Abstract
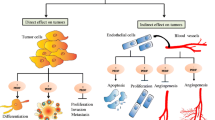
The design of new therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment is based on the combination of drugs directed against different tumor compartments, including the tumor cells themselves and components of the stroma, such as the tumor vasculature. Indeed, several antiangiogenic compounds have entered clinical trials for use alone or in combination with conventional cytotoxic drugs. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is a multifunctional natural peptide with complex neurotrophic, neuroprotective, antiangiogenic, and proapoptotic biological activities, any of which could potentially be exploited for therapeutic purposes. This review summarizes recent studies that reveal the antitumor potential of PEDF based on its antiangiogenic properties and its newly discovered direct antitumor effects, which involve the induction of differentiation or apoptosis in tumor cells. We also discuss possible therapeutic applications of PEDF, based on these mechanistic insights and on the identification of functional domains that retain specific biological activities.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PEDF:
-
pigment epithelium-derived factor
- TSP-1:
-
thrombospondin-1
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- bFGF:
-
basic-fibroblast growth factor
- NFATc2:
-
nuclear factor of activated T cells
- c-FLIP:
-
cellular-FLICE-like inhibitory protein
- VEGF-R1:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-κB
- JNK:
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- MMP-9:
-
matrix metalloproteinase-9
- Ad-PEDF:
-
adenovirus-PEDF
References
Tombran-Tink J, Johnson LV (1989) Neuronal differentiation of retinoblastoma cells induced by medium conditioned by human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30:1700–1707
Pignolo RJ, Cristofalo VJ, Rotenberg MO (1993) Senescent WI-38 cells fail to express EPC-1, a gene induced in young cells upon entry into the G0 state. J Biol Chem 268:8949–8957
Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Gillis P, Crawford SE, Xu H, Benedict W, Bouck NP (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor: a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science 285:245–248
Jimenez B, Volpert OV (2001) Mechanistic insights on the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. J Mol Med 78:663–672
Bouck N (2002) PEDF: anti-angiogenic guardian of ocular function. Trends Mol Med 8:330–334
Volpert OV, Zaichuk T, Zhou W, Reiher F, Ferguson TA, Stuart PM, Amin M, Bouck NP (2002) Inducer-stimulated Fas targets activated endothelium for destruction by anti-angiogenic thrombospondin-1 and pigment epithelium-derived factor. Nat Med 8:349–357
Zaichuk TA, Shroff EH, Emmanuel R, Filleur S, Nelius T, Volpert OV (2004) Nuclear factor of activated T cells balances angiogenesis activation and inhibition. J Exp Med 199:1513–1522
Cai J, Jiang WG, Grant MB, Boulton M (2006) Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis via regulated intracellular proteolysis of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1. J Biol Chem 281:3604–3613
Doll JA, Stellmach VM, Bouck NP, Bergh AR, Lee C, Abramson LP, Cornwell ML, Pins MR, Borensztajn J, Crawford SE (2003) Pigment epithelium-derived factor regulates the vasculature and mass of the prostate and pancreas. Nat Med 9:774–780
Abramson LP, Stellmach V, Doll JA, Cornwell M, Arensman RM, Crawford SE (2003) Wilms’ tumor growth is suppressed by antiangiogenic pigment epithelium-derived factor in a xenograft model. J Pediatr Surg 38:336–342
Crawford SE, Stellmach V, Ranalli M, Huang X, Huang L, Volpert O, De Vries GH, Abramson LP, Bouck N (2001) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in neuroblastoma: a multifunctional mediator of Schwann cell antitumor activity. J Cell Sci 114:4421–4428
Hase R, Miyamoto M, Uehara H, Kadoya M, Ebihara Y, Murakami Y, Takahashi R, Mega S, Li L, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, Kondo S (2005) Pigment epithelium-derived factor gene therapy inhibits human pancreatic cancer in mice. Clin Cancer Res 11:8737–8744
Garcia M, Fernandez-Garcia NI, Rivas V, Carretero M, Escamez MJ, Gonzalez-Martin A, Medrano EE, Volpert O, Jorcano JL, Jimenez B, Larcher F, Del Rio M (2004) Inhibition of xenografted human melanoma growth and prevention of metastasis development by dual antiangiogenic/antitumor activities of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Cancer Res 64:5632–5642
Abe R, Shimizu T, Yamagishi S, Shibaki A, Amano S, Inagaki Y, Watanabe H, Sugawara H, Nakamura H, Takeuchi M, Imaizumi T, Shimizu H (2004) Overexpression of pigment epithelium-derived factor decreases angiogenesis and inhibits the growth of human malignant melanoma cells in vivo. Am J Pathol 164:1225–1232
Halin S, Wikstrom P, Rudolfsson SH, Stattin P, Doll JA, Crawford SE, Bergh A (2004) Decreased pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with metastatic phenotype in human and rat prostate tumors. Cancer Res 64:5664–5671
Uehara H, Miyamoto M, Kato K, Ebihara Y, Kaneko H, Hashimoto H, Murakami Y, Hase R, Takahashi R, Mega S, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, Itoh T, Okushiba S, Kondo S, Katoh H (2004) Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor decreases liver metastasis and correlates with favorable prognosis for patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 64:3533–3537
Guan M, Yam HF, Su B, Chan KP, Pang CP, Liu WW, Zhang WZ, Lu Y (2003) Loss of pigment epithelium derived factor expression in glioma progression. J Clin Pathol 56:277–282
Matsumoto K, Ishikawa H, Nishimura D, Hamasaki K, Nakao K, Eguchi K (2004) Antiangiogenic property of pigment epithelium-derived factor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 40:252–259
Quan GM, Ojaimi J, Nadesapillai AP, Zhou H, Choong PF (2002) Resistance of epiphyseal cartilage to invasion by osteosarcoma is likely to be due to expression of antiangiogenic factors. Pathobiology 70:361–367
Quan GM, Ojaimi J, Li Y, Kartsogiannis V, Zhou H, Choong PF (2005) Localization of pigment epithelium-derived factor in growing mouse bone. Calcif Tissue Int 76:146–153
Tombran-Tink J, Chader GG, Johnson LV (1991) PEDF: a pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal differentiative activity. Exp Eye Res 53:411–414
Houenou LJ, D’Costa AP, Li L, Turgeon VL, Enyadike C, Alberdi E, Becerra SP (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor promotes the survival and differentiation of developing spinal motor neurons. J Comp Neurol 412:506–514
Araki T, Taniwaki T, Becerra SP, Chader GJ, Schwartz JP (1998) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) differentially protects immature but not mature cerebellar granule cells against apoptotic cell death. J Neurosci Res 53:7–15
DeCoster MA, Schabelman E, Tombran-Tink J, Bazan NG (1999) Neuroprotection by pigment epithelial-derived factor against glutamate toxicity in developing primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res 56:604–610
Bilak MM, Corse AM, Bilak SR, Lehar M, Tombran-Tink J, Kuncl RW (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) protects motor neurons from chronic glutamate-mediated neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:719–728
Cao W, Tombran-Tink J, Chen W, Mrazek D, Elias R, McGinnis JF (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor protects cultured retinal neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death. J Neurosci Res 57:789–800
Ogata N, Wang L, Jo N, Tombran-Tink J, Takahashi K, Mrazek D, Matsumura M (2001) Pigment epithelium derived factor as a neuroprotective agent against ischemic retinal injury. Curr Eye Res 22:245–252
Takita H, Yoneya S, Gehlbach PL, Duh EJ, Wei LL, Mori K (2003) Retinal neuroprotection against ischemic injury mediated by intraocular gene transfer of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:4497–4504
Cayouette M, Smith SB, Becerra SP, Gravel C (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor delays the death of photoreceptors in mouse models of inherited retinal degenerations. Neurobiol Dis 6:523–532
Cao W, Tombran-Tink J, Elias R, Sezate S, Mrazek D, McGinnis JF (2001) In vivo protection of photoreceptors from light damage by pigment epithelium-derived factor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:1646–1652
Ramirez-Castillejo C, Sanchez-Sanchez F, Andreu-Agullo C, Ferron SR, Aroca-Aguilar JD, Sanchez P, Mira H, Escribano J, Farinas I (2006) Pigment epithelium-derived factor is a niche signal for neural stem cell renewal. Nat Neurosci 9:331–339
Filleur S, Volz K, Nelius T, Mirochnik Y, Huang H, Zaichuk TA, Aymerich MS, Becerra SP, Yap R, Veliceasa D, Shroff EH, Volpert OV (2005) Two functional epitopes of pigment epithelial-derived factor block angiogenesis and induce differentiation in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 65:5144–5152
Tombran-Tink J, Barnstable CJ (2003) PEDF: a multifaceted neurotrophic factor. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:628–636
Tombran-Tink J (2005) The neuroprotective and angiogenesis inhibitory serpin, PEDF: new insights into phylogeny, function, and signaling. Front Biosci 10:2131–2149
Yabe T, Wilson D, Schwartz JP (2001) NFkappaB activation is required for the neuroprotective effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) on cerebellar granule neurons. J Biol Chem 276:43313–43319
Bilak MM, Becerra SP, Vincent AM, Moss BH, Aymerich MS, Kuncl RW (2002) Identification of the neuroprotective molecular region of pigment epithelium-derived factor and its binding sites on motor neurons. J Neurosci 22:9378–9386
Alberdi E, Aymerich MS, Becerra SP (1999) Binding of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) to retinoblastoma cells and cerebellar granule neurons. Evidence for a PEDF receptor. J Biol Chem 274:31605–31612
Aymerich MS, Alberdi EM, Martinez A, Becerra SP (2001) Evidence for pigment epithelium-derived factor receptors in the neural retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:3287–3293
Yamagishi S, Inagaki Y, Amano S, Okamoto T, Takeuchi M (2002) Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and down-regulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor messenger ribonucleic acid levels in leptin-exposed cultured retinal pericytes. Int J Tissue React 24:137–142
Tsao YP, Ho TC, Chen SL, Cheng HC (2006) Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits oxidative stress-induced cell death by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases in cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells. Life Sci 79:545–550
Maik-Rachline G, Shaltiel S, Seger R (2005) Extracellular phosphorylation converts pigment epithelium-derived factor from a neurotrophic to an antiangiogenic factor. Blood 105:670–678
Maik-Rachline G, Seger R (2006) Variable phosphorylation states of pigment-epithelium-derived factor differentially regulate its function. Blood 107:2745–2752
Guan M, Pang CP, Yam HF, Cheung KF, Liu WW, Lu Y (2004) Inhibition of glioma invasion by overexpression of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Cancer Gene Ther 11:325–332
Takenaka K, Yamagishi S, Jinnouchi Y, Nakamura K, Matsui T, Imaizumi T (2005) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)-induced apoptosis and inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in MG63 human osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci 77:3231–3241
Notari L, Miller A, Martinez A, Amaral J, Ju M, Robinson G, Smith LE, Becerra SP (2005) Pigment epithelium-derived factor is a substrate for matrix metalloproteinase type 2 and type 9: implications for downregulation in hypoxia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:2736–2747
Kozaki K, Miyaishi O, Koiwai O, Yasui Y, Kashiwai A, Nishikawa Y, Shimizu S, Saga S (1998) Isolation, purification, and characterization of a collagen-associated serpin, caspin, produced by murine colon adenocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 273:15125–15130
Zou Z, Anisowicz A, Hendrix MJ, Thor A, Neveu M, Sheng S, Rafidi K, Seftor E, Sager R (1994) Maspin, a serpin with tumor-suppressing activity in human mammary epithelial cells. Science 263:526
Sheng S, Pemberton PA, Sager R (1994) Production, purification, and characterization of recombinant maspin proteins. J Biol Chem 269:30988–30993
Blacque OE, Worrall DM (2002) Evidence for a direct interaction between the tumor suppressor serpin, maspin, and types I and III collagen. J Biol Chem 277:10783–10788
Meyer C, Notari L, Becerra SP (2002) Mapping the type I collagen-binding site on pigment epithelium-derived factor. Implications for its antiangiogenic activity. J Biol Chem 277:45400–45407
Mahtabifard A, Merritt RE, Yamada RE, Crystal RG, Korst RJ (2003) In vivo gene transfer of pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits tumor growth in syngeneic murine models of thoracic malignancies. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126:28–38
Liu H, Ren JG, Cooper WL, Hawkins CE, Cowan MR, Tong PY (2004) Identification of the antivasopermeability effect of pigment epithelium-derived factor and its active site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6605–6610
Simonovic M, Gettins PG, Volz K (2001) Crystal structure of human PEDF, a potent anti-angiogenic and neurite growth-promoting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:11131–11135
Gillis P, Savla U, Volpert OV, Jimenez B, Waters CM, Panos RJ, Bouck NP (1999) Keratinocyte growth factor induces angiogenesis and protects endothelial barrier function. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 12):2049–2057
Tolsma SS, Volpert OV, Good DJ, Frazier WA, Polverini PJ, Bouck N (1993) Peptides derived from two separate domains of the matrix protein thrombospondin-1 have anti-angiogenic activity. J Cell Biol 122:497–511
Chen ZS, Pohl J, Lawley TJ, Swerlick RA (1996) Human microvascular endothelial cells adhere to thrombospondin-1 via an RGD/CSVTCG domain independent mechanism. J Invest Dermatol 106:215–220
Shafiee A, Penn JS, Krutzsch HC, Inman JK, Roberts DD, Blake DA (2000) Inhibition of retinal angiogenesis by peptides derived from thrombospondin-1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:2378–2388
Haviv F, Bradley MF, Kalvin DM, Schneider AJ, Davidson DJ, Majest SM, McKay LM, Haskell CJ, Bell RL, Nguyen B, Marsh KC, Surber BW, Uchic JT, Ferrero J, Wang YC, Leal J, Record RD, Hodde J, Badylak SF, Lesniewski RR, Henkin J (2005) Thrombospondin-1 mimetic peptide inhibitors of angiogenesis and tumor growth: design, synthesis, and optimization of pharmacokinetics and biological activities. J Med Chem 48:2838–2846
Mori K, Gehlbach P, Ando A, McVey D, Wei L, Campochiaro PA (2002) Regression of ocular neovascularization in response to increased expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:2428–2434
Mori K, Gehlbach P, Yamamoto S, Duh E, Zack DJ, Li Q, Berns KI, Raisler BJ, Hauswirth WW, Campochiaro PA (2002) AAV-mediated gene transfer of pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1994–2000
Auricchio A, Behling KC, Maguire AM, O’Connor EM, Bennett J, Wilson JM, Tolentino MJ (2002) Inhibition of retinal neovascularization by intraocular viral-mediated delivery of anti-angiogenic agents. Mol Ther 6:490–494
Gehlbach P, Demetriades AM, Yamamoto S, Deering T, Duh EJ, Yang HS, Cingolani C, Lai H, Wei L, Campochiaro PA (2003) Periocular injection of an adenoviral vector encoding pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits choroidal neovascularization. Gene Ther 10:637–646
Raisler BJ, Berns KI, Grant MB, Beliaev D, Hauswirth WW (2002) Adeno-associated virus type-2 expression of pigmented epithelium-derived factor or Kringles 1–3 of angiostatin reduce retinal neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8909–8914
Wang L, Schmitz V, Perez-Mediavilla A, Izal I, Prieto J, Qian C (2003) Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by adenoviral-mediated gene transfer of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Mol Ther 8:72–79
Streck CJ, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Ng C, Nathwani AC, Davidoff AM (2005) Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated delivery of pigment epithelium-derived factor restricts neuroblastoma angiogenesis and growth. J Pediatr Surg 40:236–243
Merritt RE, Yamada RE, Wasif N, Crystal RG, Korst RJ (2004) Effect of inhibition of multiple steps of angiogenesis in syngeneic murine pleural mesothelioma. Ann Thorac Surg 78:1042–1051
Acknowledgements
Supported by grant SAF 2004-04152 to B. Jimenez and R01HL068033 grant to O.V. Volpert. N.I. Fernandez-Garcia has been supported by a Comunidad Autonoma de Madrid fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandez-Garcia, N.I., Volpert, O.V. & Jimenez, B. Pigment epithelium-derived factor as a multifunctional antitumor factor. J Mol Med 85, 15–22 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0111-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0111-z