Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to compare Ki-67, Bcl-2, Bax, Bak, ER, and PgR expression in postmenopausal women with ER-positive invasive breast cancer (IBC) before and after short-term hormone therapy (HT) with either tamoxifen or anastrozole in order to identify a possible biomarker profile associated with hormone resistance.
Methods
Fifty-eight patients with palpable IBC were assigned to receive neoadjuvant therapy with either anastrozole, placebo, or tamoxifen for 26 days prior to surgery. Tissue microarray blocks were constructed from pre- and post-treatment biopsy samples and used for immunohistochemical analysis. Biomarker (Ki-67, Bcl-2, Bax, Bak, ER, and PgR) levels were assessed semiquantitatively using the Allred score. A statistical analysis was performed using general estimating equations (GEE) and analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a significance level of 0.05.
Results
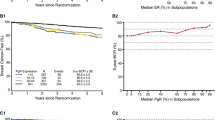
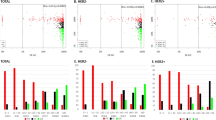
There was a significant reduction in PgR scores from baseline (mean, 4.22) to post-treatment (mean, 1.94) in the anastrozole group, but only a non-significant trend toward an increase in PgR scores was found in the tamoxifen group. There was a significant reduction in Ki-67 scores from baseline (mean, 3.61) to post-treatment (mean, 2.56) in the anastrozole group (P = 0.01), but only a non-significant trend toward a reduction in Ki-67 scores was found in the tamoxifen group.
Conclusions
There was a significant reduction in PgR and Ki-67 expression in the group treated with anastrozole. In the present study, the short-term HT was not associated with changes in apoptosis-related protein levels, regardless the type of drug used.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- GEE:
-
General estimating equations
- HT:
-
Hormone therapy
- IMPACT trial:
-
Immediate Preoperative Anastrozole, Tamoxifen, or Combined with Tamoxifen trial
- IBC:
-
Invasive breast cancer
- PgR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SERM:
-
Selective estrogen-receptor modulator
- UNIFESP:
-
Universidade Federal de São Paulo
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Colditz G (1998) Relationship between estrogen levels, use of hormone replacement therapy, and breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(11):814–823. doi:10.1093/jnci/90.11.814
Colozza M, Azambuja E, Cardoso F, Sotiriou C, Larsimont D, Piccart MJ (2005) Proliferative markers as prognostic and predictive tools in early breast cancer: where are we now? Ann Oncol 16(11):1723–1739. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi352
Dixon JM, Renshaw L, Bellamy C, Stuart M, Hoctin-Boes G, Miller WR (2000) The effects of neoadjuvant anastrozole (arimidex) on tumor volume in postmenopausal women with breast cancer: a randomized, double-blind, single-center study. Clin Cancer Res 6(6):2229–2235
Dowsett M (2003) Preoperative models to evaluate endocrine strategies for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9(1):502s–510s
Dowsett M (2004) Biomarker investigations from the atac trial: the role of ta01. Breast Cancer Res Treat 87(1):11–18
Dowsett M, Dunbier AK (2008) Emerging biomarkers and new understanding of traditional markers in personalized therapy for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(24):8019–8026. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-0974
Dowsett M, Bundred NJ, Decensi A, Sainsbury RC, Lu Y, Hills MJ, Cohen FJ, Veronesi P, O’Brien MER, Scott T, Muchmore DB (2001) Effect of raloxifene on breast cancer cell ki67 and apoptosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10(9):961–966
Dowsett M, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, Griffith C, Boeddinghaus I, Salter J, Detre S, Hills M, Ashley S, Francis S, Walsh G, Smith IE (2005a) Biomarker changes during neoadjuvant anastrozole, tamoxifen, or the combination: influence of hormonal status and her-2 in breast cancer–a study from the impact trialists. J Clin Oncol 23(11):2477–2492. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.07.559
Dowsett M, Elizabeth F, Deborah D, Ben H (2005b) The biology of steroid hormones and endocrine treatment of breast cancer. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 14(6):452–457
Dowsett M, Smith IE, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, Griffith C, Boeddinghaus I, Salter J, Detre S, Hills M, Ashley S, Francis S, Walsh G (2005c) Short-term changes in ki-67 during neoadjuvant treatment of primary breast cancer with anastrozole or tamoxifen alone or combined correlate with recurrence-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 11(2):951s–958s
Dowsett M, Smith IE, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, Griffith C, Boeddinghaus I, Salter J, Detre S, Hills M, Ashley S, Francis S, Walsh G, A’Hern R (2006) Proliferation and apoptosis as markers of benefit in neoadjuvant endocrine therapy of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(3):1024s–1030s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-05-2127
Dowsett M, Salter J, Hills M, Detre S, A’Hern R, Smith I (2007) Short-term presurgical treatment for all? Breast Cancer Res 9(Suppl 2):S13
EBCTCG (1998) Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: An overview of the randomised trials. The Lancet 351(9114):1451–1467
EBCTCG (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. The Lancet 365(9472):1687–1717
Ellis M, Ma C (2007) Letrozole in the neoadjuvant setting: The p024 trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 105:33–43
Ellis MJ, Tao Y, Luo J, A’Hern R, Evans DB, Bhatnagar AS, Chaudri Ross HA, von Kameke A, Miller WR, Smith I, Eiermann W, Dowsett M (2008) Outcome prediction for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer based on postneoadjuvant endocrine therapy tumor characteristics. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(19):1380–1388. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn309
Fisher B, Redmond C, Fisher E, Caplan R (1988) Relative worth of estrogen or progesterone receptor and pathologic characteristics of differentiation as indicators of prognosis in node negative breast cancer patients: findings from national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project protocol b-06. J Clin Oncol 6(7):1076–1087
Geisler J, Detre S, Berntsen H, Ottestad L, Lindtjørn B, Dowsett M, Lønning PE (2001) Influence of neoadjuvant anastrozole (arimidex) on intratumoral estrogen levels and proliferation markers in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7(5):1230–1236
Gompel A, Chaouat M, Hugol D, Forgez P (2004) Steroidal hormones and proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis in breast cells. Maturitas 49(1):16–24
Gruber CJ, Tschugguel W, Schneeberger C, Huber JC (2002) Production and actions of estrogens. N Engl J Med 346(5):340–352. doi:10.1056/NEJMra000471
Hankinson S, Colditz G, Willett W (2004) Towards an integrated model for breast cancer etiology: the lifelong interplay of genes, lifestyle, and hormones. Breast Cancer Res 6(5):213–218
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC (1999) Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17(5):1474
Hayes D (2008) Markers of endocrine sensitivity. Breast Cancer Res 10(Suppl 4):S18
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407(6805):770–776
Jager JJ, Jansen RLH, Arends JW (2002) Clinical relevance of apoptotic markers in breast cancer not yet clear. Apoptosis 7(4):361–365
Jensen EV, Jordan VC (2003) The estrogen receptor. Clin Cancer Res 9(6):1980–1989
Johnston SRD, Dowsett M (2003) Aromatase inhibitors for breast cancer: lessons from the laboratory. Nat Rev Cancer 3(11):821–831
Jordan VC (1994) Molecular mechanisms of antiestrogen action in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 31(1):41–52
Konstantinidou AE, Korkolopoulou P, Patsouris E (2002) Apoptotic markers for tumor recurrence: a minireview. Apoptosis 7(5):461–470
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Turner B, Pratt C, Howard B, Zapata J, Frenkel V, Robertson S, Ionov Y, Yamamoto H, Perucho M, Takayama S, Reed J (1999) Prognostic significance of apoptosis regulators in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 6(1):29–40. doi:10.1677/erc.0.0060029
Leek RD, Kaklamanis L, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1994) Bcl-2 in normal human breast and carcinoma, association with oestrogen receptor-positive, epidermal growth factor receptor-negative tumours and in situ cancer. Br J Cancer 69(1):135–139
Macaskill EJ, Renshaw L, Dixon JM (2006) Neoadjuvant use of hormonal therapy in elderly patients with early or locally advanced hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncologist 11(10):1081–1088. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.11-10-1081
Miller WR, Anderson TJ, Evans DB, Krause A, Hampton G, Dixon JM (2003) An integrated view of aromatase and its inhibition. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 86(3–5):413–421
Molino A, Micciolo R, Turazza M, Bonetti F, Piubello Q, Bonetti A, Nortilli R, Pelosi G, Cetto GL (1997) Ki-67 immunostaining in 322 primary breast cancers: associations with clinical and pathological variables and prognosis. Int J Cancer 74(4):433–437
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2009) Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9(9):631–643
Pankaj GR, Alastair MT (2006) Cyclin d1 and breast cancer. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 15(6):718–727
Pinto AE, André S, Pereira T, Nóbrega S, Soares J (2001) Prognostic comparative study of s-phase fraction and ki-67 index in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 54(7):543–549. doi:10.1136/jcp.54.7.543
Rose C, Vtoraya O, Pluzanska A, Davidson N, Gershanovich M, Thomas R, Johnson S, Caicedo JJ, Gervasio H, Manikhas G, Ayed FB, Burdette-Radoux S, Chaudri-Ross HA, Lang R (2003) An open randomised trial of second-line endocrine therapy in advanced breast cancer: comparison of the aromatase inhibitors letrozole and anastrozole. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 39(16):2318–2327
Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Daidone MG, Benini E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, Di Fronzo G, Rilke F, Veronesi U (1994) The bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 86(7):499–504. doi:10.1093/jnci/86.7.499
Silvestrini R, Benini E, Veneroni S, Daidone M, Tomasic G, Squicciarini P, Salvadori B (1996) P53 and bcl-2 expression correlates with clinical outcome in a series of node-positive breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 14(5):1604–1610
Smith IE, Dowsett M (2003) Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 348(24):2431–2442. doi:10.1056/NEJMra023246
Stendahl M, Kronblad A, Ryden L, Emdin S, Bengtsson NO, Landberg G (2004) Cyclin d1 overexpression is a negative predictive factor for tamoxifen response in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 90(10):1942–1948
Trihia H, Murray S, Price K, Gelber RD, Golouh R, Goldhirsch A, Coates AS, Collins J, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gusterson BA (2003) Ki-67 expression in breast carcinoma. Cancer 97(5):1321–1331
Whitfield ML, George LK, Grant GD, Perou CM (2006) Common markers of proliferation. Nat Rev Cancer 6 (2):99-106. doi:http://www.nature.com/nrc/journal/v6/n2/suppinfo/nrc1802_S1.html
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all the patients who gave their consent to participate in this trial. The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The authors also declare that they have no financial and/or non-financial competing interests (political, personal, religious, ideological, academic, intellectual, commercial, or any other) in relation to this manuscript. There was no external funding for this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattar, A., Logullo, A.F., Facina, G. et al. Short-term anastrozole therapy reduces Ki-67 and progesterone receptor expression in invasive breast cancer: a prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137, 897–905 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0950-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0950-4