Abstract
Purpose
The specific aim of this study was to investigate whether the PDCD4 gene is involved in the development and progression of gastric cancer.
Methods
We examined the genetic and epigenetic alterations of the PDCD4 gene as well as the expression of PDCD4 protein in gastric cancers. The mRNA expression of PDCD4 and miRNA-21 expression were also analyzed using quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
Results
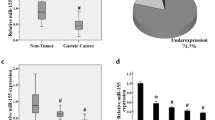
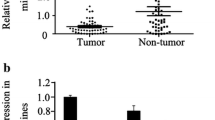
Loss or reduced PDCD4 expression was observed in 79 (36.7%) of 215 gastric cancer specimens. Statistically, altered PDCD4 expression was not associated with the clinicopathological parameters, including tumor differentiation, location, lymph node metastasis and overall survival (P > 0.05). miRNA-21 overexpression was frequently detected in gastric cancers (31 of 46, 67.4%), and there was a significant inverse correlation between miRNA-21 and PDCD4 protein expression (P = 0.029), but not between miRNA-21 and PDCD4 mRNA expression. In genetic analysis, no mutation was detected in the coding region of the PDCD4 gene, and promoter hypermethylation was found in 24 (36.4%) of the 66 gastric cancer samples.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that overexpression of miRNA-21 and reduced or loss of PDCD4 expression may play a role in the development and progression of gastric cancers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allgayer H (2010) Pdcd4, a colon cancer prognostic that is regulated by a microRNA. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 73:185–191
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA et al (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27:2128–2136
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M et al (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15524–15529
Chen Y, Knösel T, Kristiansen G et al (2003) Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung cancer correlates with tumour progression and prognosis. J Pathol 200:640–646
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ et al (2005) Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e179
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A et al (2008) Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:1026–1033
Gao F, Wang X, Zhu F et al (2009) PDCD4 gene silencing in gliomas is associated with 5′CpG island methylation and unfavorable prognosis. J Cell Mol Med 13:4257–4267
Goke R, Barth P, Schmidt A et al (2004) Programmed cell death protein 4 suppresses CDK1/cdc2 via induction of p21(Waf1/Cip1). Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C1541–C1546
Grunau C, Clark SJ, Rosenthal A (2001) Bisulfite genomic sequencing: systematic investigation of critical experimental parameters. Nucleic Acids Res 29:E65–E75
Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R et al (2009) MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15:1915–1922
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J et al (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A et al (1998) Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med 4:844–847
Kusenda B, Mraz M, Mayer J et al (2006) MicroRNA biogenesis, functionality, and cancer relevance. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 150:205–215
Lee JY, Dong SM, Kim SY et al (1998) A simple, precise and economical microdissection technique for analysis of genomic DNA from archival tissue sections. Virchows Arch 433:305–309
Lehmann U, Hasemeier B, Lilischkis R et al (2001) Quantitative analysis of promoter hypermethylation in laser-microdissected archival specimens. Lab Invest 81:635–638
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449:682–688
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H et al (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133:647–658
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Mimori K et al (2010) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PDCD4 and microRNA-21 in human gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 36:1089–1095
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Scott GK, Mattie MD, Berger CE et al (2006) Rapid alteration of microRNA levels by histone deacetylase inhibition. Cancer Res 66:1277–1281
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:369–378
Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y et al (1995) Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death. Gene 215:297–301
Shin HR, Jung KM, Won YJ et al (2004) 2002 Annual report of the Korea central cancer registry: based on registered data from 139 hospitals. Cancer Res Treat 36:103–114
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H et al (2007) miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 26:2799–2803
Soejima H, Miyoshi O, Yoshinaga H et al (1999) Assignment of the programmed cell death 4 gene (PDCD4) to human chromosome band 10q24 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 87:113–114
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K et al (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64:3753–3756
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Alder H et al (2010) Resveratrol modulates the levels of microRNAs targeting genes encoding tumor-suppressors and effectors of TGFβ signaling pathway in SW480 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 12:2057–2065
Wang Q, Sun ZX, Allgayer H et al (2010) Downregulation of E-cadherin is an essential event in activating beta-catenin/Tcf-dependent transcription and expression of its target genes in Pdcd4 knockdown cells. Oncogene 29:128–138
Wei NA, Liu SS, Leung TH et al (2009) Loss of Programmed cell death 4 (Pdcd4) associates with the progression of ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer 8:70
Wen YH, Shi X, Chiriboga L et al (2007) Alterations in the expression of PDCD4 in ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncol Rep 18:1387–1393
Werner M, Becker KF, Keller G et al (2001) Gastric adenocarcinoma: pathomorphology and molecular pathology. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127:207–216
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R et al (2001) A novel transformation suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but not NF-kappaB or ODC transactivation. Oncogene 20:669–676
Yoon JH, Song JW, Zhang C et al (2011) Inactivation of the Gastrokine 1 gene in gastric adenomas and carcinomas. J Pathol 223:618–625
Zamore PD, Haley B (2005) Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science 309:1519–1524
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C et al (2008) miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest 88:1358–1366
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H et al (2007) MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282:14328–14336
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F et al (2008) Micro-RNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res 18:350–359
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Public welfare & Safety research program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0020764).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhang Cao and Jung Hwan Yoon contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Z., Yoon, J.H., Nam, S.W. et al. PDCD4 expression inversely correlated with miR-21 levels in gastric cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 611–619 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-1140-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-1140-8