Abstract
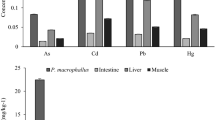
Bioaccumulation of 13 trace elements in the livers of 38 Pelophylax sinkl. hispanicus (Ranidae) and its helminth communities were studied and compared among three sites, each with a different degree of pollution along River Neto (south Italy) during September, 2014. Trace element concentrations in water and liver were measured using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. For most elements, the highest concentration was recorded in the frogs inhabiting the third site, the one with the highest degree of pollution. The trend of trace element concentration in the liver can be represented as follows: Cu > Zn > Mn > Se > Cr. Concentrations of some elements in water and liver samples were significantly different among the three sites and this is evidenced by the bioaccumulation in the frogs. Four species of helminths, all belonging to Nematoda, were found: Rhabdias sp., Oswaldocruzia filiformis (Goeze, 1782), Cosmocerca ornata (Dujarden, 1845), Seuratascaris numidica (Seurat, 1917). The parasite survey presents an important difference of prevalence and average number of helminths in frogs between the three sites. Correlating parasitological and ecotoxicological data showed a strong positive correlation between prevalence and number of parasites with some trace elements such as Mn, Co, Ni, As, Se, and Cd.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlassnig W, Sassmann S, Grawunder A, Puschenreiter M, Horvath A, Koller-Peroutka M (2013) Amphibians in metal-contaminated habitats. Salamandra 49:149–158
Anderson RC, Bain O (1982) Keys to genera of the superfamilies Rhabditoidea, Dioctophymatoidea, Trichinelloidea and Muspiceoidea. CIG keys to the nematode parasites of vertebrates. No. 9, Common wealth Agricultural Bureaux, Farnham Royal, UK
Andreani P, Santucci F, Nascetti G (2003) Le rane verdi del complesso Rana esculenta come bioindicatori della qualità degli ambienti fluviali italiani. Biologia Ambientale 17:35–44
Apollaro C, Accornero M, Marini L, Barca D, De Rosa R (2009) The impact of dolomite and plagioclase weathering on the chemistry of shallow groundwaters circulating in a granodiorite-dominated catchment of the Sila massif (Calabria, southern Italy). Appl Geochem 24:957–979
Ben Slimane B, Durette-Desset MC, Chabaud AG (1993) Oswaldocruzia (Trichostrongyloidea) parasites d’amphibiens des collections du muséum de Paris. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 68:88–100
Bernabò I, Gallo L, Sperone E, Tripepi S, Brunelli E (2011a) Toxicity of chlorpyrifos to larval Rana dalmatina: acute and chronic effects on survival, development, growth and gill apparatus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61:704–718
Bernabò I, Sperone E, Tripepi S, Brunelli E (2011b) Survival, development, and gonadal differentiation in Rana dalmatina chronically exposed to chlorpyrifos. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol 315:314–327
Berzins DW, Bundy KJ (2002) Bioaccumulation of lead in Xenopus laevis tadpoles from water and sediment. Environ Int 28:69–77
Bonacci A, Brunelli E, Sperone E, Tripepi S (2008) The oral apparatus of tadpoles of Rana dalmatina, Bombina variegata, Bufo bufo, and Bufo viridis (Anura). Zool Anz 247:47–54
Bulog B, Mihajl K, Jeran Z, Toman MJ (2002) Trace element concentrations in the tissues of Proteus anguinus (Amphibia, Caudata) and the surrounding environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 136:147–163
Burger J, Snodgrass J (2001) Metal levels in southern leopard frogs from the Savannah River site: location and body compartment effects. Environ Res 86:157–166
Byrne AR, Kosta L, Stegnar P (1975) The occurrence of mercury in amphibia. Environ Lett 8:147–155
Charter RA, Tabatabai MA, Schafer JW (1995) Arsenic, molybdenum, selenium, and tungsten contents of fertilizers and phosphate rocks. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:3051–3062
Comas M, Ribas A, Milazzo C, Sperone E, Tripepi S (2014) High levels of prevalence related to age and body condition: host-parasite interactions in a water frog Pelophylax kl. hispanicus. Acta Herpetol 9:25–31
De Vivo B, Lima A, Siegel FR (2004) Geochimica ambientale. Metalli potenzialmente tossici. Liguori Editore, Napoli
Devier MH, Augagneur S, Budzinski H, Le Menach K, Mora P, Narbonne JF, Garrigues P (2005) One year monitoring survey of organic compounds (PAHs, PCBs, TBT), heavy metals and biomarkers in blue mussels from the Arcachon Bay, France. J Environ Monitor 7:224–240
Dušek L, Gelnar M, Šebelová Š (1998) Biodiversity of parasites in a freshwater environment with respect to pollution: metazoan parasites of chub (Leuciscus cephalus L.) as a model for statistical evaluation. Int J Parasitol 28:1555–1571
Eisler R (1993) Zinc hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. Biological report 10:33–47
Franzellitti S, Locatelli C, Gerosa G, Vallini C, Fabbri E (2004) Heavy metals in tissues of loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from the northwestern Adriatic Sea. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 138:187–194
Hall RJ, Mulhern BM (1984) Are anuran amphibians heavy metal accumulators? In: Fitch HS, Seigel RA, et al (eds) Vertebrate ecology and systematics – A Tribute. University of Kansas, Lawrence, pp 123–133
Kennedy CR (1997) Freshwater fish parasites and environmental quality: an overview and caution. Parassitologia 39:249–254
Koprivnikar J, Marcogliese DJ, Rohr JR, Orlofske SA, Raffel TR, Johnson PT (2012) Macroparasite infections of amphibians: what can they tell us? Eco Health 9:342–360
Lafferty KD, Kuris AM (1999) How environmental stress affects the impacts of parasites. Limnol Oceanogr 44:925–931
Le Pera E, Arribas J, Critelli S, Tortosa A (2001) The effects of source rocks and chemical weathering on the petrogenesis of siliciclastic sand from the river Neto (Calabria, Italy): implications for provenance studies. Sedimentology 48(2):357–378
Loumbourdis NS, Wray D (1998) Heavy-metal concentration in the frog Rana ridibunda from a small river of Macedonia, northern Greece. Environ Int 24:427–431
Loumbourdis NS, Kostaropoulos I, Theodoropoulou B, Kalmanti D (2007) Heavy metal accumulation and metallothionein concentration in the frog Rana ridibunda after exposure to chromium or a mixture of chromium and cadmium. Environ Poll 145:787–792
Marcogliese DJ (2005) Parasites of the superorganism: are they indicators of ecosystem health? Int J Parasitol 35:705–716
Micó C, Recatalá L, Peris M, Sánchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of a European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65:863–872
Mori E, Bruni G, Domeneghetti D, Menchetti M (2013) Pelophylax synklepton hispanicus (Bonaparte, 1839) on the branches of a tree: description of an unusual behaviour. Herpetol Notes 6:515–517
Mwita CJ (2011) Variability in parasites’ community structure and composition in cat fish with respect to level of pollution in Mwanza gulf, Lake Victoria, Tanzania. Tanzania J Sci 37:51–57
Nachev M, Sures B (2009) The endohelminth fauna of barbel (Barbus barbus) correlates with water quality of the Danube River in Bulgaria. Parasitology 136:545–552
Ohlendorf HM, Hothem RL, Aldrich TW (1988) Bioaccumulation of selenium by snakes and frogs in the San Joaquin Valley, California. Copeia 3:704–710
Palm HW (2011) Fish parasites as biological indicators in a changing world: can we monitor environmental impact and climate change? In: Melhorn H (ed) Progress in parasitology, research monographs 2. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Papadimitriou E, Loumbourdis NS (2002) Exposure of the frog Rana ridibunda to copper: impact on two biomarkers, lipid peroxidation, and glutathione. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:885–891
Papadimitriou EA, Loumbourdis NS (2003) Copper kinetics and hepatic metallothionein levels in the frog Rana ridibunda, after exposure to CuCl2. Biometals 16:271–277
Priyadarshani S, Madhushani WAN, Jayawardena UA, Wickramasinghe DD, Udagama PV (2015) Heavy metal mediated immunomodulation of the Indian green frog, Euphlyctis hexadactylus (Anura: Ranidae) in urban wetlands. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 116:40–49
Riggs MR, Lemly AD, Esch GW (1987) The growth, biomass, and fecundity of Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in a North Carolina cooling reservoir. J Parasitol 73:893–900
Sagerup K, Savinov V, Savinova T, Kuklin V, Muir DC, Gabrielsen GW (2009) Persistent organic pollutants, heavy metals and parasites in the glaucous gull (Larus hyperboreus) on Spitsbergen. Environ Poll 157:2282–2290
Schludermann C, Konecny R, Laimgruber S, Lewis JW, Schiemer F, Chovanec A, Sures B (2003) Fish macroparasites as indicators of heavy metal pollution in river sites in Austria. Parasitology 126:61–69
Seiler HG, Sigel H, Sigel A (1988) Handbook on Toxicity of inorganic compounds. Marcel Dekker, New York
Shaapera U, Nnamonu LA, Eneji IS (2013) Assessment of heavy metals in Rana esculenta organs from river Guma, Benue state Nigeria. Am J Anal Chem 4:496
Siddall R, Des Clers S (1994) Effect of sewage sludge on the miracidium and cercaria of Zoogonoides viviparus (Trematoda: Digenea). Helminthologia 31:143–153
Skrjabin KI (1964) Keys to the trematodes of animals and man. English translation edited by H. P. Arai. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Soliman MFM (2012) Heavy metal pollution across sites affecting the intestinal helminth communities of the Egyptian lizard, Chalcides ocellatus (Forskal, 1775). Environ Monit Assess 184:7677–7685
Sparling DW, Lowe TP (1996) Metal concentrations of tadpoles in experimental ponds. Environ Poll 91:149–159
Sperone E, Bonacci A, Brunelli E, Tripepi S, Jamieson BGM (2009) Male reproductive system in the Italian newt Lissotriton italicus (Peracca 1898) (Amphibia, Urodela): ultrastructural and morphological study with description of spermiogenesis, spermatozoon and spermatophore. Zoomorphology 128:183–195
Stolyar OB, Mykhayliv RL, Mishchuk YV (2004) Influence of the environmental conditions on binding of heavy metals and oxidative decomposition of biomolecules in tissues of Anodonta cygnea (Bivalvia). Hydrobiol J 40:70–79
Stolyar OB, Loumbourdis NS, Falfushinska HI, Romanchuk LD (2008) Comparison of metal bioavailability in frogs from urban and rural sites of western Ukraine. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:107–113
Sures B (2001) The use of fish parasites as bioindicators of heavy metals in aquatic ecosystems: a review. Aquat Ecol 35:245–255
Sures B (2008) Host–parasite interactions in polluted environments. J Fish Biol 73:2133–2142
Taiwo IE, Henry AN, Imbufe AP, Adetoro OO (2014) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and biomarkers of oxidative stress in the wild African tiger frog, Hoplobatrachus occipitalis. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 8:6–15
Talarico E, Sperone E, Tripepi S (2004) Amphibians of the Pollino National Park: distribution and notes on conservation. Ital J Zool 71:203–208
Tonazzi A, Giangregorio N, Console L, Scalise M, La Russa D, Notaristefano C, Indiveri C (2015) Mitochondrial carnitine/Acylcarnitine transporter, a novel target of mercury Toxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 28:1015–1022
Valtonen ET, Holmes JC, Koskivaara M (1997) Eutrophication, pollution and fragmentation: effects on parasite communities in roach (Rutilus rutilus) and perch (Perca fluviatilis) in four lakes in central Finland. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:572–585
Vogiatzis AK, Loumbourdis NS (1998) Cadmium accumulation in liver and kidneys and hepatic metallothionein and glutathione levels in Rana ridibunda, after exposure to CdCl2. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 34:64–68
Wagemann R, Snow NB, Rosenberg DM, Lutz A (1978) Arsenic in sediments, water and aquatic biota from lakes in the vicinity of Yellowknife, northwest territories, Canada. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 7:169–191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Donato, C., Barca, D., Milazzo, C. et al. Is trace element concentration correlated to parasite abundance? A case study in a population of the green frog Pelophylax synkl. hispanicus from the Neto River (Calabria, southern Italy). Parasitol Res 116, 1745–1753 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5453-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5453-7