Abstract
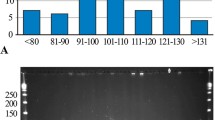
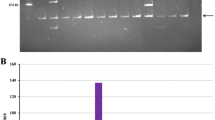
We estimated the genome size of Korean ginseng ( Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer), a medicinal herb, constructed a Hin dIII BAC library, and analyzed BAC-end sequences to provide an initial characterization of the library. The 1C nuclear DNA content of Korean ginseng was estimated to be 3.33 pg (3.12×103 Mb). The BAC library consists of 106,368 clones with an average size of 98.61 kb, amounting to 3.34 genome equivalents. Sequencing of 2167 BAC clones generated 2492 BAC-end sequences with an average length of 400 bp. Analysis using BLAST and motif searches revealed that 10.2%, 20.9% and 3.8% of the BAC-end sequences contained protein-coding regions, transposable elements and microsatellites, respectively. A comparison of the functional categories represented by the protein-coding regions found in BAC-end sequences with those of Arabidopsis revealed that proteins pertaining to energy metabolism, subcellular localization, cofactor requirement and transport facilitation were more highly represented in the P. ginseng sample. In addition, a sequence encoding a glucosyltransferase-like protein implicated in the ginsenoside biosynthesis pathway was also found. The majority of the transposable element sequences found belonged to the gypsy type (67.6%), followed by copia (11.7%) and LINE (8.0%) retrotransposons, whereas DNA transposons accounted for only 2.1% of the total in our sequence sample. Higher levels of transposable elements than protein-coding regions suggest that mobile elements have played an important role in the evolution of the genome of Korean ginseng, and contributed significantly to its complexity. We also identified 103 microsatellites with 3–38 repeats in their motifs. The BAC library and BAC-end sequences will serve as a useful resource for physical mapping, positional cloning and genome sequencing of P. ginseng.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Meyers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Awadalla P, Ritland K (1997) Microsatellite variation and evolution in the Mimulus guttatus species complex with contrasting mating systems. Mol Biol Evol 14:1023–1034
Bennetzen JL, Chandler VL, Schnable P (2001) Maize genome sequencing project. Plant Physiol 127:1572–1578
Bowen NJ, Jordan IK (2002) Transposable elements and the evolution of eukaryotic complexity. Curr Issues Mol Biol 4:65–76
Boysen C, Simon MI, Hood L (1997) Analysis of the 1.1-Mb human α/δ T-cell receptor locus with bacterial artificial chromosome clones. Genome Res 7:330–338
Budiman MA, Mao L, Wood TC, Wing RA (2000) A deep-coverage tomato BAC library and prospects toward development of an STC framework for genome sequencing. Genome Res 10:129–136
Choi SD, Creelman R, Mullet, Wing RA (1995) Construction and characterization of a bacterial artificial chromosome library from Arabidopsis thaliana. Weed World 2:17–20
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using Phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Fedoroff N (2000) Transposons and genome evolution in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7002–7007
Friesen N, Brandes A, Heslop-Harrison JS (2001) Diversity, origin, and distribution of retrotransposons ( gypsy and copia) in conifers. Mol Biol Evol 18:1176–1188
Grandbastien MA, Lucas H, Morel JB, Mhiri C, Vernhettes S, Casacuberta JM (1997) The expression of the tobacco Tnt1 retrotransposon is linked to plant defense response. Genetica 100:241–252
Green ED, Riethman HC, Dutchik JE, Olson MV (1991) Detection and characterization of chimeric yeast artificial-chromosome clones. Genomics 11:658–669
Harn C, Whang J (1963) Development of female gametophyte of Panax ginseng. Korean J Bot 6:3–6
Ho ISH, Leung FC (2002) Isolation and characterization of repetitive DNA sequences from Panax ginseng. Mol Genet Genomics 266:951–961
Islam-Faridi MN, Childs KL, Klein PE, Hodnett G, Menz MA, Klein RR, Rooney WL, Mullet JE, Stelly DM, Price HJ (2002) A molecular cytogenetic map of sorghum chromosome 1. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with mapped bacterial artificial chromosomes. Genetics 161:345–353
Jung JD, Park HW, Hahn Y, Hur CG, In DS, Chung HJ, Liu JR, Choi DW (2003) Discovery of genes for ginsenoside biosynthesis by analysis of ginseng expressed sequence tags. Plant Cell Rep 22:224-230
Kelley JM, Field CE, Craven MB, Bocskai DB, Kim UJ, Rounsley SD, Adams MD (1999) High-throughput direct end sequencing of BAC clones. Nucleic Acids Res 27:1539–1546
Kilian A, Chen J, Han F, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (1997) Towards map-based cloning of the barley stem rust resistance genes Rpg1 and rpg4 using rice as an intergenomic cloning vehicle. Plant Mol Biol 35:187–195
Kim UJ, Birren BW, Slepak T, Mancino V, Boysen C, Kang HL, Simon MI, Shizuya H (1996) Construction and characterization of a human bacterial artificial chromosome library. Genomics 34:213-218
Le QH, Wright S, Yu Z, Bureau T (2000) Transposon diversity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7376-7381
Lee JH, Yen Y, Kaeppler SM, Baenziger PS, Arumuganathan K (1997) Synchronization of cell cycle in root-tips and flow karyotype of metaphase chromosomes of common wheat ( Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 40:633–638
Leeton PR, Smyth DR (1993) An abundant LINE-like element amplified in the genome of Lilium speciosum. Mol Gen Genet 237:97–104
Leutwiler LS, Hough-Evans BR, Meyerowitz EM (1984) The DNA of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 194:15–23
Lim YP, Shin CS, Lee SJ, Youn YN, Jo JS (1993) Survey of proper primers and genetic analysis of Korean ginseng ( Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) variants using the RAPD technique. Korean J Ginseng Sci 17:153–158
Luo M, Wang YH, Frisch D, Joobeur T, Wing RA, Dean RA (2001) Melon bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library construction using improved methods and identification of clones linked to the locus conferring resistance to melon Fusarium wilt ( Fom -2). Genome 44:154-162
Mahady GB, Gyllenhaal C, Fong HHS, Farnsworth NR (2000) Ginseng: a review of safety and efficacy. Nutr Clin Care 3:90–101
Mahairas GG, Wallace JC, Smith K, Swartzell S, Holzman T, Keller A, Shaker R, Furlong J, Young J, Zhao S, Adams M, Hood L (1999) Sequence-tagged connectors: a sequence approach to mapping and scanning the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:9739–9744
Mao L, Wood TC, Yu Y, Budiman MA, Tomkins J, Woo S, Sasinowski M, Presting G, Frisch D, Goff S, Dean RA, Wing RA (2000) Rice transposable elements: a survey of 73,000 sequence-tagged-connectors. Genome Res 10:982–990
Marra M, et al (1999) A map for sequence analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Nat Genet 22:265–270
Meyers BC, Tingey SV, Morgante M (2001) Abundance, distribution, and transcriptional activity of repetitive elements in the maize genome. Genome Res 11:1660-1676
Nam KY (2002) Clinical application and efficacy of Korean ginseng ( Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer). J Ginseng Res 26:111–131
Ngan F, Shaw P, But P, Wang J (1999) Molecular authentication of Panax species. Phytochemistry 50:787–791
O’Neill CM, Bancroft I (2000) Comparative physical mapping of segments of the genome of Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra that are homoeologous to sequenced regions of chromosomes 4 and 5 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 23:233–243
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd edn). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Shizuya H, Birren B, Kim UJ, Mancino V, Slepak T, Tachiiri Y, Simon M (1992) Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8794–8797
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice ( Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequencing of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Tomkins JP, Mahalingam R, Smith H, Goicoechea JL, Knap HT, Wing RA (1999) A bacterial artificial chromosome library for soybean PI 437654 and identification of clones associated with cyst nematode resistance. Plant Mol Biol 41:25-32
Venter JC, Smith HO, Hood L (1996) A new strategy for genome sequencing. Nature 381:364–366
Vogler BK, Pittler MH, Ernst E (1999) The efficacy of ginseng. A systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 55:567–575
Wang GL, Holsten TE, Song WY, Wang HP, Ronald PC (1995) Construction of a rice bacterial artificial chromosome library and identification of clones linked to the Xa-21 disease resistance locus. Plant J 7:525–533
Wang GL, Warren R, Innes R, Osborne B, Baker B, Ronald PC (1996) Construction of an Arabidopsis BAC library and isolation of clones hybridizing with disease-resistance gene-like sequences. Plant Mol Biol Rep 14:107-114
Woo SS, Jiang J, Gill BS, Paterson AH, Wing RA (1994) Construction and characterization of a bacterial artificial chromosome library of Sorghum bicolor. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4922–4931
Yim YS, Davis GL, Duru NA, Musket TA, Linton EW, Messing JW, McMullen MD, Soderlund CA, Polacco ML, Gardiner JM, Coe EH Jr (2002) Characterization of three maize bacterial artificial chromosome libraries toward anchoring of the physical map to the genetic map using high-density bacterial artificial chromosome filter hybridization. Plant Physiol 130:1686–1696
Yu J, et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome ( Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Zhang HB, Choi SD, Woo SS, Li ZK, Wing RA (1996) Construction and characterization of two rice bacterial artificial chromosome libraries from the parents of a permanent recombinant inbred population. Mol Breed 2:11–24
Zhao S (2000) Human BAC ends. Nucleic Acids Res 28:129–132
Zhao S, Malek J, Mahairas G, Fu L, Nierman W, Venter JC, Adams MD (2000) Human BAC ends quality assessment and sequence analysis. Genomics 63:321–332
Zhao S, et al (2001) Mouse BAC ends quality assessment and sequence analysis. Genome Res 11:1736–1745
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by Plant Diversity Research Center (PDRC) Grant No. PF003101-01
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.-A. Grandbastien
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, C.P., Lee, S.J., Park, J.Y. et al. Construction of a BAC library of Korean ginseng and initial analysis of BAC-end sequences. Mol Genet Genomics 271, 709–716 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1021-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1021-9