Abstract
Purpose
Angiogenesis, which plays an important role in tumor growth and metastasis, is regulated by a balance between angiogenic stimulators and inhibitors. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), a secreted glycoprotein is an important inhibitor of angiogenesis. Although the precise mechanisms by which PEDF exerts its actions remain poorly understood, there is growing evidence supporting the role of PEDF as a candidate antitumor agent. In this study, we investigated the role of PEDF in breast cancer.
Methods
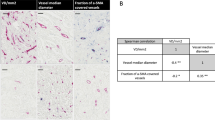
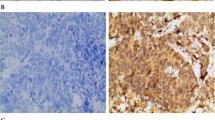
We investigated the correlation of PEDF protein levels with cancer progression and prognosis in patients with invasive ductal breast cancer (IDC). We used immunohistochemistry in a cohort of 119 breast cancer patients to examine the expression of PEDF protein with an anti-PEDF antibody and to measure the microvessel density (MVD) with an anti-CD34 antibody.
Results
PEDF was an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis in endothelial cells. Decreased intratumoral expression of PEDF was associated with a higher microvessel density (MVD), a more metastatic phenotype, and poorer clinical outcome. PEDF was positive in 43.7% patients. Patients with low PEDF expression had a significantly higher MVD count when compared with patients with high PEDF expression. In univariate and multivariate analysis, PEDF was an independent prognostic factor.
Conclusion
The inverse correlation between PEDF expression and MVD in human breast cancer suggests that low PEDF expression is associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. PEDF expression is therefore a potentially useful prognostic marker for breast cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard MP, Hegmans JP, Hemmes A et al (2004) Proteomic analysis of exosomes isolated from human malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 31:114–121
Blacque OE, Worrall DM (2002) Evidence for a direct interaction between the tumor suppressor serpin, maspin, and types and collagen. J Biol Chem 277:10783–10788
Cai J, Jiang WG, Grant M, Boulton M (2006a) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) inhibits angiogenesis via regulated intracellular proteolysis of VEGFR1. J Biol Chem 281:3604–3613
Cai J, Parr C, Watkins G (2006b) Decreased pigment epithelium-derived factor expression in human breast cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 12(11):3510–3517
Cao Y, Paner GP, Kahn LB, Rajan PB (2004) Noninvasive carcinoma of the breast angiogenesis and cell proliferation. Arch Parhol Lab Med 128:893–896
Dawson DW, Volper OV, Gills P, Crawford SE, Xu H, Benedict W et al (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor: a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science 285:245–248
Dhakal HP, Bassarova A, Naume B et al (2009) Breast carcinoma vascularity: a comparison of manual microvessel count and Chalkley count. Histol Histopathol 24:1049–1059
Ek ET, Choong PF (2006) The role of high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for pediatric bone and soft tissue sarcomas. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 6(2):225–237
Fernandez-Garcia NL, Volpert OV, Jimenez B (2007) Pigment epithelium-derived factor as a multifunctional antitumor factor. J Mol Med 85(1):15–22
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implication. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Goldberg RM (2005) Cetuximab. Nat Rev Drug Discov (suppl 1):10–11
Guang-Wu H, Sunagawa M, Jie-Em L et al (2000) The relationship between microvessel density, the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and the extension of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 110:2066–2069
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarkers of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Haybittle JL, Blamey RW, Elston CW et al (1982) A prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer 45:361–366
Jimenez B, Volpert OV (2001) Mechanistic insights on the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. J Mol Med 78:663–672
Kerr DG (2004) Targeting angiogenesis in cancer: clinical development of bevacizumab. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 1:39–43
Notari L, Miller A, Martinez A, Amaral J, Ju M, Robinson G, Smith LE, Becerra SP (2005) Pigment epithelium-derived factor is a substrate for matrix metalloproteinase type 2 and type 9: implications for downregulation in hypoxia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:2736–2747
Offersen BV, Borre M, Overgaard J (2003) Quantification of angiogenesis as a prognostic marker I human carcinomas: a critical evaluation of histopathological methods for estimation of vascular density. Eur J Cancer 39:881–890
Ohta M, Konno H, Tanaka T et al (2003) The significance of circulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett 192:215–225
Parkin DM, Brey F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Seo Y, Baba H, Fukuda T, Takashima M, Sugimachi K (2000) High expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with liver metastasis and a poor prognosis for patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 88:2239–2245
Teo NB, Shoker BS, Jarvis C, Martin L, Sloane JP, Holcombe C (2003) Angiogenesis and invasive recurrence in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Eur J Cancer 39:38–44
Tombran-Tink J, Johnson LV (1989) Neuronal differentiation of retinoblastoma cells induced by medium conditioned by human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30:1700–1707
Uehara H, Miyamoto M, Kato K et al (2004) Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor decrease liver metastasis and correlates with favorable prognosis for patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 64:3533–3537
Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB, Colpaert C, Marson LP, Gion M, Belien JAM, de Waal RMW, Van Marck E, Magnani E, Weidner N, Harris AL, Dirix LY (2002) Second international consensus on the methodology and criteria of evaluation of angiogenesis quantification in solid human tumours. Eur J Cancer 38(12):1564–1579
Viacava P, Naccarato AG, Bocci G, Fanelli G, Aretini P, Lonobile A, Evangelista G, Montruccoli G, Bevilacqua G (2004) Angiogenesis and VEGF expression in pre-invasive lesions of the human breast. J Pathol 204:140–146
Weigelt B, Wessels LF, Bosma AJ, Glas AM, Nuyten DS, He YD, Dai H, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ (2005) No common denominator for breast cancer lymph node metastasis. Br J Cancer 93:924–932
Weir HK, Thun MJ, Hankey BF, Rises LA, Howe HL, Wingo PA, Jemal A, Ward E, Anderson RN, Edwards BK (2003) Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2000, featuring the uses of surveillance data for cancer prevention and control. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:1276–1299
Zhang LJ, Chen JF, Ke Y, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2006a) Expression of pigment epithelial derived factor is reduced in non-small cell lung cancer and is linked to clinical outcome. Int J Mol Med 17:937–944
Zhang SX, Wang JJ, Gao G, Shao C, Mott R, Ma JX (2006b) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is an endogenous antiinflammatory factor. FASEB J 20:323–325
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Hong-Fei Ji, Yi Hong-Li, and Wei-Xu, for their contribution to experiments and data. This work was supported by project grants from the Science Foundation of Department of Public Health in China (Code WKJ2007-3-001).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors had any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The authors D. Zhou and S.-Q. Cheng are contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, D., Cheng, SQ., Ji, HF. et al. Evaluation of protein pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) and microvessel density (MVD) as prognostic indicators in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1719–1727 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0830-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0830-y