Abstract
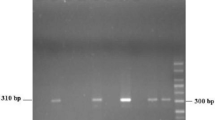
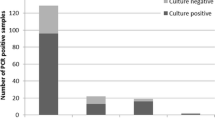
We developed a real-time LC PCR assay to detect a 152 bp sequence in an uncharacterized region of the Blastocystis genome. The described assay detected 11 of 11 ATCC strains of Blastocystis from subtypes 1, 3, and 4. Three of three stool samples from Oregon and California military personnel that were negative for Blastocystis by an ova and parasite test as well as a conventional PCR assay were positive for Blastocystis using our real-time LC PCR assay. Diagnosis of Blastocystis infections using this sensitive method, including DNA extraction and real-time PCR, only requires 3 h. The lower limit of detection for Blastocystis in stool using the real-time LC PCR assay was calculated to be 760 cells of Blastocystis per 100 mg of stool, an estimated 760 parasites per reaction. The assay did not cross-react with Ruminococcus hansenii, Anarococcus hydrogenalis, Bifidobacterium adolescentis, Fusobacterium prausnitzii, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, or Lactobacillus acidophilus. Because of the ease of use, sensitivity, specificity, and increase in Blastocystis infections in the USA we believe this assay has the potential to be useful as a clinical diagnosis tool of Blastocystis infection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin OM (2002) Seasonal prevalence of intestinal parasites in the United States during. Am J Trop Med Hyg 66:799–803
rmentia A et al (1993) Urticaria by Blastocystis hominis. Successful treatment with paromomycin {paromycin}. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 21:149–151
Biedermann T, Hartmann K, Sing A, Przybilla B (2002) Hypersensitivity to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chronic urticaria cured by treatment of Blastocystis hominis infection. Br J Dermatol 146:1113–1114
Boorom KF (2006) Commensal and pathogenic Blastocystis with case studies from Oregon’s Willamette Valley. BRF Press, Corvallis OR USA
Cassano N, Scoppio BM, Loviglio MC, Vena GA (2005) Remission of delayed pressure urticaria after eradication of Blastocystis hominis. Acta Derm Venereol 85:357–358
Center for Disease Control Fact Sheet, Blastocystis hominis, available online
Hoevers J, Holman P, Logan K, Hommel M, Ashford R, Snowden K (2000) Restriction-fragment-length polymorphism analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes of Blastocystis hominis isolates from geographically diverse human hosts. Parasitol Res 86:57–61
Kruger K, Kamilli I, Schattenkirchner M (1994) Blastocystis hominis as a rare arthritogenic pathogen. A case report. Z Rheumatol 53:83–85
Lee MG, Rawlins SC, Didier M, DeCeulaer K (1990) Infective arthritis due to Blastocystis hominis. Ann Rheum Dis 49:192–193
Menounos PG, Spanakos G, Tegos N, Vassalos CM, Papadopoulou C, Vakalis NC (2008) Direct detection of Blastocystis sp. in human faecal samples and subtype assignment using single strand conformational polymorphism and sequencing. Mol Cell Probes 22:24–29
O’Gorman MA, Orenstein SR, Proujansky R, Wadowsky RM, Putnam PE, Kocoshis SA (1993) Prevalence and characteristics of Blastocystis hominis infection in children. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 32:91–96
Parkar U, Traub RJ, Kumar S, Mungthin M, Vitali S, Leelayoova S, Morris K, Thompson RC (2006) Direct characterization of Blastocystis from faeces by PCR and evidence of zoonotic potential. Parasitology 19:1–9
Pasqui AL, Savini E, Saletti M, Guzzo C, Puccetti L, Auteri A (2004) Chronic urticaria and Blastocystis hominis infection: a case report. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 8:117–120
Qadri SM, al-Okaili GA, al-Dayel F (1989) Clinical significance of Blastocystis hominis. J Clin Microbiol 27:2407–2409
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Sheehan DJ, Raucher BG, McKitrick JC (1986) Association of Blastocystis hominis with signs and symptoms of human disease. J Clin Microbiol 24:548–550
Stensvold CR, Suresh GK, Tan KS, Thompson RC, Traub RJ, Viscogliosi E, Yoshikawa H, Clark CG (2007) Terminology for Blastocystis subtypes–a consensus. Trends Parasitol 23:93–96
Stensvold R, Brillowska-Dabrowska A, Nielsen HV, Arendrup C (2006) Detection of Blastocystis hominis in unpreserved stool specimens by using polymerase chain reaction. J Parasitol 92:1081–1087
Stenzel DJ, Boreham PF (1996) Blastocystis hominis revisited. Clin Microbiol Rev 9:563–584
Suresh K, Smith H (2004) Comparison of methods for detecting Blastocystis hominis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:509–511
Swofford DL, Waddell PJ, Huelsenbeck JP, Foster PG, Lewis PO, Rogers JS (2001) Bias in phylogenetic estimation and its relevance to the choice between parsimony and likelihood methods. Syst Biol 50:525–539
Termmathurapoj S et al (2004) The usefulness of Short-Term In-Vitro cultivation for the detection and molecular study of Blastocystis hominis in stool specimens. Parasitol Res 93:445–447
Vennila GD, Suresh Kumar G, Khairul Anuar A, Rajah S, Saminathan R, Sivanandan S, Ramakrishnan K (1999) Irregular shedding of Blastocystis hominis. Parasitol Res 85:162–164
Wang KX, Li CP, Wang J, Cui YB (2002) Epidemiological survey of Blastocystis hominis in Huainan City, Anhui Province, China. World J Gastroenterol 8:928–932
Whipps CM, Kent ML (2006) Phylogeography of the cosmopolitan marine parasite Kudoa thyrsites (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). J Eukaryot Microbiol 53:364–373
Yoshikawa H, Wu Z, Howe J, Hashimoto T, Geok-Choo N, Tan KS (2007) Ultrastructural and phylogenetic studies on Blastocystis isolates from cockroaches. J Eukaryot Microbiol 54:33–37
Acknowledgments
The work reported herein was performed under United States Air Force Surgeon General-approved Clinical Investigation No. FDG20070009N, FDG20070010N. The experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed. The views expressed in this material are those of the authors, and do not reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Government, the Department of Defense, or the Department of the Air Force.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work reported herein was performed under United States Air Force Surgeon General-approved Clinical Investigation No. FDG20070009N, FDG20070010N.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones II, M.S., Ganac, R.D., Hiser, G. et al. Detection of Blastocystis from stool samples using real-time PCR. Parasitol Res 103, 551–557 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1006-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1006-4