution by repeat expansion and diversification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:3286–3291
Fry WE, Goodwin SB (1997) Resurgence of the Irish potato famine fungus. Bioscience 47:363–371
Gonzalez IL, Sylvester JE (2001) Human rDNA: evolutionary patterns within the genes and tandem arrays derived from multiple chromosomes. Genomics 73:255–263
Goodwin SB, Smart CD, Sandrock RW, Deahl KL, Punja ZK, Fry WE (1998) Genetic charge within populations of Phytophthora infestans in the United States and Canada during 1994 to 1996: role of migration and recombination. Phytopathology 88:939–949
Gotesson A, Marshall JS, Jones DA, Hardham AR (2002) Characterization and evolutionary analysis of a large polygalacturonase gene family in the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora cinnamomi. Mol Plant-Microbe Inter 15:907–921
Gumucio DL, Wiebauer K, Caldwell RM, Samuelson LC, Meisler MH (1988) Concerted evolution of human amylase genes. Mol Cell Biol 8:1197–1205
Haberer G, Hindemitt T, Myeres BC, Mayer KFX (2004) Transcriptional similarities, dissimilarities, and conservation of cis-elements in duplicated genes of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136:3009–3022
Hozumi N, Tonegawa S (1976) Evidence for somatic rearrangement of immuno globulin genes coding for variable and constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci.USA 73:3628–3632
Hurst LD (2002) The K a/K s ratio: diagnosing the form of sequence evolution. Trends Genet 18:486–487
Judd SR, Petes TD (1988) Physical lengths of meiotic and mitotic gene conversion tracts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 118:401–410
Judelson HS, Randall TA (1998) Families of repeated DNA in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans and their distribution within the genus. Genome 41:605–615
Judelson HS, Roberts S (2002) Novel protein kinase induced during sporangial cleavage in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans. Eukaryot Cell 1:687–695
Judelson HS, Tooley PW (2000) Enhanced polymerase chain reaction methods for detecting and quantifying Phytophthora infestans in plants. Phytopathology 90:1112–1119
Kim KS, Judelson HS (2003) Sporangia-specific gene expression in the oomyceteous phytopathogen Phytophthora infestans. Eukaryot Cell 2:1376–1385
Kitano T, Saitou N (1999) Evolution of Rh blood group genes have experienced gene conversions and positive selection. J Mol Evol 49:615–626
Kuang H, Woo S-S, Meyers BC, Nevo E, Michelmore RW (2004) Multiple genetic processes result in heterogeneous rates of evolution within the major cluster disease resistance genes in lettuce. Plant Cell 16:2870–2894
Lagow E, DeSouza MM, Carson DD (1999) Mammalian reproductive tract mucins. Human Reprod Update 5:280–292
Liao D (1999) Concerted evolution: molecular mechanism and biological implications. Am J Hum Genet 64:24–30
Liao D (2000) Gene conversion drives within genic sequences: concerted evolution of ribosomal RNA genes in bacteria and archaea. J Mol Evol 51:305–317
Liu Z, Bos JI, Armstrong M, Whisson SC, da Cunha L, Torto-Alalibo T, Win J, Avrova AO, Wright F, Birch PR, Kamoun S (2005) Patterns of diversifying selection in the phytotoxin-like scr74 gene family of Phytophthora infestans. Mol Biol Evol 22:659–672
Makalowski W, Boguski MS (1998) Evolutionary parameters of the transcribed mammalian genome: an analysis of 2,820 orthologous rodent and human sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:9407–9412
Mao Y, Tyler BM (1991) Genome organization of Phytophthora megasperma f. sp glycinea. Exper Mycol 15:283–291
Moeller EM, De Cock AWAM, Prell HH (1993) Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA restriction enzyme analysis of the closely related Phytophthora species P. infestans, P. mirabilis, and P. phaseoli. J Phytopathol 139:309–321
Morgenstern B (1999) DIALIGN 2: improvement of the segment-to-segment approach to multiple sequence alignment. Bioinformatics 15:211–218
Muller HJ (1964) The relation of recombination to mutational advance. Mutat Res 1:29
Nasrallah JB (2002) Recognition and rejection of self in plant reproduction. Science 296:305–308
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7799–7806
O’Neill RJ, O’Neill MJ, Graves JAM (1998) Undermethylation associated with retroelement activation and chromosome remodelling in an interspecific mammalian hybrid. Nature 393:68–72
Pond SLK, Frost SDW (2005) Not so different after all: a comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol Biol Evol 22:1208–1222
Posada D, Crandall KA, Holmes EC (2002) Recombination in evolutionary genomics. Ann Rev Genet 36:75–97
Randall TA, Dwyer RA, Huitema E, Beyer K, Cvitanich C, Kelkar H, Ah Fong AMV, Gates K, Roberts S, Yatzkan E, Gaffney T, Law M, Testa A, Torto T, Zhang M, Zheng L, Mueller E, Windass J, Binder A, Birch PRJ, Gisi U, Govers F, Gow NAR, Mauch F, van West P, Waugh ME, Yu J, Boller T, Kamoun S, Lam ST, Judelson HS (2005) Large-scale gene discovery in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans reveals likely components of phytopathogenicity shared with true fungi. Mol Plant Microbe Inter 18:229–243
Randall TA, Judelson HS (1999) Construction of a bacterial artificial chromosome library of Phytophthora infestans and transformation of clones into P. infestans. Fungal Genet Biol 28:160–170
Sachetto-Martins G, Franco LO, de Oliveira DE (2000) Plant glycine-rich proteins: a family or just proteins with a common motif? Biochim Biophys Acta 1492:1–14
Sawyer S (1989) Statistical tests for detecting gene conversion. Mol Biol Evol 6:526–538
Schardl C, Craven K (2003) Interspecific hybridization in plant-associated fungi and oomycetes: a review. Mol Ecol 12:2681–2723
Schloetterer C, Tautz D (1994) Chromosomal homogeneity of Drosophila ribosomal DNA arrays suggests intrachromosomal exchanges drive concerted evolution. Curr Biol 4:777–783
Shuldiner AR, Nirula A, Roth J (1989) Hybrid DNA artifact from PCR of closely related target sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4409
Sogin ML, Silberman JD (1998) Evolution of the protists and protistan parasites from the perspective of molecular systematics. Int J Parasit 28:11–20
Swanson WJ, Vacquier VD (2002) The rapid evolution of reproductive proteins. Nature Rev Genet 3:137–144
Swanson WJ, Yang Z, Wolfner MF, Aquadro CF (2001) Positive Darwinian selection drives the evolution of several female reproductive proteins in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2509–2514
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tiffin P, Hahn MW (2002) Coding sequence divergence between two closely related plant species: Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis. J Mol Evol 54:746–753
Viguera E, Canceill D, Ehrlich SD (2001) Replication slippage involves DNA polymerase pausing and dissociation. EMBO J 20:2587–2595
Voglmayr H, Greilhuber J (1998) Genome size determination in peronosporales (Oomycota) by Feulgen image analysis. Fungal Genet Biol 25:181–195
Wendel JF, Schnabel A, Seelanan T (1995) Bidirectional interlocus concerted evolution following allopolyploid speciation in cotton. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:280–284
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Springer for helpful discussions, T. Girke for assistance with databases, M. Coffey and P. Tooley for providing strains, and the National Science Foundation of the United States for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P.Punt
Sequence data from this article have been deposited with the GenBank Data Libraries under accessions DQ196155 to DQ196175.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cvitanich, C., Salcido, M. & Judelson, H.S. Concerted evolution of a tandemly arrayed family of mating-specific genes in Phytophthora analyzed through inter- and intraspecific comparisons. Mol Genet Genomics 275, 169–184 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0074-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0074-8