Abstract
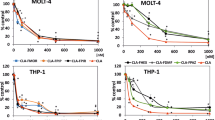
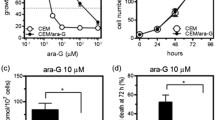
The arabinofuranosylcytosine (AraC) derivative N 4-octadecyl-1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (NOAC) and its (5′ → 5′)-heterodinucleoside phosphate analog NOAC-AraC were compared with AraC for cytotoxicity, cell-cycle dependence, phosphorylation by deoxycytidine (dC) kinase and apoptosis induction in native, AraC- or NOAC-resistant HL-60 cells. NOAC was cytotoxic in all cells with three to seven-fold lower IC50 concentrations than those of NOAC-AraC or AraC. In contrast to NOAC-AraC, the lipophilic monomer NOAC overcame AraC resistance, inducing apoptosis in more than 80% of native and AraC-resistant HL-60 cells. This suggests that NOAC-AraC may be cleaved intracellularly only at very slow rates to AraC and NOAC or to the 5′-monophosphates, whereas NOAC exerts different mechanisms of action from AraC. In vitro the dimer was cleaved by phosphodiesterase or human serum to NOAC, AraC and AraC monophosphate. In contrast to AraC, N 4-alkylated AraC derivatives with alkyl chains ranging from 6–18 C atoms were not substrates for dC kinase. Furthermore, treatment of the multidrug-resistant cell lines KB-ChR-8-5 and KB-V1 with the N 4-hexadecyl-AraC derivative NHAC did not induce P-170 glycoprotein expression, suggesting that the N 4-alkyl-AraC derivatives are able to circumvent MDR1 multidrug resistance. The in vivo activity of liposomal NOAC in a human acute lymphatic leukemia xenograft model confirmed the antitumor activity of this representative of the N 4-alkyl-arabinofuranosylcytosines.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 October 1999 / Accepted: 13 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horber, D., Cattaneo-Pangrazzi, R., von Ballmoos, P. et al. Cytotoxicity, cell-cycle perturbations and apoptosis in human tumor cells by lipophilic N 4-alkyl-1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine derivatives and the new heteronucleoside phosphate dimer arabinocytidylyl-(5′→ 5′)-N 4-octadecyl-1-β-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126, 311–319 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004320050349
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004320050349