Abstract
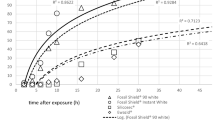
Poultry red mite infestation still is an unsolved problem in poultry farms. Legal regulations, residue risks, and resistances limit chemical control of mites. Alternatives to chemical acaricides for control of poultry red mite are silica-based products, which have as a main constituent silicon dioxide. The acaricidal effect is attributed to sorptive properties of the particles, which result in the mite’s death by desiccation. In the present study, the acaricidal efficacy of 12 products containing natural or synthetic silica, 9 in powder form, and 3 for liquid application was tested under laboratory conditions. Mite mortality was measured at several intervals and the mean lethal time (LT50) determined by Probit analysis after Abbott’s correction. The LT50 values of the products significantly differed (Tukey’s HSD p < 0.05). LT50 values of powdery formulations ranged from 5.1 to 18.7 h and overlapped with those of the fluid ones which ranged from 5.5 to 12.7 h. In order to explain the differences in efficacy of the tested silica products, further characterizations were carried out. X-ray fluorescence, specific surface, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and water absorption capacity (WAC) were measured. Furthermore, electron microscopy was conducted and different products compared. Silicon dioxide content (ranging from 65 to 89 % for powders and 57 to 80 % for fluids) had no significant impact on efficacy, while specific surface and CEC (2.4–23.2 mEq 100−1 g−1 for powders and 18–30.8 mEq 100−1 g−1) were positively and WAC (1.3–4.4 wt% for powders and 3.3–4.8 wt% for fluids) negatively related to the acaricidal efficacy. Influence of these parameters on acaricidal efficacy was significant according to the results of a stepwise regression analysis (p < 0.01).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entom 18:265–267
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Sobhy HM, Al-Quraishy S, Semmler M (2008) Field study on the efficacy of an extract of neem seed (Mite-Stop (R)) against the red mite Dermanyssus gallinae naturally infecting poultry in Egypt. Parasitol Res 103:481–485
Akbar W, Lord JC, Nechols JR, Howard RW (2004) Diatomaceous earth increases the efficacy of Beauveria bassiana against Tribolium castaneum larvae and increases conidia attachment. J Econ Entom 2:273–280
Arnaud L, Tran Thi Lan H, Brostaux Y, Haubruge E (2005) Efficacy of diatomaceous earth formulations admixed with grain against populations of Tribolium castaneum. J Stored Prod Res 2:121–130
Badii BK, Adarklwah C, Obeng-Ofori D, Ulrichs C (2013) Efficacy of diatomaceous earth formulations against Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in Kersting’s groundnut (Macrotyloma geocarpum Harms): influence of dosage rate and relative humidity. J Pest Sci. doi:10.1007/s10340-013-0548-0
Bennett DC, Yee A, Rhee Y-J, Cheng KM (2011) Effect of diatomaceous earth on parasite load, egg production, and egg quality of free-range organic laying hens. Poult Sci 7:1416–1426
Biocidal Products Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (1998) Concerning the placing of biocidal products on the market
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Chauve C (1998) The poultry red mite Dermanyssus gallinae (De Geer, 1778): current situation and future prospects for control. Vet Parasitol 3:239–245
Ebeling W (1971) Sorptive dusts for pest control. Annual Rev Entomol 1:123–158
EFSA (2009) Calcium silicate and silicon dioxide/silicic acid gel added for nutritional purposes to food supplements, scientific opinion of the panel on food additives and nutrient sources added to food. EFSA Journal 1132:1–24
EVM (2003) Expert Group on Vitamins and Minerals. Safe upper levels for vitamins and minerals, silicon & calcium, UK Food Standards Agency. ISBN 1-904026-11-7
Faulde MK, Tisch M, Scharninghausen JJ (2006) Efficacy of modified diatomaceous earth on different cockroach species (Orthoptera, Blattellidae) and silverfish (Thysanura, Lepismatidae). J Pest Sci 3:155–161
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York, 333
Finney DJ (1978) Statistical method in biological assay. Charles Griffin, London, 508
Ghiazza M, Polimeni M, Fenoglio I, Gazzano E, Ghigo D, Fubini B (2010) Does vitreous silica contradict the toxicity of the crystalline silica paradigm? Chem Res Toxicol 23:620–629
Golob P (1997) Current status and future perspectives for inert dusts for control of stored product insects. J Stored Prods Res 1:69–79
Hadley NF (1994) Water relations of terrestrial arthropods. Academic Press, New York
Hamscher G, Priess B, Nau H (2007) Determination of phoxim residues in eggs by using high-performance liquid chromatography diode array detection after treatment of stocked housing facilities for the poultry red mite (Dermanyssus gallinae). Anal Chim Acta 1–2:330–335
Islam MS, Hasan MM, Lei C, Mucha-Pelzer T, Mewis I, Ulrichs C (2009) Direct and admixture toxicity of diatomaceous earth and monoterpenoids against the storage pests Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) and Sitophilus oryzae (L.). J Pest Sci 2:105–112
Kilpinen O, Steenberg T (2009) Inert dusts and their effects on the poultry red mite (Dermanyssus gallinae). Exp Appl Acarol 1–2:51–62
Kilpinen O, Roepstorff A, Permin A, Nørgaard-Nielsen G, Lawson LG, Simonsen HB (2005) Influence of Dermanyssus gallinae and Ascaridia galli infections on behaviour and health of laying hens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Br Poult Sci 1:26–34
Korunic Z (1998) Review diatomaceous earths, a group of natural insecticides. J Stored Prod Res 2–3:87–97
Lamina J, Kruner N (1965) Die insektizide Wirkung hochdisperser Kieselsäuren auf die Ektoparasiten des Geflügels. Dtsch tierärztl Wochenschr 73:124–129
Le Patourel GNJ, Singh J (1984) Toxicity of amorphous silicas and silica-pyrethroid mixtures to Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Stored Prod Res 4:183–190
Lehane MJ (2005) The biology of blood-sucking in insects. University Press, Cambridge
Liebisch A, Liebisch G (1999) Erfolgreiche Ektoparasitenbekämpfung. In: Jahrbuch für die Geflügelwirtschaft 60–63
Liebisch A, Liebisch G (2003) Biologie, Schäden und Bekämpfung beim Befall durch die Rote Vogelmilbe (Dermanyssus gallinae). Lohmann Information 4:1–7
Limbach KL, Li Y, Grass RN, Brunner TJ, Hintermann MA, Muller M, Gunther D, Stark WJ (2005) Oxide nanoparticle uptake in human lung fibroblasts: effects of particle size, agglomeration, and diffusion at low concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 39:9370–9376
Marangi M, Cafiero MA, Capelli G, Camarda A, Sparagano OAE, Giangaspero A (2009) Evaluation of the poultry red mite, Dermanyssus gallinae (Acari: Dermanyssidae) susceptibility to some acaricides in field populations from Italy. Exp Appl Acarol 1–2:11–18
Marangi M, Morelli V, Pati S, Camarda A, Cafiero MA, Giangaspero A (2012) Acaricide residues in laying hens naturally infested by Red Mite Dermanyssus gallinae. PLoS ONE 2:e31795
Maurer V, Perler E (2006) Silicas for control of the poultry red mite Dermanyssus gallinae. Organic congress 2006. Odense 504–505
Maurer V, Bieri M, Folsch DW (1988) Host-finding of Dermanyssus gallinae in poultry-houses. Archiv für Geflügelkunde 59:209–215
Maurer V, Perler E, Heckendorn F (2009) In vitro efficacies of oils, silicas and plant preparations against the poultry red mite Dermanyssus gallinae. Exp Appl Acarol 1–2:31–41
Meier LP, Kahr G (1999) Determination of the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of clay minerals using the complexes of copper(II) ion with triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. Clay Clay Miner 47:386–388
Mewis I, Ulrichs C (1999) Wirkungsweise amorpher Diatomeenerden auf vorratsschädliche Insekten. Untersuchung der abrasiven sowie sorptiven Effekte. Anz Schädlingskde. Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz 5:113–121
Mewis I, Ulrichs C (2001) Action of amorphous diatomaceous earth against different stages of the stored product pests Tribolium confusum, Tenebrio molitor, Sitophilus granarius and Plodia interpunctella. J Stored Prod Res 2:153–164
Mucha-Pelzer T, Debnath N, Goswami A, Mewis I (2008) Comparison of different silicas of natural origin as possible insecticides. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 3:621–628
Mucha-Pelzer T, Mewis I, Ulrichs C (2010) Efficacy of different natural and synthetic silicas against two stored grain pests: Sitophilus granarius (L.) and Sitophilus oryzae (L.). Acta Hort 858:311–318
Rigaux M, Haubruge E, Fields PG (2001) Mechanisms for tolerance to diatomaceous earth between strains of Tribolium castaneum. Entom Exp Applicata 1:33–39
Sparagano O, Pavlićević A, Murano T, Camarda A, Sahibi H, Kilpinen O, Mul M, Emous R, Bouquin S, Hoel K, Cafiero MA (2009) Prevalence and key figures for the poultry red mite Dermanyssus gallinae infections in poultry farm systems. Exp Appl Acarol 1–2:3–10
Trofymluk O, Levchenko AA, Tolbert SH, Navrotsky A (2005) Energetics of mesoporous silica: investigation into pore size and symmetry. Chem Mat 17:3772–3783
Ulrichs C, Mewis I, Reichmuth C (2004) Diatomeenerden—Wirksamkeit bei hohen Luftfeuchten. Der Praktische Schädlingsbekämpfer 56:11
Ulrichs C, Entenmann S, Goswami A, Mewis I (2006) Abrasive und hydrophil/lipophile Effekte unterschiedlicher inerter Stäube im Einsatz gegen Schadinsekten am Beispiel des Kornkäfers Sitophilus granarius L. Ges Pflanzen 3:173–181
Ulrichs C, Krause F, Goswami A, Kaufhold S, Mewis I (2008) Insektizide Wirkung eines natürlichen Silikates (AL06) im Vergleich zu anderen silikathaltigen Stäuben gegenüber dem Kornkäfer: Sitophilus granarius (L.). Mitt Dtsch Ges Allg Angew Ent 16:269–272
Zhang H, Dunphy DR, Jiang X, Meng H, Sun B, Tarn D, Xue M, Wang X, Lin S, Ji Z, Li R, Garcia FL, Yang J, Kirk ML, Xia T, Zink JI, Nel A, Jeffrey C (2012) Processing pathway dependence of amorphous silica nanoparticle toxicity—colloidal versus pyrolytic. J Am Chem Soc 26:15790–15804
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Hiepe from the Department of Molecular Parasitology (HU Berlin) and Dr. Liebisch from Zecklab (Burgwedel) for supporting this research. The authors wish to express appreciation to the Federal Programme for Organic and Sustainable Farming (BÖLN), which supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, J., Berk, J., Suhl, J. et al. Characterization, mode of action, and efficacy of twelve silica-based acaricides against poultry red mite (Dermanyssus gallinae) in vitro. Parasitol Res 113, 3167–3175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3978-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3978-6