Abstract
Aims
EphB2 is a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family that has been involved in the regulation of cytoskeleton organization and cell migration in various cell types. Its role and regulation in carcinogenesis is controversial, especially in gastric cancer. We detected EphB2 expression and determined its clinical significance and explored its underlying molecular mechanism in gastric cancers.
Methods
Tissue microarray blocks containing primary gastric cancer, lymph node metastases, and adjacent normal mucosa specimens obtained from 337 Chinese patients were constructed. Expression of EphB2 in these specimens was analyzed using immunohistochemistry. Mutation analysis at the A9 tract in exon 17 and loss of heterozygosity analysis at the EphB2 gene locus were carried out in 13 sporadic EphB2-negative gastric cancers.
Results
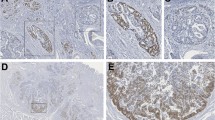
Complete loss of EphB2 expression was observed in 177 (52.5%) of the 337 primary tumor and 41 (82%) of the 50 nodal metastases. Loss of EphB2 expression was significantly associated with advanced T stage, nodal metastasis, advanced disease stage, and poor histological differentiation. Loss of EphB2 expression correlated significantly with poor survival rates in both univariate and multivariate analysis. No frameshift mutation, but a higher frequency of allelic loss, was found in EphB2-negative primary and metastatic tumor samples.
Conclusions
Frequent deletion and decreased expression of EphB2 protein suggested it as a negative biomarker for gastric carcinogenesis and a potential predictor of the outcome of patients with gastric cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LN:
-
Lymph node
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- LOH:
-
Loss of heterozygosity
References
Alazzouzi H, Davalos V, Kokko A, Domingo E, Woerner SM, Wilson AJ, Konrad L, Laiho P, Espin E, Armengol M, Imai K, Yamamoto H, Mariadason JM, Gebert JF, Aaltonen LA, Schwartz S Jr, Arango D (2005) Mechanisms of inactivation of the receptor tyrosine kinase EPHB2 in colorectal tumors. Cancer Res 65:10170–10173
Cortina C, Palomo-Ponce S, Iglesias M, Fernandez-Masip JL, Vivancos A, Whissell G, Huma M, Peiro N, Gallego L, Jonkheer S, Davy A, Lloreta J, Sancho E, Batlle E (2007) EphB-ephrin-B interactions suppress colorectal cancer progression by compartmentalizing tumor cells. Nat Genet 39:1376–1383
Davalos V, Dopeso H, Velho S, Ferreira AM, Cirnes L, Diaz-Chico N, Bilbao C, Ramirez R, Rodriguez G, Falcon O, Leon L, Niessen RC, Keller G, Dallenbach-Hellweg G, Espin E, Armengol M, Plaja A, Perucho M, Imai K, Yamamoto H, Gebert JF, Diaz-Chico JC, Hofstra RM, Woerner SM, Seruca R, Schwartz S Jr, Arango D (2007) High EPHB2 mutation rate in gastric but not endometrial tumors with microsatellite instability. Oncogene 26:308–311
Dodelet VC, Pasquale EB (2000) Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: embryogenesis to tumorigenesis. Oncogene 19:5614–5619
Dong JT (2006) Prevalent mutations in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem 97:433–447
Guo DL, Zhang J, Yuen ST, Tsui WY, Chan AS, Ho C, Ji J, Leung SY, Chen X (2006) Reduced expression of EphB2 that parallels invasion and metastasis in colorectal tumours. Carcinogenesis 27:454–464
Huusko P, Ponciano-Jackson D, Wolf M, Kiefer JA, Azorsa DO, Tuzmen S, Weaver D, Robbins C, Moses T, Allinen M, Hautaniemi S, Chen Y, Elkahloun A, Basik M, Bova GS, Bubendorf L, Lugli A, Sauter G, Schleutker J, Ozcelik H, Elowe S, Pawson T, Trent JM, Carpten JD, Kallioniemi OP, Mousses S (2004) Nonsense-mediated decay microarray analysis identifies mutations of EPHB2 in human prostate cancer. Nat Genet 36:979–983
Jubb AM, Zhong F, Bheddah S, Grabsch HI, Frantz GD, Mueller W, Kavi V, Quirke P, Polakis P, Koeppen H (2005) EphB2 is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:5181–5187
Kataoka H, Tanaka M, Kanamori M, Yoshii S, Ihara M, Wang YJ, Song JP, Li ZY, Arai H, Otsuki Y, Kobayashi T, Konno H, Hanai H, Sugimura H (2002) Expression profile of EFNB1, EFNB2, two ligands of EPHB2 in human gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 128:343–348
Lefeuvre M, Gunduz M, Nagatsuka H, Gunduz E, Al Sheikh Ali M, Beder L, Fukushima K, Yamanaka N, Shimizu K, Nagai N (2009) Fine deletion analysis of 1p36 chromosomal region in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med 38(1):94–98
Lugli A, Spichtin H, Maurer R, Mirlacher M, Kiefer J, Huusko P, Azorsa D, Terracciano L, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP, Mousses S, Tornillo L (2005) EphB2 expression across 138 human tumor types in a tissue microarray: high levels of expression in gastrointestinal cancers. Clin Cancer Res 11:6450–6458
Mellitzer G, Xu Q, Wilkinson DG (1999) Eph receptors and ephrins restrict cell intermingling and communication. Nature 400:77–81
Oba SM, Wang YJ, Song JP, Li ZY, Kobayashi K, Tsugane S, Hamada GS, Tanaka M, Sugimura H (2001) Genomic structure and loss of heterozygosity of EPHB2 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 164:97–104
Oshima T, Akaike M, Yoshihara K, Shiozawa M, Yamamoto N, Sato T, Akihito N, Nagano Y, Fujii S, Kunisaki C, Wada N, Rino Y, Tanaka K, Masuda M, Imada T (2008) Overexpression of EphA4 gene and reduced expression of EphB2 gene correlates with liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol 33:573–577
Song JH, Kim CJ, Cho YG, Kwak HJ, Nam SW, Yoo NJ, Lee JY, Park WS (2007) Genetic and epigenetic analysis of the EPHB2 gene in gastric cancers. Apmis 115:164–168
Wu Q, Suo Z, Risberg B, Karlsson MG, Villman K, Nesland JM (2004) Expression of Ephb2 and Ephb4 in breast carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res 10:26–33
Wu Q, Suo Z, Kristensen GB, Baekelandt M, Nesland JM (2006) The prognostic impact of EphB2/B4 expression on patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 102:15–21
Yu GZ, Zhu MH, Zhu Z, Ni CR, Zheng JM, Li FM (2004) Genetic alterations and reduced expression of tumor suppressor p33(ING1b) in human exocrine pancreatic carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 10:3597–3601
Yu G, Wang J, Chen Y, Wang X, Pan J, Li Q, Xie K (2008) Tissue microarray analysis reveals strong clinical evidence for a close association between loss of annexin A1 expression and nodal metastasis in gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 25:695–702
Zisch AH, Pasquale EB (1997) The Eph family: a multitude of receptors that mediate cell recognition signals. Cell Tissue Res 290:217–226
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflicts of interest with any other person or units.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
G. Yu and Y. Gao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, G., Gao, Y., Ni, C. et al. Reduced expression of EphB2 is significantly associated with nodal metastasis in Chinese patients with gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137, 73–80 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0861-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0861-4