Abstract
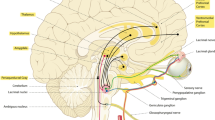
The basal forebrain (BF) contains at least three distinct populations of neurons (cholinergic, glutamatergic, and GABA-ergic) across its different regions (medial septum, diagonal band, magnocellular preoptic area, and substantia innominata). Much attention has focused on the BF’s ascending projections to cortex, but less is known about descending projections to subcortical regions. Given the neurochemical and anatomical heterogeneity of the BF, we used conditional anterograde tracing to map the patterns of subcortical projections from multiple BF regions and neurochemical cell types using mice that express Cre recombinase only in cholinergic, glutamatergic, or GABAergic neurons. We confirmed that different BF regions innervate distinct subcortical targets, with more subcortical projections arising from neurons in the caudal and lateral BF (substantia innominata and magnocellular preoptic area). Additionally, glutamatergic and GABAergic BF neurons have distinct patterns of descending projections, while cholinergic descending projections are sparse. Considering the intensity of glutamatergic and GABAergic descending projections, the BF likely acts through subcortical targets to promote arousal, motivation, and other behaviors.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3V:
-
Third ventricle
- AAV:
-
Adeno-associated viral vector
- ac:
-
Anterior commissure
- BF:
-
Basal forebrain
- BLA:
-
Basolateral amygdala
- BST (al):
-
Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, anterolateral area
- CEL:
-
Central amygdala nucleus, lateral
- CEM:
-
Central amygdala nucleus, medial
- ChAT:
-
Choline acetyltransferase
- ChR2:
-
Channelrhodopsin-2
- CM:
-
Central medial nucleus of the thalamus
- CPu:
-
Caudate putamen
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- DMH:
-
Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
- DR:
-
Dorsal raphe
- DTg:
-
Dorsal tegmental nucleus
- f:
-
Fornix
- GP:
-
Globus pallidus
- HDB:
-
Horizontal nucleus of the diagonal band
- IAM:
-
Interanteromedial nucleus of the thalamus
- ic:
-
Internal capsule
- IMD:
-
Intermediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus
- ip:
-
Intraperitoneal
- IPACm:
-
Interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure, medial
- IPN:
-
Interpeduncular nucleus
- LC:
-
Locus coeruleus
- LDT:
-
Laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
- LHb:
-
Lateral habenula
- LPB:
-
Lateral parabrachial nucleus
- LH:
-
Lateral hypothalamus
- LSD:
-
Lateral septum, dorsal
- LSI:
-
Lateral septum, intermediate
- LPO:
-
Lateral preoptic area
- MEA:
-
Medial amygdala nucleus
- MCPO:
-
Magnocellular preoptic nucleus
- MD:
-
Mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus
- MHb:
-
Medial habenula
- MM:
-
Medial mammillary nucleus
- MPA:
-
Medial preoptic area
- MPB:
-
Medial parabrachial nucleus
- MPO:
-
Medial preoptic nucleus
- MRF:
-
Medullary reticular formation
- MS:
-
Medial septum
- NI:
-
Nucleus incertus
- NTS:
-
Nucleus of the solitary tract
- opt:
-
Optic tract
- PBel:
-
Parabrachial nucleus, external lateral subnucleus
- PCRt:
-
Parvicellular reticular nucleus
- PeF:
-
Perifornical nucleus of the hypothalamus
- PF:
-
Parafascicular nucleus
- PH:
-
Posterior lateral hypothalamus
- PPT:
-
Pedunculopontine nucleus
- PVH:
-
Paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
- PVT:
-
Paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus
- RRF:
-
Retrorubral field
- SCN:
-
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
- scp:
-
Superior cerebellar peduncle
- SI:
-
Substantia innominata
- SNc:
-
Substantia nigra: compact part
- SNr:
-
Substantia nigra: reticular part
- st:
-
Stria terminalis
- STIA:
-
Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, intraamygdaloid
- SUM:
-
Supramammillary nucleus
- TRN:
-
Reticular nucleus of the thalamus
- VDB:
-
Vertical nucleus of the diagonal band
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
- vPAG:
-
Ventral periaqueductal gray
- vGAT:
-
Vesicular GABA transporter
- vGluT1:
-
Vesicular glutamate transporter, type 1
- vGluT2:
-
Vesicular glutamate transporter, type 2
- vGluT3:
-
Vesicular glutamate transporter, type 3
- VMH:
-
Ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus
- VP:
-
Ventral pallidum
References
Adamantidis A, Carter MC, de Lecea L (2010) Optogenetic deconstruction of sleep-wake circuitry in the brain. Front Mol Neurosci 2:31. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.02.031.2009
Agostinelli LJ, Ferrari LL, Mahoney CE, Mochizuki T, Lowell BB, Arrigoni E, Scammell TE (2017) Descending projections from the basal forebrain to the orexin neurons in mice. J Comp Neurol 525(7):1668–1684. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24158
Alheid GF (2003) Extended amygdala and basal forebrain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:185–205
Alheid GF, Heimer L (1988) New perspectives in basal forebrain organization of special relevance for neuropsychiatric disorders: the striatopallidal, amygdaloid, and corticopetal components of substantia innominata. Neuroscience 27(1):1–39
Amaral DG, Cowan WM (1980) Subcortical afferents to the hippocampal formation in the monkey. J Comp Neurol 189(4):573–591. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901890402
Anaclet C, Pedersen NP, Ferrari LL, Venner A, Bass CE, Arrigoni E, Fuller PM (2015) Basal forebrain control of wakefulness and cortical rhythms. Nat Commun 6:8744. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9744
Armstrong DM, Saper CB, Levey AI, Wainer BH, Terry RD (1983) Distribution of cholinergic neurons in rat brain: demonstrated by the immunocytochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase. J Comp Neurol 216(1):53–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902160106
Bernard JF, Huang GF, Besson JM (1994) The parabrachial area: electrophysiological evidence for an involvement in visceral nociceptive processes. J Neurophysiol 71(5):1646–1660. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1994.71.5.1646
Bickford ME, Gunluk AE, Van Horn SC, Sherman SM (1994) GABAergic projection from the basal forebrain to the visual sector of the thalamic reticular nucleus in the cat. J Comp Neurol 348(4):481–510. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903480402
Blouin AM, Fried I, Wilson CL, Staba RJ, Behnke EJ, Lam HA, Maidment NT, Karlsson KAE, Lapierre JL, Siegel JM (2013) Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction. Nat Commun 4:1547. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2461
Brown RE, McKenna JT (2015) Turning a negative into a positive: ascending GABAergic control of cortical activation and arousal. Front Neurol 6:135. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00135
Brown RE, Basheer R, McKenna JT, Strecker RE, McCarley RW (2012) Control of sleep and wakefulness. Physiol Rev 92(3):1087–1187. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00032.2011
Burgess CR, Oishi Y, Mochizuki T, Peever JH, Scammell TE (2013) Amygdala lesions reduce cataplexy in orexin knock-out mice. J Neurosci 33(23):9734–9742. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5632-12.2013
Buzsaki G, Bickford RG, Ponomareff G, Thal LJ, Mandel R, Gage FH (1988) Nucleus basalis and thalamic control of neocortical activity in the freely moving rat. J Neurosci 8(11):4007–4026
Campos CA, Bowen AJ, Han S, Wisse BE, Palmiter RD, Schwartz MW (2017) Cancer-induced anorexia and malaise are mediated by CGRP neurons in the parabrachial nucleus. Nat Neurosci 20(7):934–942. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4574
Campos CA, Bowen AJ, Roman CW, Palmiter RD (2018) Encoding of danger by parabrachial CGRP neurons. Nature 555(7698):617–622. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25511
Canteras NS, Simerly RB, Swanson LW (1995) Organization of projections from the medial nucleus of the amygdala: a PHAL study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 360(2):213–245. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903600203
Carlsen J, Zaborszky L, Heimer L (1985) Cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain to the basolateral amygdaloid complex: a combined retrograde fluorescent and immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol 234(2):155–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902340203
Carter ME, Soden ME, Zweifel LS, Palmiter RD (2013) Genetic identification of a neural circuit that suppresses appetite. Nature 503(7474):111–114. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12596
Carter ME, Han S, Palmiter RD (2015) Parabrachial calcitonin gene-related peptide neurons mediate conditioned taste aversion. J Neurosci 35(11):4582–4586. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3729-14.2015
Cassell MD, Gray TS, Kiss JZ (1986) Neuronal architecture in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala: a cytological, hodological, and immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 246(4):478–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902460406
Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M (1999) Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell 98(4):437–451
Dlouhy BJ, Gehlbach BK, Kreple CJ, Kawasaki H, Oya H, Buzza C, Granner MA, Welsh MJ, Howard MA, Wemmie JA, Richerson GB (2015) Breathing inhibited when seizures spread to the amygdala and upon amygdala stimulation. J Neurosci 35(28):10281–10289. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0888-15.2015
Do JP, Xu M, Lee SH, Chang WC, Zhang S, Chung S, Yung TJ, Fan JL, Miyamichi K, Luo L, Dan Y (2016) Cell type-specific long-range connections of basal forebrain circuit. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13214
Elmquist JK, Scammell TE, Jacobson CD, Saper CB (1996) Distribution of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain following intravenous lipopolysaccharide administration. J Comp Neurol 371 (1):85–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960715)371:1<85::AID-CNE5>3.0.CO;2-H
Ericsson A, Kovacs KJ, Sawchenko PE (1994) A functional anatomical analysis of central pathways subserving the effects of interleukin-1 on stress-related neuroendocrine neurons. J Neurosci 14(2):897–913
Estabrooke IV, McCarthy MT, Ko E, Chou TC, Chemelli RM, Yanagisawa M, Saper CB, Scammell TE (2001) Fos expression in orexin neurons varies with behavioral state. J Neurosci 21(5):1656–1662
Fallon JH, Leslie FM (1986) Distribution of dynorphin and enkephalin peptides in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 249(3):293–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902490302
Fischer TH, Eiringhaus J, Dybkova N, Forster A, Herting J, Kleinwachter A, Ljubojevic S, Schmitto JD, Streckfuss-Bomeke K, Renner A, Gummert J, Hasenfuss G, Maier LS, Sossalla S (2014) Ca(2+) /calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II equally induces sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) leak in human ischaemic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail 16(12):1292–1300. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.163
Franklin KB, Paxinos G (2007) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Fuller PM, Sherman D, Pedersen NP, Saper CB, Lu J (2011) Reassessment of the structural basis of the ascending arousal system. J Comp Neurol 519(5):933–956. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.22559
Geisler S, Trimble M (2008) The lateral habenula: no longer neglected. CNS Spectr 13(6):484–489
Gielow MR, Zaborszky L (2017) The Input–output relationship of the cholinergic basal forebrain. Cell Rep 18(7):1817–1830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.060
Goard M, Dan Y (2009) Basal forebrain activation enhances cortical coding of natural scenes. Nat Neurosci 12(11):1444–1449. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2402
Gonzalo-Ruiz A, Alonso A, Sanz JM, Llinas RR (1992) Afferent projections to the mammillary complex of the rat, with special reference to those from surrounding hypothalamic regions. J Comp Neurol 321(2):277–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903210208
Goto M, Swanson LW, Canteras NS (2001) Connections of the nucleus incertus. J Comp Neurol 438(1):86–122
Gray TS, Magnuson DJ (1987) Neuropeptide neuronal efferents from the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and central amygdaloid nucleus to the dorsal vagal complex in the rat. J Comp Neurol 262(3):365–374. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902620304
Gritti I, Mainville L, Mancia M, Jones BE (1997) GABAergic and other noncholinergic basal forebrain neurons, together with cholinergic neurons, project to the mesocortex and isocortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol 383(2):163–177
Gritti I, Henny P, Galloni F, Mainville L, Mariotti M, Jones BE (2006) Stereological estimates of the basal forebrain cell population in the rat, including neurons containing choline acetyltransferase, glutamic acid decarboxylase or phosphate-activated glutaminase and colocalizing vesicular glutamate transporters. Neuroscience 143(4):1051–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.024
Grove EA (1988a) Efferent connections of the substantia innominata in the rat. J Comp Neurol 277(3):347–364
Grove EA (1988b) Neural associations of the substantia innominata in the rat: afferent connections. J Comp Neurol 277(3):315–346. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902770302
Haber SN, Nauta WJ (1983) Ramifications of the globus pallidus in the rat as indicated by patterns of immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience 9(2):245–260
Haglund L, Swanson LW, Kohler C (1984) The projection of the supramammillary nucleus to the hippocampal formation: an immunohistochemical and anterograde transport study with the lectin PHA-L in the rat. J Comp Neurol 229(2):171–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902290204
Halassa MM, Siegle JH, Ritt JT, Ting JT, Feng G, Moore CI (2011) Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts and cortical spindles. Nat Neurosci 14(9):1118–1120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2880
Halassa MM, Chen Z, Wimmer RD, Brunetti PM, Zhao S, Zikopoulos B, Wang F, Brown EN, Wilson MA (2014) State-dependent architecture of thalamic reticular subnetworks. Cell 158(4):808–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.025
Han Y, Shi YF, Xi W, Zhou R, Tan ZB, Wang H, Li XM, Chen Z, Feng G, Luo M, Huang ZL, Duan S, Yu YQ (2014) Selective activation of cholinergic basal forebrain neurons induces immediate sleep-wake transitions. Curr Biol 24(6):693–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.02.011
Han S, Soleiman MT, Soden ME, Zweifel LS, Palmiter RD (2015) Elucidating an affective pain circuit that creates a threat memory. Cell 162(2):363–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.057
Harkany T, Hartig W, Berghuis P, Dobszay MB, Zilberter Y, Edwards RH, Mackie K, Ernfors P (2003) Complementary distribution of type 1 cannabinoid receptors and vesicular glutamate transporter 3 in basal forebrain suggests input-specific retrograde signalling by cholinergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18(7):1979–1992
Hasue RH, Shammah-Lagnado SJ (2002) Origin of the dopaminergic innervation of the central extended amygdala and accumbens shell: a combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemical study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 454(1):15–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10420
Hedreen JC, Struble RG, Whitehouse PJ, Price DL (1984) Topography of the magnocellular basal forebrain system in human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43(1):1–21
Heimer L, Wilson RD (1975) The subcortical projections of the allocortex: similarities in the neural associations of the hippocampus, the piriform cortex, and the neocortex. In: M. Santini (ed) Golgi Centennial Symposium, Raven Press, New York, pp 177–193
Heimer L, Harlan RE, Alheid GF, Garcia MM, de Olmos J (1997) Substantia innominata: a notion which impedes clinical-anatomical correlations in neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuroscience 76(4):957–1006
Henny P, Jones BE (2006a) Innervation of orexin/hypocretin neurons by GABAergic, glutamatergic or cholinergic basal forebrain terminals evidenced by immunostaining for presynaptic vesicular transporter and postsynaptic scaffolding proteins. J Comp Neurol 499(4):645–661. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21131
Henny P, Jones BE (2006b) Vesicular glutamate (VGlut), GABA (VGAT), and acetylcholine (VACht) transporters in basal forebrain axon terminals innervating the lateral hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 496(4):453–467. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20928
Herbert H, Moga MM, Saper CB (1990) Connections of the parabrachial nucleus with the nucleus of the solitary tract and the medullary reticular formation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 293(4):540–580
Herkenham M, Nauta WJ (1977) Afferent connections of the habenular nuclei in the rat. A horseradish peroxidase study, with a note on the fiber-of-passage problem. J Comp Neurol 173(1):123–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901730107
Higley MJ, Gittis AH, Oldenburg IA, Balthasar N, Seal RP, Edwards RH, Lowell BB, Kreitzer AC, Sabatini BL (2011) Cholinergic interneurons mediate fast VGluT3-dependent glutamatergic transmission in the striatum. PLoS One 6(4):e19155. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019155
Hikosaka O (2010) The habenula: from stress evasion to value-based decision-making. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(7):503–513. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2866
Hong S, Jhou TC, Smith M, Saleem KS, Hikosaka O (2011) Negative reward signals from the lateral habenula to dopamine neurons are mediated by rostromedial tegmental nucleus in primates. J Neurosci 31(32):11457–11471. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1384-11.2011
Hopkins DA, Holstege G (1978) Amygdaloid projections to the mesencephalon, pons and medulla oblongata in the cat. Exp Brain Res 32(4):529–547
Hur EE, Zaborszky L (2005) Vglut2 afferents to the medial prefrontal and primary somatosensory cortices: a combined retrograde tracing in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol 483(3):351–373. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20444
Irmak SO, de Lecea L (2014) Basal forebrain cholinergic modulation of sleep transitions. Sleep 37(12):1941–1951. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.4246
Jhou TC, Geisler S, Marinelli M, Degarmo BA, Zahm DS (2009a) The mesopontine rostromedial tegmental nucleus: a structure targeted by the lateral habenula that projects to the ventral tegmental area of Tsai and substantia nigra compacta. J Comp Neurol 513(6):566–596. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21891
Jhou TC, Fields HL, Baxter MG, Saper CB, Holland PC (2009b) The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), a GABAergic afferent to midbrain dopamine neurons, encodes aversive stimuli and inhibits motor responses. Neuron 61(5):786–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.02.001
Jones BE (2004) Activity, modulation and role of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons innervating the cerebral cortex. Prog Brain Res 145:157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(03)45011-5
Jourdain A, Semba K, Fibiger HC (1989) Basal forebrain and mesopontine tegmental projections to the reticular thalamic nucleus: an axonal collateralization and immunohistochemical study in the rat. Brain Res 505(1):55–65
Kaur S, Wang JL, Ferrari L, Thankachan S, Kroeger D, Venner A, Lazarus M, Wellman A, Arrigoni E, Fuller PM, Saper CB (2017) A genetically defined circuit for arousal from sleep during hypercapnia. Neuron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.10.009
Kirk IJ, McNaughton N (1991) Supramammillary cell firing and hippocampal rhythmical slow activity. Neuroreport 2(11):723–725
Kocsis B, Vertes RP (1994) Characterization of neurons of the supramammillary nucleus and mammillary body that discharge rhythmically with the hippocampal theta rhythm in the rat. J Neurosci 14(11 Pt 2):7040–7052
Kolmac C, Mitrofanis J (1999) Organization of the basal forebrain projection to the thalamus in rats. Neurosci Lett 272(3):151–154
Lee MG, Hassani OK, Jones BE (2005) Discharge of identified orexin/hypocretin neurons across the sleep-waking cycle. J Neurosci 25(28):6716–6720. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1887-05.2005
Lin SC, Nicolelis MA (2008) Neuronal ensemble bursting in the basal forebrain encodes salience irrespective of valence. Neuron 59(1):138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.031
Lin SC, Brown RE, Hussain Shuler MG, Petersen CC, Kepecs A (2015) Optogenetic dissection of the basal forebrain neuromodulatory control of cortical activation, plasticity, and cognition. J Neurosci 35(41):13896–13903. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2590-15.2015
Lu J, Sherman D, Devor M, Saper CB (2006) A putative flip-flop switch for control of REM sleep. Nature 441(7093):589–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04767
Mahoney CE, Agostinelli LJ, Brooks JN, Lowell BB, Scammell TE (2017) GABAergic neurons of the central amygdala promote cataplexy. J Neurosci 37(15):3995–4006. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4065-15.2017
Martinez V, Parikh V, Sarter M (2005) Sensitized attentional performance and Fos-immunoreactive cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain of amphetamine-pretreated rats. Biol Psychiatry 57(10):1138–1146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.02.005
Matsumoto M, Hikosaka O (2007) Lateral habenula as a source of negative reward signals in dopamine neurons. Nature 447(7148):1111–1115. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05860
Mayse JD, Nelson GM, Avila I, Gallagher M, Lin SC (2015) Basal forebrain neuronal inhibition enables rapid behavioral stopping. Nat Neurosci 18(10):1501–1508. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4110
McDonald AJ, Mascagni F (2010) Neuronal localization of m1 muscarinic receptor immunoreactivity in the rat basolateral amygdala. Brain Struct Funct 215(1):37–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0272-y
Mileykovskiy BY, Kiyashchenko LI, Siegel JM (2005) Behavioral correlates of activity in identified hypocretin/orexin neurons. Neuron 46(5):787–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.04.035
Miller RL, Knuepfer MM, Wang MH, Denny GO, Gray PA, Loewy AD (2012) Fos-activation of FoxP2 and Lmx1b neurons in the parabrachial nucleus evoked by hypotension and hypertension in conscious rats. Neuroscience 218:110–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.05.049
Milner TA, Joh TH, Pickel VM (1986) Tyrosine hydroxylase in the rat parabrachial region: ultrastructural localization and extrinsic sources of immunoreactivity. J Neurosci 6(9):2585–2603
Moga MM, Herbert H, Hurley KM, Yasui Y, Gray TS, Saper CB (1990) Organization of cortical, basal forebrain, and hypothalamic afferents to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 295(4):624–661. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902950408
Nickerson Poulin A, Guerci A, El Mestikawy S, Semba K (2006) Vesicular glutamate transporter 3 immunoreactivity is present in cholinergic basal forebrain neurons projecting to the basolateral amygdala in rat. J Comp Neurol 498(5):690–711. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21081
Nunez A, Cervera-Ferri A, Olucha-Bordonau F, Ruiz-Torner A, Teruel V (2006) Nucleus incertus contribution to hippocampal theta rhythm generation. Eur J Neurosci 23(10):2731–2738. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04797.x
Olszewski J, Baxter DW (1953) Cytoarchitecture of the human brain stem. Anat Rec 115(2):435–435
Palmiter RD (2018) The parabrachial nucleus: CGRP neurons function as a general alarm. Trends Neurosci 41(5):280–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2018.03.007
Papez J (1937) A proposed mechanism of emotion. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 38:725–743
Pedersen NP, Ferrari L, Venner A, Wang JL, Abbott SBG, Vujovic N, Arrigoni E, Saper CB, Fuller PM (2017) Supramammillary glutamate neurons are a key node of the arousal system. Nat Commun 8(1):1405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01004-6
Petrovich GD, Swanson LW (1997) Projections from the lateral part of the central amygdalar nucleus to the postulated fear conditioning circuit. Brain Res 763(2):247–254
Pinto L, Goard MJ, Estandian D, Xu M, Kwan AC, Lee SH, Harrison TC, Feng G, Dan Y (2013) Fast modulation of visual perception by basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Nat Neurosci 16(12):1857–1863. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3552
Price JL, Amaral DG (1981) An autoradiographic study of the projections of the central nucleus of the monkey amygdala. J Neurosci 1(11):1242–1259
Price JL, Stern R (1983) Individual cells in the nucleus basalis–diagonal band complex have restricted axonal projections to the cerebral cortex in the rat. Brain Res 269(2):352–356
Qin C, Luo M (2009) Neurochemical phenotypes of the afferent and efferent projections of the mouse medial habenula. Neuroscience 161(3):827–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.085
Risold PY, Swanson LW (1997) Connections of the rat lateral septal complex. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 24(2–3):115–195
Rizvi TA, Ennis M, Behbehani MM, Shipley MT (1991) Connections between the central nucleus of the amygdala and the midbrain periaqueductal gray: topography and reciprocity. J Comp Neurol 303(1):121–131. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903030111
Rossi J, Balthasar N, Olson D, Scott M, Berglund E, Lee CE, Choi MJ, Lauzon D, Lowell BB, Elmquist JK (2011) Melanocortin-4 receptors expressed by cholinergic neurons regulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab 13(2):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.01.010
Rye DB, Wainer BH, Mesulam MM, Mufson EJ, Saper CB (1984) Cortical projections arising from the basal forebrain: a study of cholinergic and noncholinergic components employing combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase. Neuroscience 13(3):627–643
Rye DB, Saper CB, Lee HJ, Wainer BH (1987) Pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus of the rat: cytoarchitecture, cytochemistry, and some extrapyramidal connections of the mesopontine tegmentum. J Comp Neurol 259(4):483–528. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902590403
Saper CB (1984) Organization of cerebral cortical afferent systems in the rat. II. Magnocellular basal nucleus. J Comp Neurol 222(3):313–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902220302
Saper CB (2016) The house alarm. Cell Metab 23(5):754–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.021
Scammell T, Gerashchenko D, Urade Y, Onoe H, Saper C, Hayaishi O (1998) Activation of ventrolateral preoptic neurons by the somnogen prostaglandin D2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(13):7754–7759
Schwaber JS, Rogers WT, Satoh K, Fibiger HC (1987) Distribution and organization of cholinergic neurons in the rat forebrain demonstrated by computer-aided data acquisition and three-dimensional reconstruction. J Comp Neurol 263(3):309–325. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902630302
Semba K (2000) Multiple output pathways of the basal forebrain: organization, chemical heterogeneity, and roles in vigilance. Behav Brain Res 115(2):117–141
Shammah-Lagnado SJ, Alheid GF, Heimer L (2001) Striatal and central extended amygdala parts of the interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure: evidence from tract-tracing techniques in the rat. J Comp Neurol 439(1):104–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.1999
Shi YF, Han Y, Su YT, Yang JH, Yu YQ (2015) Silencing of cholinergic basal forebrain neurons using archaerhodopsin prolongs slow-wave sleep in mice. PLoS One 10(7):e0130130. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130130
Shibata H (1989) Descending projections to the mammillary nuclei in the rat, as studied by retrograde and anterograde transport of wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 285(4):436–452. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902850403
Swanson LW, Cowan WM (1979) The connections of the septal region in the rat. J Comp Neurol 186(4):621–655. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901860408
Swanson LW, Mogenson GJ, Gerfen CR, Robinson P (1984) Evidence for a projection from the lateral preoptic area and substantia innominata to the ‘mesencephalic locomotor region’ in the rat. Brain Res 295(1):161–178
Tokita K, Inoue T, Boughter JD Jr (2009) Afferent connections of the parabrachial nucleus in C57BL/6J mice. Neuroscience 161(2):475–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.046
Tovote P, Esposito MS, Botta P, Chaudun F, Fadok JP, Markovic M, Wolff SB, Ramakrishnan C, Fenno L, Deisseroth K, Herry C, Arber S, Luthi A (2016) Midbrain circuits for defensive behaviour. Nature 534(7606):206–212. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17996
Unal CT, Pare D, Zaborszky L (2015) Impact of basal forebrain cholinergic inputs on basolateral amygdala neurons. J Neurosci 35(2):853–863. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2706-14.2015
Veening JG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE (1984) The organization of projections from the central nucleus of the amygdala to brainstem sites involved in central autonomic regulation: a combined retrograde transport-immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 303(2):337–357
Vertes RP (2015) Major diencephalic inputs to the hippocampus: supramammillary nucleus and nucleus reuniens. Circuitry and function. Prog Brain Res 219:121–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.03.008
Vong L, Ye C, Yang Z, Choi B, Chua S Jr, Lowell BB (2011) Leptin action on GABAergic neurons prevents obesity and reduces inhibitory tone to POMC neurons. Neuron 71(1):142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.028
Voytko ML, Olton DS, Richardson RT, Gorman LK, Tobin JR, Price DL (1994) Basal forebrain lesions in monkeys disrupt attention but not learning and memory. J Neurosci 14(1):167–186
Wallace DM, Magnuson DJ, Gray TS (1992) Organization of amygdaloid projections to brainstem dopaminergic, noradrenergic, and adrenergic cell groups in the rat. Brain Res Bull 28(3):447–454
Wilkinson LS, Dias R, Thomas KL, Augood SJ, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW, Roberts AC (1997) Contrasting effects of excitotoxic lesions of the prefrontal cortex on the behavioural response to d-amphetamine and presynaptic and postsynaptic measures of striatal dopamine function in monkeys. Neuroscience 80(3):717–730
Woolf NJ, Butcher LL (1982) Cholinergic projections to the basolateral amygdala: a combined Evans Blue and acetylcholinesterase analysis. Brain Res Bull 8(6):751–763
Wyss JM, Swanson LW, Cowan WM (1979) Evidence for an input to the molecular layer and the stratum granulosum of the dentate gyrus from the supramammillary region of the hypothalamus. Anat Embryol (Berl) 156(2):165–176
Xu M, Chung S, Zhang S, Zhong P, Ma C, Chang WC, Weissbourd B, Sakai N, Luo L, Nishino S, Dan Y (2015) Basal forebrain circuit for sleep-wake control. Nat Neurosci 18(11):1641–1647. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4143
Yetnikoff L, Lavezzi HN, Reichard RA, Zahm DS (2014) An update on the connections of the ventral mesencephalic dopaminergic complex. Neuroscience 282:23–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.04.010
Yokota S, Kaur S, VanderHorst VG, Saper CB, Chamberlin NL (2015) Respiratory-related outputs of glutamatergic, hypercapnia-responsive parabrachial neurons in mice. J Comp Neurol 523(6):907–920. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23720
Yoshida K, McCormack S, Espana RA, Crocker A, Scammell TE (2006) Afferents to the orexin neurons of the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 494(5):845–861. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20859
Zaborszky L, Duque A (2003) Sleep-wake mechanisms and basal forebrain circuitry. Front Biosci 8:d1146–1169
Zahm DS, Cheng AY, Lee TJ, Ghobadi CW, Schwartz ZM, Geisler S, Parsely KP, Gruber C, Veh RW (2011) Inputs to the midbrain dopaminergic complex in the rat, with emphasis on extended amygdala-recipient sectors. J Comp Neurol 519(16):3159–3188. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.22670
Funding
NIH P01 HL095491 to TS, NIH P01 HL095491-02S1 to LJA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agostinelli, L.J., Geerling, J.C. & Scammell, T.E. Basal forebrain subcortical projections. Brain Struct Funct 224, 1097–1117 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-01820-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-01820-6