Abstract
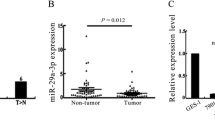
miRNAs have emerged as crucial regulators in the regulation of development as well as human diseases, especially tumorigenesis. The aims of this study are to evaluate miR-30b-5p expression pattern and mechanism in gastric carcinogenesis due to which remains to be determined. Expression of miR-30b-5p was analyzed in 51 gastric cancer cases and 4 cell lines by qRT-PCR. The effect of DNA methylation on miR-30b-5p expression was assessed by MSP and BGS. In order to know whether DNMT1 increased miR-30b-5p promoter methylation, DNMT1 was depleted in cell lines AGS and BGC-823. The role of miR-30b-5p on cell migration was evaluated by wound healing assays. Decreased expression of miR-30b-5p was found in gastric cancer samples. In tumor, the expression level of miR-30b-5p was profound correlated with lymph node metastasis (P = 0.019). The level of miR-30b-5p may be restored by DNA demethylation and DNMT1 induced miR-30b-5p promoter methylation. In vitro functional assays implied that enforced miR-30b-5p expression affected cell migration, consistent with tissues analysis. Our findings uncovered that miR-30b-5p is significantly diminished in gastric cancer tissues, providing the first insight into the epigenetic mechanism of miR-30b-5p down-regulation, induced by DNMT1, and the role of miR-30b-5p in gastric cancer carcinogenesis. Overexpression of miR-30b-5p inhibited cell migration. Thus, miR-30b-5p may represent a potential therapeutic target for gastric cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
- DNMT1:
-
DNA methyltransferase 1
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Ghafoor A, Jemal A, Cokkinides V, Cardinez C, Murray T, Samuels A, Thun MJ (2002) Cancer statistics for African Americans. CA Cancer J Clin 52(6):326–341
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136(4):642–655. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19(1):92–105. doi:10.1101/gr.082701.108
Quintavalle C, Donnarumma E, Iaboni M, Roscigno G, Garofalo M, Romano G, Fiore D, De Marinis P, Croce CM, Condorelli G (2012) Effect of miR-21 and miR-30b/c on TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.410
Huang YH, Lin KH, Chen HC, Chang ML, Hsu CW, Lai MW, Chen TC, Lee WC, Tseng YH, Yeh CT (2012) Identification of postoperative prognostic microRNA predictors in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37188. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037188
Fischer L, Hummel M, Korfel A, Lenze D, Joehrens K, Thiel E (2011) Differential micro-RNA expression in primary CNS and nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Neuro-oncology 13(10):1090–1098. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor107
Van der Auwera I, Limame R, van Dam P, Vermeulen PB, Dirix LY, Van Laere SJ (2010) Integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiling of the inflammatory breast cancer subtype. Br J Cancer 103(4):532–541. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605787
Husted S, Sokilde R, Rask L, Cirera S, Busk PK, Eriksen J, Litman T (2011) MicroRNA expression profiles associated with development of drug resistance in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Mol Pharm 8(6):2055–2062. doi:10.1021/mp200255d
Rahbari R, Holloway AK, He M, Khanafshar E, Clark OH, Kebebew E (2011) Identification of differentially expressed microRNA in parathyroid tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 18(4):1158–1165. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-1359-7
Yabushita S, Fukamachi K, Tanaka H, Sumida K, Deguchi Y, Sukata T, Kawamura S, Uwagawa S, Suzui M, Tsuda H (2012) Circulating microRNAs in serum of human K-ras oncogene transgenic rats with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Pancreas 41(7):1013–1018. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e31824ac3a5
Tao Q, Huang H, Geiman TM, Lim CY, Fu L, Qiu GH, Robertson KD (2002) Defective de novo methylation of viral and cellular DNA sequences in ICF syndrome cells. Hum Mol Genet 11(18):2091–2102
Fan H, Xu J, Wu S, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Xie W (2005) Construction of DNMT1 siRNA stable expressing vector and evaluation of its silenced efficiency in blocking gene expression (Zhonghua yi xue yi chuan xue za zhi = Zhonghua yixue yichuanxue zazhi). Chin J Med Genet 22 (2):142–145
Corcoran DL, Pandit KV, Gordon B, Bhattacharjee A, Kaminski N, Benos PV (2009) Features of mammalian microRNA promoters emerge from polymerase II chromatin immunoprecipitation data. PLoS ONE 4(4):e5279. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005279
Christman JK (2002) 5-Azacytidine and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine as inhibitors of DNA methylation: mechanistic studies and their implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene 21(35):5483–5495. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205699
Ghoshal K, Datta J, Majumder S, Bai S, Kutay H, Motiwala T, Jacob ST (2005) 5-Aza-deoxycytidine induces selective degradation of DNA methyltransferase 1 by a proteasomal pathway that requires the KEN box, bromo-adjacent homology domain, and nuclear localization signal. Mol Cell Biol 25(11):4727–4741. doi:10.1128/mcb.25.11.4727-4741.2005
Inoue T, Iinuma H, Ogawa E, Inaba T, Fukushima R (2012) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of microRNA-107 and its relationship to DICER1 mRNA expression in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep 27(6):1759–1764. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1709
Barker HE, Chang J, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird D, Nicolau M, Evans HR, Gartland A, Erler JT (2011) LOXL2-mediated matrix remodeling in metastasis and mammary gland involution. Cancer Res 71(5):1561–1572. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-10-2868
Zhang J, Zhang H, Liu J, Tu X, Zang Y, Zhu J, Chen J, Dong L (2012) miR-30 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting Snail1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 417(3):1100–1105. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.121
Gaziel-Sovran A, Segura MF, Di Micco R, Collins MK, Hanniford D, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Rakus JF, Dankert JF, Shang S, Kerbel RS, Bhardwaj N, Shao Y, Darvishian F, Zavadil J, Erlebacher A, Mahal LK, Osman I, Hernando E (2011) miR-30b/30d regulation of GalNAc transferases enhances invasion and immunosuppression during metastasis. Cancer Cell 20(1):104–118. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.05.027
Wu T, Li Y, Liu X, Lu J, He X, Wang Q, Li J, Du X (2011) Identification of high-risk stage II and stage III colorectal cancer by analysis of MMP-21 expression. J Surg Oncol 104(7):787–791. doi:10.1002/jso.21970
Huang Y, Li W, Chu D, Zheng J, Ji G, Li M, Zhang H, Wang W, Du J, Li J (2011) Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-21 is associated with poor overall survival of patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 15(7):1188–1194. doi:10.1007/s11605-011-1519-5
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, Chen P, Chen J, Liu W, Xiao S, Lu H (2008) miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest 88(12):1358–1366. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2008.94
Mani M, Carrasco DE, Zhang Y, Takada K, Gatt ME, Dutta-Simmons J, Ikeda H, Diaz-Griffero F, Pena-Cruz V, Bertagnolli M, Myeroff LL, Markowitz SD, Anderson KC, Carrasco DR (2009) BCL9 promotes tumor progression by conferring enhanced proliferative, metastatic, and angiogenic properties to cancer cells. Cancer Res 69(19):7577–7586. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-0773
Rehman AO, Wang CY (2009) CXCL12/SDF-1 alpha activates NF-kappaB and promotes oral cancer invasion through the Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1 complex. Int J Oral Sci 1(3):105–118. doi:10.4248/ijos.09059
Baylin SB, Ohm JE (2006) Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer - a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer 6(2):107–116. doi:10.1038/nrc1799
Smith LT, Otterson GA, Plass C (2007) Unraveling the epigenetic code of cancer for therapy. Trends Genet 23(9):449–456. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2007.07.005
Feinberg AP (2007) Phenotypic plasticity and the epigenetics of human disease. Nature 447(7143):433–440. doi:10.1038/nature05919
Baylin SB (2005) DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2(Suppl 1):S4–S11. doi:10.1038/ncponc0354
Goll MG, Bestor TH (2005) Eukaryotic cytosine methyl transferases. Annu Rev Biochem 74:481–514. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.010904.153721
Zuo J, Xia J, Ju F, Yan J, Zhu A, Jin S, Shan T, Zhou H (2013) MicroRNA-148a can regulate runt-related transcription factor 3 gene expression via modulation of DNA methyltransferase 1 in gastric cancer. Mol Cells 35(4):313–319. doi:10.1007/s10059-013-2314-9
Xu Q, Jiang Y, Yin Y, Li Q, He J, Jing Y, Qi YT, Li W, Lu B, Peiper SS, Jiang BH, Liu LZ (2013) A regulatory circuit of miR-148a/152 and DNMT1 in modulating cell transformation and tumor angiogenesis through IGF-IR and IRS1. J Mol Cell Biol 5(1):3–13. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjs049
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171915 and 91229107, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (CXLX12_0074).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fengchang Qiao and Kun Zhang have equal contribution to this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, F., Zhang, K., Gong, P. et al. Decreased miR-30b-5p expression by DNMT1 methylation regulation involved in gastric cancer metastasis. Mol Biol Rep 41, 5693–5700 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3439-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3439-4