Abstract
Aim
This study is designed to ascertain the relative molecular targets of effective Chinese herbs in treating stage IV lung adenocarcinoma based on clinical data and network pharmacology. In addition, we showed that Chinese Herbal Medicine (CHM) treatment was associated with survival benefit for patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma and identified 18 herbs beneficial to survival through correlation analysis.
Background
Increasing evidence has shown that CHM has efficient therapeutic effects for advanced lung adenocarcinoma, while active ingredients and potential targets remain unclear.
Methods
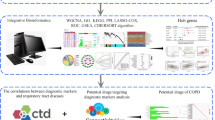
Kaplan–Meier method and Cox regression analysis were used to evaluate the survival benefit of CHM treatment, and correlation analysis was applied to identify the most effective components in the formulas. A network pharmacological approach was used to decipher the potential therapeutic mechanisms of CHM.
Results
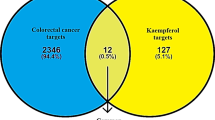
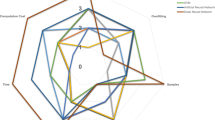
CHM treatment was an independent protective factor. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.487 (95% CI 0.293–0.807; P = 0.005). Patients in the CHM group had a longer median survival time (31 months) compared with the non-CHM group (19 months; P < 0.001). 18 out of the total 241 herbs were significantly correlated with favorable survival outcomes (P < 0.05), likely representing the most effective components in these formulas. Bioinformatics analysis suggested that the 18 herbs realize anti-lung-adenocarcinoma activity mainly through (1) inhibiting the activity of some growth factors’ receptors, such as HGFR, EGFR, and IGFR. (2) Suppressing angiogenesis not only through VEGFR and PDGFR, but also through the function of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin. (3) Inhibiting the Ras signaling pathway directly through Ras as well as through ALK and FNTA/FNTB.
Conclusions
We performed a network pharmacological method to decipher the underlying mechanisms, which provides a good foundation for herbal research based on clinical data.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asada M, Ebihara S, Yamanda S et al (2009) Depletion of serotonin and selective inhibition of 2B receptor suppressed tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting endothelial nitric oxide synthase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation. Neoplasia 11:408IN10-417
Bhattacharya R, Sinha S, Yang SP et al (2008) The neurotransmitter dopamine modulates vascular permeability in the endothelium. J Mol Signal 3:14
Cattaneo MG, Fesce R, Vicentini LM (1995) Mitogenic effect of serotonin in human small cell lung carcinoma cells via both 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 291:209–211
Chen S, Flower A, Ritchie A, Liu J, Molassiotis A, Yu H, Lewith G et al (2010) Oral Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) as an adjuvant treatment during chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. Lung cancer 68:137–145
Chen YF, Yang JS, Chang WS et al (2013) Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract modulates G0/G1 arrest and Fas/CD95-mediated death receptor apoptotic cell death in human lung cancer A549 cells. J Bio Sci 20:18
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S et al (2014) Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010. Chin J Cancer Res 26:48–58
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ et al (2017) The comparative toxicogenomics database: update 2017. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D972–D978
Ding X, Chi JD, Yang X et al (2017) Cucurbitacin B synergistically enhances the apoptosis-inducing effect of arsenic trioxide by inhibiting STAT3 phosphorylation in lymphoma Ramos cells. Leukemia Lymphoma 58:1–13
Dizeyi N, Bjartell A, Hedlund P et al (2005) Expression of serotonin receptors 2B and 4 in human prostate cancer tissue and effects of their antagonists on prostate cancer cell lines. Eur Urol 47:895–900
Gao L, Hao J, Niu YY et al (2016) Network pharmacology dissection of multiscale mechanisms of herbal medicines in stage IV gastric adenocarcinoma treatment. Medicine (Baltimore) 95: e4389
Gao L, Wang X, Niu Y et al (2016) Molecular targets of Chinese herbs: a clinical study of hepatoma based on network pharmacology. Sci Rep 6:24944
Gibbs JB, Oliff A, Kohl NE (1994) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: Ras research yields a potential cancer therapeutic. Cell 77:175–178
Gong J, Cai C, Liu X et al (2013) ChemMapper: a versatile web server for exploring pharmacology and chemical structure association based on molecular 3D similarity method. Bioinformatics 29:1827–1829
Hopkins AL (2008) Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol 4:682–690
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin CC (2004) Proliferative inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation, and induction of apoptosis by ursolic acid in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Life Sci 75:2303–2316
Iwabayashi M, Taniyama Y, Sanada F et al (2012) Role of serotonin in angiogenesis: induction of angiogenesis by sarpogrelate via endothelial 5-HT1B/Akt/eNOS pathway in diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis 220:337–342
Kohl NE, Mosser SD, Giuliani EA et al (1993) Selection inhibition of ras-dependent transformation by a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Science 260:1934–1938
Konkimalla VB, Efferth T (2008) Evidence-based Chinese medicine for cancer therapy. J Ethnopharmacol 116(2):207–210
Li Y, Gong Y, Li L et al (2013a) Bioactive tanshinone I inhibits the growth of lung cancer in part via downregulation of Aurora A function. Mol Carcinogen 52:535–543
Li X, Yang G, Li X et al (2013b) Traditional Chinese medicine in cancer care: a review of controlled clinical studies published in Chinese. PLoS ONE 8:e60338
Li SG, Chen HY, Ou-Yang CS et al (2013c) The efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine as an adjunctive therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 8:e57604
Li S, Fan TP, Jia W et al (2014) Network pharmacology in traditional chinese medicine. Evid-based Compl Alt 2014:138460
Mao Y, Hao J, Jin ZQ et al (2017) Network pharmacology-based and clinically relevant prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbs in metastatic breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 8:27007
Matsusaka S, Wakabayashi I (2005) 5-Hydroxytryptamine as a potent migration enhancer of human aortic endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 579:6721–6725
McCulloch M, See C, Shu XJ et al (2006) Astragalus-based Chinese herbs and platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Clinical Oncol 24:419–430
Mok TSK, Yeo W, Johnson PJ et al (2007) A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized study of Chinese herbal medicine as complementary therapy for reduction of chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Ann Oncol 18:768–774
Moreno-Smith M, Lu C, Shahzad MMK et al (2011) Dopamine blocks stress-mediated ovarian carcinoma growth. Clin Cancer Res 17:3649–3659
Nagini S (2012) Carcinoma of the stomach: a review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular genetics and chemoprevention. World Gastrointestinal Oncol 4:156
Nguyen TTT, Tran E, Nguyen TH et al (2004) The role of activated MEK-ERK pathway in quercetin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 25(5):647–659
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Qi F (2015) The advantages of using traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy in the whole course of cancer treatment instead of only terminal stage of cancer. Biosci Trends 9:16–34
Rowinsky EK, Windle JJ, Von Hoff DD (1999) Ras protein farnesyltransferase: a strategic target for anticancer therapeutic development. J Clin Oncol 17:3631–3652
Ru J, Li P, Wang J et al (2014) TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform 6:13
Senogles SE (2007) D2 dopamine receptor-mediated antiproliferation in a small cell lung cancer cell line, NCI-H69. Anti-cancer Drug 18:801–807
Shao LI, Zhang B (2013) Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med 11:110–120
Shu X, McCulloch M, Xiao H et al (2005) Chinese herbal medicine and chemotherapy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Integr Cancer Ther 4(3):219–229
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65:5–29
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J et al (2011) Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27:431–432
Soll C, Jang JH, Riener MO et al (2010) Serotonin promotes tumor growth in human hepatocellular cancer. Hepatology 51:1244–1254
Sui Y, Li S, Shi P et al (2016) Ethyl acetate extract from Selaginella doederleinii Hieron inhibits the growth of human lung cancer cells A549 via caspase-dependent apoptosis pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 190:261–271
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S et al (2014) STRING v10: protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic acids Res 43:D447–D452
Tsai LH, Lees E, Faha B et al (1993) The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene 8:1593–1602
Wang L-C, Chang Y-Y, Lee I-C, Kuo H-C, Tsai M-Y (2020) Systematic review and meta-analysis of Chinese herbal medicine as adjuvant treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Complement Ther Med. 52:102472
Yan S, Huang C, Wu S et al (2010) Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid induce apoptosis in four human liver cancer cell lines. Toxicol in vitro 24(3):842–848
Yang CJ, Huang YJ, Wang CY et al (2010) Antiproliferative effect of Toona sinensis leaf extract on non–small-cell lung cancer. Trans Res 155:305–314
Yang X, Hao J, Zhu CH et al (2015) Survival benefits of western and traditional Chinese medicine treatment for patients with pancreatic cancer. Medicine 94:e1008
Yang H, Qin C, Li YH et al (2016) Therapeutic target database update 2016: enriched resource for bench to clinical drug target and targeted pathway information. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D1069–D1074
Yoshida M, Sakai T, Hosokawa N et al (1990) The effect of quercetin on cell cycle progression and growth of human gastric cancer cells. FEBS Lett 260:10–13
Zhang F, Xu L, Qu X et al (2011) Synergistic antitumor effect of elemene and etoposide is mediated via induction of cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 4:1189–1193
Acknowledgements
The National Science Foundation of China (81903934) supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Hao, J., Niu, Y. et al. Network pharmacology-based and clinically relevant prediction of active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbs on stage IV lung adenocarcinoma patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 2079–2092 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03488-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03488-0