Abstract
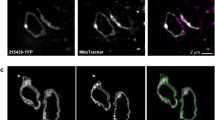
Apicomplexa including the causative agents of toxoplasmosis and malaria reportedly possess one or few tubular-shaped mitochondria that permeate, more or less branched, throughout these unicellular parasites. Electron micrographs generated herein from serial-sectioned Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites demonstrated, however, a greater diversity regarding both the shape of the cultured parasite’s single mitochondrion and its sub-structural organization. Moreover, a unique subcellular construction was detected that basically comprised a pouch-shaped subdivision of the tachyzoite mitochondrion plus a fraction of parasitic cytoplasm enclosed therein. This composite assembling, termed ovoid mitochondrial cytoplasmic (OMC) complex, characteristically displayed a highly reduced matrix lumen of its mitochondrial border construction, which furthermore often failed to possess any cristae or contained tightly pleated cristae, thus creating a pouch-shaped multi-laminar wall of four or more membranous layers, respectively. Given this architecture, cross-sectioned OMC complexes of T. gondii tachyzoites frequently mimicked in size and shape the parasites’ plastid-like organelle (apicoplast). Moreover, like the apicoplast, the OMC complex was often found adjacent to the tachyzoite’s single Golgi complex and constantly located in close proximity to the outer membrane of the parasite’s nuclear envelope. The T. gondii OMC complex differed, however, from the apicoplast in its exact fine structural organization and a stage-restricted presence that was apparently linked to mitochondrial growth and/or division. Any special function(s) possibly performed by the T. gondii OMC complex remains, nevertheless, to be elucidated.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsen MS, Templeton TJ, Enomoto S, Abrahante JE, Zhu G, Lancto CA, Deng M, Liu C, Widmer G, Tzipori S, Buck GA, Xu P, Bankier AT, Dear PH, Konfortov BA, Spriggs HF, Iyer L, Anantharaman V, Aravind L, Kapur V (2004) Complete genome sequence of the Apicomplexan, Cryptosporidium parvum. Science 304:441–445
Balczon R (1996) The centrosome in animal cells and its functional homologs in plant and yeast cells. Int Rev Cytol 169:25–82
Black MW, Boothroyd JC (2000) Lytic cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:607–623
Bowsher CG, Tobin AK (2001) Compartmentation of metabolism within mitochondria and plastids. J Exp Bot 52:513–527
Chaubey S, Kumar A, Singh D, Habib S (2005) The apicoplast of Plasmodium falciparum is translationally active. Mol Microbiol 56:81–89
Cheresh P, Harrison T, Fujioka H, Haldar K (2002) Targeting the malarial plastid via the parasitophorous vacuole. J Biol Chem 277:16265–16277
DeRocher A, Hagen CB, Froehlich JE, Feagin JE, Parsons M (2000) Analysis of targeting sequences demonstrates that trafficking to the Toxoplasma gondii plastid branches off the secretory system. J Cell Sci 113:3969–3977
Divo AA, Geary TG, Jensen JB, Ginsburg H (1985) The mitochondrion of Plasmodium falciparum visualized by rhodamine 123 fluorescence. J Protozool 32:442–446
Dubey JP, Lindsay DS, Speer CA (1998) Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:267–299
Ferguson DJP, Henriquez FL, Kirisits MJ, Muench SP, Prigge ST, Rice DW, Roberts CW, McLeod RL (2005) Maternal inheritance and stage-specific variation of the apicoplast in Toxoplasma gondii during development in the intermediate and definitive host. Eukaryot Cell 4:814–826
Fitzpatrick T, Ricken S, Lanzer M, Amrhein N, Macheroux P, Kappes B (2001) Subcellular localization and characterization of chorismate synthase in the apicomplexan Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Microbiol 40:65–75
Foth BJ, Stimmler LM, Handman E, Crabb BS, Hodder AN, McFadden GI (2005) The malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum has only one pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which is located in the apicoplast. Mol Microbiol 55:39–53
Fry M, Beesley JE (1991) Mitochondria of mammalian Plasmodium spp. Parasitology 102:17–26
Gardner MJ, Hall N, Fung E, White O, Berriman M, Hyman RW, Carlton RW, Carlton JM, Pain A, Nelson KE, Bowman S, Paulson IT, James K, Eisen JA, Rutherford K, Salzberg SL, Craig A, Kyes S, Chan MS, Nene V, Shallom SJ, Suh B, Peterson J, Angluoli S, Pertea M, Allen J, Selengut J, Haft D, Mather MW, Vaidya AB, Martin DMA, Fairlamb AH, Fraunholz MJ, Roos DS, Ralph SA, McFadden GI, Cummings LM, Subramanian GM, Mungall C, Venter JC, Carucci DJ, Hoffman SL, Newbold C, Davis RW, Fraser CM, Barrell B (2002) Genome sequence of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 419:498–511
Gardner MJ, Bishop R, Shah T, de Villiers EP, Carlton JM, Hall N, Ren Q, Paulsen IT, Pain A, Berriman M, Wilson R JM, Sato S, Ralph S, Mann DJ, Xiong Z, Shallom SJ, Weidman J, Jiang L, Lynn J, Weaver B, Shoaibi A, Domingo AR, Wasawo D, Crabtree J, Wortman JR, Haas B, Angiuoli SV, Creasy TH, Lu C, Suh B, Silva JC, Utterback TR, Feldblyum TV, Pertea M, Allen J, Nierman WC, Taracha ELN, Salzberg SL, White OR, Fitzhugh HA, Morzaria S, Venter JC, Fraser CM, Nene V (2005) Genome sequence of Theileria parva, a bovine pathogen that transforms lymphocytes. Science 309:134–137
Goldenthal MJ, Marín-García J (2004) Mitochondrial signaling pathways: a receiver/integrator organelle. Mol Cell Biochem 262:1–16
Gray MW, Burger G, Lang BF (1999) Mitochondrial evolution. Science 283:1476–1481
Hager KM, Striepen B, Tilney LG, Roos DS (1999) The nuclear envelope serves as an intermediary between the ER and Golgi complex in the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii. J Cell Sci 112:2631–2638
He CY, Shaw MK, Pletcher CH, Striepen B, Tilney LG, Roos DS (2001a) A plastid segregation defect in the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. EMBO J 20:330–339
He CY, Striepen B, Pletcher CH, Murray JM, Roos DS (2001b) Targeting and processing of nuclear-encoded apicoplast proteins in plastid segregation mutants of Toxoplasma gondii. J Biol Chem 276:28436–28442
Hopkins J, Fowler R, Krishna S, Wilson I, Mitchell G, Bannister L (1999) The plastid in Plasmodium falciparum asexual blood stages: a three-dimensional ultrastructural analysis. Protist 150:283–295
Howells RE (1970) Mitochondrial changes during the life cycle of Plasmodium berghei. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 64:181–187
Izumo A, Tanabe K, Kato M (1988) The plasma membrane and mitochondrial membrane potentials of Plasmodium yoelii. Comp Biochem Physiol B 91:735–739
Joiner KA, Roos DS (2002) Secretory traffic in the eukaryotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii: less is more. J Cell Biol 157:557–563
Keithly JS, Langreth SG, Buttle KF, Mannella CA (2005) Electron tomographic and ultrastructural analysis of the Cryptosporidium parvum relict mitochondrion, its associated membranes, and organelles. J Eukaryot Microbiol 52:132–140
Köhler S (2005) Multi-membrane-bound structures of Apicomplexa: I. The architecture of the Toxoplasma gondii apicoplast. Parasit Res 96:258–272
Köhler S, Delwiche C, Denny PW, Tilney LG, Webster P, Wilson RJM, Palmer JD, Roos DS (1997) A plastid of probable green algal origin in Apicomplexan parasites. Science 275:1485–1489
Krungkrai J (2004) The multiple roles of the mitochondrion of the malarial parasite. Parasitology 129:511–524
Krungkrai J, Prapunwattana P, Krungkrai SR (2000) Ultrastructure and function of mitochondria in gametocytic stage of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasite 7:19–26
Matsumoto Y, Matsuda S, Yoshida Y (1986) Ultrastructure of erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium ovale in humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg 35:689–696
Matsuzaki M, Kikuchi T, Kita K, Kojima S, Kuroiwa T (2001) Large amounts of apicoplast nucleoid DNA and its segregation in Toxoplasma gondii. Protoplasma 218:180–191
McFadden GI, Reith ME, Munholland J, Lang-Unnasch N (1996) Plastid in human parasite. Nature 381:482
McFadden GI, Waller RF, Reith ME, Lang-Unnasch N (1997) Plastids in apicomplexan parasites. In: Bhattachary D (ed) Origins of algae and their plastids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 261–287
McMillan PJ, Stimmler LM, Foth BJ, McFadden GI, Müller S (2005) The human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum possesses two distinct dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases. Mol Microbiol 55:27–38
Melo EJL, Attais M, De Souza W (2000) The single mitochondrion of tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. J Struct Biol 130:27–33
Morrissette NS, Sibley LD (2002a) Disruption of microtubules uncouples budding and nuclear division in Toxoplasma gondii. J Cell Sci 115:1017–1025
Morrissette NS, Sibley LD (2002b) Cytoskeleton of Apicomplexan parasites. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:21–38
Newmeyer DD, Ferguson-Miller S (2003) Mitochondria: releasing power for life and unleashing the machineries of death. Cell 112:481–490
Okamoto K, Shaw JM (2005) Mitochondrial morphology and dynamics in yeast and multicellular eukaryotes. Annu Rev Genet 39:503–536
Pfeffer S (2003) Membrane domains in the secretory and endocytotic pathways. Cell 112:507–517
Poot M, Zhang YZ, Kramer JA, Wells KS, Jones LJ, Hanzel DK, Lugade AG, Singer VL, Haugland RP (1996) Analysis of mitochondrial morphology and function with novel fixable fluorescent stains. J Histochem Cytochem 44:1363–1372
Riordan CE, Ault JG, Langreth SG, Keithly JS (2003) Cryptosporidium parvum Cpn 60 targets a relict organelle. Curr Genet 44:138–147
Saraste M (1999) Oxidative phosphorylation at the fin de siècle. Science 283:1488–1498
Sato S, Rangachari K, Wilson RJ (2003) Targeting GFP to the malarial mitochondrion. Mol Biochem Parasitol 130:155–158
Schmit AC (2002) Acentrosomal microtubule nucleation in higher plants. Int Rev Cytol 220:257–289
Scott SV, Cassidy-Stone A, Meeusen SL, Nunnari J (2003) Staying in aerobic shape: how the structural integrity of mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA is maintained. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:482–488
Shaw MK, Compton HL, Roos DS, Tilney LG (2000) Microtubules, but not actin filaments, drive daughter cell budding and cell division in Toxoplasma gondii. J Cell Sci 113:1241–1254
Sheffield HG, Melton ML (1968) The fine structure and reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasit 54:209–226
Siddall ME (1992) Hohlzylinder. Parasitol Today 8:90–91
Slomianny C, Prensier G (1986) Application of the serial sectioning and tridimensional reconstriuction techniques to the morphological study of the Plasmodium falciparum mitochondrion. J Parasit 72:595–598
Striepen B, Crawford MJ, Shaw MK, Tilney LG, Seeber F, Roos DS (2000) The plastid of Toxoplasma gondii is divided by association with the centrosomes. J Cell Biol 151:1423–1434
Tonkin CJ, van Dooren GG, Spurck TP, Struck NS, Good RT, Handman E, Cowman AF, McFadden GI (2004) Localization of organellar proteins in Plasmodium falciparum using a novel set of transfection vectors and a new immunofluorescence fixation method. Mol Biochem Parasitol 137:13–21
Vaishnava S, Morrison DP, Rajshekhar YG, Murray JM, Entzeroth R, Howe DK, Striepen B (2005) Plastid segregation and cell division in the apicomplexan parasite Sarcocystis neurona. J Cell Sci 118:3397–3407
van der Zypen E, Piekarski G (1967) Ultrastrukturelle Unterschiede zwischen der sogenannten Proliferationsform (RH-Stamm, BK-Stamm) und dem sogenannten Cysten-Stadium (DX-Stamm) von Toxoplasma gondii. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg 203:495–517
van Dooren GG, Marti M, Tonkin C, Stimmler LM, Cowman AF, McFadden GI (2005) Development of the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion and apicoplast during the asexual life cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Microbiol 57:405–419
Varmark H (2004) Functional role of centrosomes in spindle assembly and organization. J Cell Biochem 91:904–914
Vivier E, Petitprez A (1969) Le complexe membranaire superficiel et son evolution lors de l’elaboration des individus-fils chez Toxoplasma gondii. J CellBiol 43:329–342
Waller RF, Reed MB, Cowman AF, McFadden GI (2000) Protein trafficking to the plastid of Plasmodium falciparum is via the secretory pathway. EMBO J 19:1794–1802
Warren G, Wickner W (1996) Organelle inheritance. Cell 84:395–400
Wrenger C, Müller S (2004) The human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum has distinct organelle-specific lipoylation pathways. Mol Microbiol 53:103–113
Xu P, Widmer G, Wang Y, Ozaki LS, Alves JM, Serrano MG, Pulu D, Manque P, Akiyoshi D, Mackey AJ, Pearson WR, Dear PH, Bankier AT, Peterson DL, Abrahamsen MS, Kapur V, Tzipori S, Buck GA (2004) The genome of Cryptosporidium hominis. Nature 431:1107–1112
Acknowledgements
The author thanks John Boothroyd and Heinz Mehlhorn for critical reading of the manuscript and helpful discussion. We also thank Inge Latka for the technical assistance. This paper was supported by the Heinrich Heine University of Düsseldorf and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ko1871/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köhler, S. Multi-membrane-bound structures of Apicomplexa: II. the ovoid mitochondrial cytoplasmic (OMC) complex of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. Parasitol Res 98, 355–369 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-005-0066-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-005-0066-y