Abstract
Purpose
Bladder cancer is one of the world’s top ten malignant tumors. The crucial role of microRNA in carcinogenesis has been well emphasized. Considering miRNA expression was tumor stage-, tissue-, or even development-specific, more experimental evidences about the functions of miRNAs in bladder cancer should be discovered to advance applying of miRNA in the diagnosis or therapy of cancer.
Methods
MiR-708 level in bladder carcinoma and adjacent noncancerous tissues was tested by real-time qPCR. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by using flow cytometry. The tumorigenicity of bladder carcinoma cells was evaluated in nude mice model. Luciferase reporter gene assays were performed to identify the interaction between miR-708 and 3′UTR of Caspase-2 mRNA. The protein level of Caspase-2 was determined by western blotting.
Results
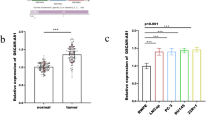
In this study, we reported that miR-708 was frequently dysregulated in human bladder carcinoma tissues compared to normal tissues. In addition, we found that silencing of miR-708 could promote the T24 and 5637 cells to apoptosis and inhibit the bladder tumor growth in vivo. Also, Caspase-2 was proved to be one of direct targets of miR-708 in T24 and 5637 cells. Further results showed that Caspase-2 was involved in the miR-708 regulated cell apoptosis.
Conclusions
All together, these results suggest miR-708 may act as an oncogene and induce the carcinogenicity of bladder cancer by down-regulating Caspase-2 level.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez A, Lokeshwar VB (2007) Bladder cancer biomarkers: current developments and future implementation. Curr Opin Urol 17(5):341–346
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Chen YH, Wang SQ, Wu XL, Shen M, Chen ZG, Chen XG, Liu YX, Zhu XL, Guo F, Duan XZ, Han XC, Tao ZH (2011) Characterization of microRNAs expression profiling in one group of Chinese urothelial cell carcinoma identified by Solexa sequencing. Urol Oncol. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.031
Cookson MS, Herr HW, Zhang ZF, Soloway S, Sogani PC, Fair WR (1997) The treated natural history of high risk superficial bladder cancer: 15-year outcome. J Urol 158:62–67
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Fendler A, Stephan C, Yousef GM, Jung K (2011) MicroRNAs as regulators of signal transduction in urological tumors. Clin Chem 57(7):954–968
Green DR, Evan GI (2000) A matter of life and death. Nature 407(6805):802–809
Hammond SM (2006) MicroRNAs as oncogenes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16(1):4–9
Han BW, Feng DD, Li ZG, Luo XQ, Zhang H, Li XJ, Zhang XJ, Zheng LL, Zeng CW, Lin KY, Zhang P, Xu L, Chen YQ (2011) A set of miRNAs that involve in the pathways of drug resistance and leukemic stem-cell differentiation is associated with the risk of relapse and glucocorticoid response in childhood ALL. Hum Mol Genet 20(24):4903–4915
Herr HW (1997) Natural history of superficial bladder tumors: 10- to 20-year follow-up of treated patients. World J Urol 15:84–88
Huang X, Yu HS, Chen Z, Li JL, Hu ZM, Gao JM (2010) A novel immunotherapy for superficial bladder cancer by the immobilization of streptavidin-tagged bioactive IL-2 on the biotinylated mucosal surface of the bladder wall. Chin J Cancer 29(6):611–616
Imre G, Heering J, Takeda AN, Husmann M, Thiede B, zu Heringdorf DM, Green DR, van der Goot FG, Sinha B, Dötsch V, Rajalingam K (2012) Caspase-2 is an initiator caspase responsible for pore-forming toxin-mediated apoptosis.The. EMBO J 31:2615–2628
Ismaili N, Amzerin M, Flechon A (2011) Chemotherapy in advanced bladder cancer: current status and future. J Hematol Oncol 4:35
Jang JS, Jeon HS, Sun Z, Aubry MC, Tang H, Park CH, Rakhshan F, Schultz DA, Kolbert CP, Lupu R, Park JY, Harris CC, Yang P, Jen J (2012) Increased miR-708 expression in NSCLC and its association with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma from never smokers. Clin Cancer Res 18(13):3658–3667
Kim BM, Rode AB, Han EJ, Hong IS, Hong SH (2012) 5-Phenylselenyl- and 5-methylselenyl-methyl-2′-deoxyuridine induce oxidative stress, DNA damage, and caspase-2-dependent apoptosis in cancer cells. Apoptosis 17(2):200–216
Kitevska T, Spencer DM, Hawkins CJ (2009) Caspase-2: controversial killer or checkpoint controller? Apoptosis 14(7):829–848
Lamkanfi M, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P (2007) Caspases in cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 14(1):44–55
Lee YS, Dutta A (2006) MicroRNAs: small but potent oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7(6):560–564
Li C, Feng Y, Coukos G (2009a) Therapeutic microRNA strategies in human cancer. AAPS J 11(4):747–757
Li S, Fu H, Wang Y, Tie Y, Xing R, Zhu J, Sun Z, Wei L, Zheng X (2009b) MicroRNA-101 regulates expression of the v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (FOS) oncogene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49(4):1194–1202
Lynam-Lennon N, Maher SG, Reynolds JV (2009) The roles of microRNA in cancer and apoptosis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 84:55–71
Muppani N, Nyman U, Joseph B (2011) TAp73alpha protects small cell lung carcinoma cells from caspase-2 induced mitochondrial mediated apoptotic cell death. Oncotarget 2(12):1145–1154
Noguchi S, Mori T, Hoshino Y, Maruo K, Yamada N, Kitade Y, Naoe T, Akao Y (2011) MicroRNA-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in human bladder. Cancer Lett 307(2):211–220
Papagiannakopoulos T, Kosik KS (2008) MicroRNAs: regulators of oncogenesis and stemness. BMC Med 6:15
Ren K, Lu J, Porollo A, Du C (2012) Tumor-suppressing function of caspase-2 requires catalytic site Cys-320 and site Ser-139 in mice. J Biol Chem 287(18):14792–14802
Saini S, Yamamura S, Majid S, Shahryari V, Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Dahiya R (2011) MicroRNA-708 induces apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity in renal cancer cells. Cancer Res 71(19):6208–6219
Saini S, Majid S, Shahryari V, Arora S, Yamamura S, Chang I, Zaman MS, Deng G, Tanaka Y, Dahiya R (2012) miRNA-708 control of CD44 + prostate cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Res 72(14):3618–3630
Shelley MD, Wilt TJ, Barber J, Mason MD (2004) A meta-analysis of randomised trials suggests a survival benefit for combined radiotherapy and radical cystectomy compared with radical radiotherapy for invasive bladder cancer: are these data relevant to modern practice. Clin Oncol 16:166–171
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(3–4):369–378
Song T, Xia W, Shao N, Zhang X, Wang C, Wu Y, Dong J, Cai W, Li H (2010) Differential miRNA expression profiles in bladder urothelial carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 11(4):905–911
Sudarshan S, Holman DH, Hyer ML, Voelkel-Johnson C, Dong JY, Norris JS (2005) In vitro efficacy of Fas ligand gene therapy for the treatment of bladder cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 12:12–18
Tang Y, Wells JA, Arkin MR (2011) Structural and enzymatic insights into caspase-2 protein substrate recognition and catalysis. J Biol Chem 286(39):34147–34154
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281(5381):1312–1316
Tiwari M, Lopez-Cruzan M, Morgan WW, Herman B (2011) Loss of caspase-2-dependent apoptosis induces autophagy after mitochondrial oxidative stress in primary cultures of young adult cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 286(10):8493–8506
Trang P, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ (2008) MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene 27:S52–S57
Wang V, Wu W (2009) MicroRNA-based therapeutics for cancer. BioDrugs 23:15–23
Wang CC, Chiang YM, Kuo PL, Chang JK, Hsu YL (2008) Norsolorinic acid inhibits proliferation of T24 human bladder cancer cells by arresting the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase and inducing a Fas/membrane-bound Fas ligand-mediated apoptotic pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 35:1301–1308
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS, Borre M, Peter ME, Ørntoft TF, Kjems J, Clark SJ (2011) Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200 family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 128(6):1327–1334
Yuan J, Yankner BA (2000) Apoptosis in the nervous system. Nature 407(6805):802–809
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. We have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work. There is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2013_1392_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Analysis of miR-708 expression in cancer cell lines and human bladder cancer tissue by northern blot. 1, adjacent noncancerous tissue. 2, bladder cancer tissue. 3, 5637 cells. 4, HepG2 cells. 5, Hela cells. 6,T24 cells. (TIFF 813 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, T., Zhang, X., Zhang, L. et al. miR-708 promotes the development of bladder carcinoma via direct repression of Caspase-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 1189–1198 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1392-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1392-6