Abstract.
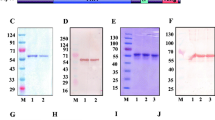
A cDNA encoding transportin, a protein involved in the nuclear import of M9 nuclear localization signal-bearing proteins, has been cloned from the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The complete cDNA consists of 3,667 bp encoding 1,136 amino acid residues. Amino acid sequence analysis revealed that Ran-GTP and M9 binding domains are highly conserved in P. falciparum, suggesting that the transportin-mediated nuclear transport pathway exists in this protozoan parasite. Southern blot analysis revealed that the transportin gene exists as a single copy in the malarial genome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Yamasaki, H., Feng, Z. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of Plasmodium falciparum transportin. Parasitol Res 88, 391–394 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-001-0578-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-001-0578-z