Summary
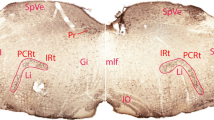
Amygdalotegmental projections were studied in 26 cats after injections of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the diencephalon, midbrain and lower brain stem and in 6 cats after injection of 3H-leucine in the amygdala. Following HRP injections in the posterior hypothalamus, periaqueductal gray (PAG) and tegmentum many retrogradely labeled neurons were present in the central nucleus (CE) of the amygdala, primarily ipsilaterally. Injections of HRP in the posterior hypothalamus and mesencephalon also resulted in the labeling of neurons in the basal nucleus, pars magnocellularis.
Following 3H-leucine injections in CE and adjacent structures autoradiographically labeled fibers were present in the stria terminalis and ventral amygdalofugal pathways. In the mesencephalon heavily labeled fiber bundles were located lateral to the red nucleus. Labeled fibers and terminals were distributed to the mesencephalic reticular formation, substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area and PAG. In the pontine and medullary tegmentum the bulk of passing fibers was located laterally in the reticular formation. Many labeled fibers and terminals were distributed to the parabrachial nuclei, locus coeruleus, nucleus subcoeruleus and lateral tegmental fields. Many terminals were also present in the solitary nucleus and dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve.
The location of the cells of origin and the distribution of the terminals of the amygdalotegmental projection suggest that this pathway plays an important role in the integration of somatic and autonomic responses associated with affective defense.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
nucleus ambiguus
- AL:
-
lateral amygdaloid nucleus
- AQ:
-
cerebral aqueduct
- BC:
-
brachium conjunctivum
- BL:
-
basal amygdaloid nucleus, pars magnocellularis
- BM:
-
basal amygdaloid nucleus, pars parvocellularis
- BP:
-
brachium pontis
- CE:
-
central amygdaloid nucleus
- CI:
-
internal capsule
- CN:
-
cochlear nucleus
- CO:
-
cortical amygdaloid nucleus
- CP:
-
cerebral peduncle
- DCN:
-
dorsal column nuclei
- DMV:
-
dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve
- E:
-
entopeduncular nucleus
- F:
-
fornix
- FLA:
-
longitudinal association bundle
- GP:
-
globus pallidus
- H:
-
hippocampal formation
- 1C:
-
inferior colliculus
- INJ:
-
injection site
- LC:
-
locus coeruleus
- IO:
-
inferior olive
- LG:
-
lateral geniculate nucleus
- LRN:
-
lateral reticular nucleus
- LT:
-
lateral tegmental field
- M:
-
medial amygdaloid nucleus
- MB:
-
mammilary body
- MG:
-
medial geniculate nucleus
- ML:
-
medial lemniscus
- MT:
-
medial tegmental field
- MV:
-
motor nucleus of the trigeminus
- OC:
-
optic chiasm
- OT:
-
optic tract
- P:
-
putamen
- PAG:
-
periaqueductal gray
- PB:
-
parabrachial nuclei
- PC:
-
posterior commissure
- PH:
-
posterior hypothalamus
- PT:
-
pyramidal tract
- PV:
-
principal sensory nucleus of the trigeminus
- PYR:
-
pyriform cortex
- R:
-
red nucleus
- RF:
-
reticular formation
- S:
-
solitary nucleus
- SC:
-
nucleus subcoeruleus
- SN:
-
substantia nigra
- SO:
-
superior olive
- SOL:
-
solitary nucleus
- SPV:
-
spinal trigeminal complex
- ST:
-
stria terminalis
- VC:
-
vestibular complex
- VTA:
-
ventral tegmental area
- VII:
-
facial nucleus
- XII:
-
hypoglossal nucleus
References
Abrahams, V.C., Hilton, S.M., Zbrozyna, A.V.: Active muscle vasodilatation produced by stimulation of the brain stem: its significance in the defence reaction. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 154, 419–513 (1960)
Bertrand, F., Hugelin, A.: Respiratory synchronizing function of nucleus parabrachialis medialis: pneumotaxic mechanisms. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 189–207 (1971)
Bonvallet, M., Gary Bobo, E.: Changes in phrenic activity and heart rate elicited by localized stimulation of amygdala and adjacent structures. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 32, 1–16 (1972)
Bunney, B.S., Aghajanian, G.K.: The precise localization of nigral afferents in the rat as determined by a retrograde tracing technique. Brain Res. 117, 423–435 (1976)
Coote, J.H., Hilton, S.M., Zbrozyna, A.W.: The pontomedullary area integrating the defence reaction in the cat and its influence on muscle blood flow. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 229, 257–274 (1973)
Cottle, M.K.W., Calaresu, F.R.: Projections from the nucleus and tractus solitarius in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 161, 143–158 (1975)
Cowan, W.M., Gottlieb, D.I., Hendrickson, A.E., Price, J.L., Woolsey, T.A.: The autoradiographic demonstration of axonal connections in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 37, 21–51 (1972)
Cowan, W.M., Raisman, G., Powell, T.P.S.: The connexions of the amygdala. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 28, 137–151 (1965)
de Olmos, J.S.: The amygdaloid projection field in the rat as studied with the cupric-silver method. In: The Neurobiology of the Amygdala (ed. B.E. Eleftheriou), pp. 145–204. New York: Plenum Press 1972
de Olmos, J.S., Ingram, W.R.: The projection field of the stria terminalis in the rat brain. An experimental study. J. comp. Neurol. 146, 303–334 (1972)
Elde, R., Hökfelt, T., Johansson, O., Terenius, L.: Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-encephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience 1, 349–351 (1976)
Euler, C. von, Hayward, J.N., Marttila, I., Wyman, R.J.: Respiratory neurones of the ventrolateral nucleus of the solitary tract of cat: vagal input, spinal connections and morphological identification. Brain Res. 61, 1–22 (1973)
Fernandez de Molina, A., Hunsperger, R.W.: Central representation of affective reactions in forebrain and brainstem: electrical stimulation of amygdala, stria terminalis, and adjacent structures. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 145, 251–269 (1959)
Fernandez de Molina, A., Hunsperger, R.W.: Organization of the subcortical system governing defence and flight reactions in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 200–213 (1962)
Fox, C.A.: Certain basal telencephalic centers in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 72, 1–62 (1940)
Gloor, P.: Electrophysiological studies on the connections of the amygdaloid nucleus in the cat. Part I: The neural organization of the amygdaloid projection system. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 7, 223–242 (1955)
Gloor, P.: The pattern of conduction of amygdaloid seizure discharge. An experimental study in the cat. A.M.A. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 77, 247–258 (1957)
Gloor, P.: Amygdala. In: Handbook of Physiology, Section I: Neurophysiology, Vol. II (eds. J. Field, H.W. Magoun, V.E. Hall), pp. 1395–1420. Washington: American Physiological Society 1960
Goddard, G.V.: Functions of the amygdala. Psychol. Bull. 62, 89–109 (1964)
Goddard, G.V.: Prologue. In: The Neurobiology of the Amygdala (ed. B.E. Eleftheriou), pp. 11–18. New York: Plenum Press 1972
Graham, R.C., Karnovsky, M.J.: The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 291–302 (1966)
Gunn, C.G., Sevelius, G., Puiggari, M.J., Myers, F.K.: Vagal cardiomotor mechanisms in the hindbrain of the dog and cat. Amer. J. Physiol. 214, 258–262 (1968)
Hall, E.: Efferent connections of the basal and lateral nuclei of the amygdala in the cat. Amer. J. Anat. 113, 139–151 (1963)
Hall, E.: Some aspects of the structural organization of the amygdala. In: The Neurobiology of the Amygdala (ed. B.E. Eleftheriou), pp. 95–121. New York: Plenum Press 1972
Heimer, L., Nauta, W.J.H.: The hypothalamic distribution of the stria terminalis in the rat. Brain Res. 13, 284–297 (1969)
Hendrickson, A., Moe, L., Noble, B.: Staining for autoradiography of the central nervous system. Stain Technol. 47, 283–290 (1972)
Hilton, S.M., Zbrozyna, A.W.: Amygdaloid region for defence reactions and its efferent pathway to the brain stem. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 165, 160–173 (1963)
Holstege, G., Kuypers, H.G.J.M., Dekker, J.J.: The organization of the bulbar fibre connections to the trigeminal, facial and hypoglossal motor nuclei. II. An autoradiographic tracing study in cat. Brain 100, 265–286 (1977)
Hopkins, D.A.: Amygdalotegmental projections in the rat, cat and rhesus monkey. Neurosci. Letters 1, 263–270 (1975)
Hopkins, D.A.: Basal ganglia projections to the brain stem in the rat, cat and monkey. In: Parkinson's Disease — Concepts and Prospects (eds. J.P.W.F. Lakke, J. Korf and H. Wesseling), pp. 11–24. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica 1977
Hopkins, D.A., Holstege, G.: Central amygdaloid nucleus projections to the lower brain stem in the cat. A horseradish peroxidase and autoradiographic study. Anat. Rec. 184, 432 (1976)
Hopkins, D.A., Niessen, L.W.: Substantia nigra projections to the reticular formation, superior colliculus and central gray in the rat, cat and monkey. Neurosci. Letters, 2, 253–259 (1976)
Hunsperger, R.W.: Affektreaktionen auf elektrische Reizung im Hirnstamm der Katze. Helv. physiol. Acta 14, 70–92 (1956)
Jacquet, Y.F., Lajtha, A.: Paradoxical effects after microinjection of morphine in the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. Science 185, 1055–1057 (1974)
Kaada, B.R.: Stimulation and regional ablation of the amygdaloid complex with reference to functional representation. In: The Neurobiology of the Amygdala (ed. B.E. Eleftheriou), pp. 205–281. New York: Plenum Press 1972
Kerr, F.W.L.: Preserved vagal visceromotor function following destruction of the dorsal motor nucleus. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 202, 755–769 (1969)
Klingler, J., Gloor, P.: The connections of the amygdala and of the anterior temporal cortex in the human brain. J. comp. Neurol. 115, 333–369 (1960)
Kuhar, M.J., Pert, C.B., Snyder, S.H.: Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature (Lond.) 245, 447–450 (1973)
Kuypers, H.G.J.M., Lawrence, D.G.: Cortical projections to the red nucleus and the brain stem in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 4, 151–188 (1967)
Kuypers, H.G.J.M., Maisky, V.A.: Retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase from spinal cord to brain stem cell groups in the cat. Neurosci. Letters 1, 9–14 (1975)
Leonard, C.M., Scott, J.W.: Origin and distribution of the amygdalofugal pathways in the rat: An experimental neuroanatomical study. J. comp. Neurol. 141, 313–330 (1971)
Loo, Y.T.: The forebrain of the opossum, Didelphis virginiana. Part II. Histology. J. comp. Neurol. 52, 1–148 (1931)
Mayer, D.J., Price, D.D.: Central nervous system mechanisms of analgesia. Pain 2, 379–404 (1976)
McBride, R.L., Sutin, J.: Projections of the locus coeruleus and adjacent pontine tegmentum in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 165, 265–284 (1976)
Meessen, H., Olsewski, J.: Cytoarchitektonischer Atlas der Rautenhirn des Kaninchens. Basel: Karger 1949
Mehler, W.R.: Some neurological species differences — a posteriori. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 167, 424–468 (1969)
Morest, D.K.: Experimental study of the projections of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius and the area postrema in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 130, 277–300 (1967)
Morin, G., Naquet, R., Badier, M.: Stimulation électrique de la région amygdalienne et pression arterielle chez le chat. J. Physiol. (Paris) 44, 303–305 (1952)
Nauta, W.J.H.: Hippocampal projections and related neural pathways to the mid-brain in the cat. Brain 81, 319–340 (1958)
Nauta, W.J.H.: Fibre degeneration following lesions of the amygdaloid complex in the monkey. J. Anat. (Lond.) 95, 515–531 (1961)
Nauta, W.J.H., Mehler, W.R.: Projections of the lentiform nucleus in the monkey. Brain Res. 1, 3–42 (1966)
Norgren, R.: Taste pathways to hypothalamus and amygdala. J. comp. Neurol. 166, 17–30 (1976)
Oliveras, J.L., Besson, J.M., Guilbaud, G., Liebeskind, J.C.: Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence of pain inhibition from midbrain stimulation in the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 20, 32–44 (1974)
Saper, C.B., Loewy, A.D., Swanson, L.W., Cowan, W.M.: Direct hypothalamo-autonomic connections. Brain Res. 117, 305–312 (1976a)
Saper, C.B., Swanson, L.W., Cowan, W.M.: The efferent connections of the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus of the rat. J. comp. Neurol. 169, 409–442 (1976b)
Swanson, L.W., Hartman, B.K.: The central adrenergic system. An immunofluorescence study of the location of cell bodies and their efferent connections in the rat utilizing dopamine-β-hydroxylase as a marker. J. comp. Neurol. 163, 467–506 (1975)
Urca, G., Frenk, H., Liebeskind, J.C., Taylor, A.N.: Morphine and encephalin: analgesic and epileptic properties. Science 197, 83–86 (1977)
Valverde, F.: Studies on the Piriform Lobe. Cambridge: Harvard University Press 1965
Yaksh, T.L., Yeung, J.C., Rudy, T.A.: Systematic examination in the rat of brain sites sensitive to the direct application of morphine: observation of differential effects within the periaqueductal gray. Brain Res. 114, 83–103 (1976)
Zeier, H., Karten, H.J.: The archistriatum of the pigeon: organization of afferent and efferent connections. Brain Res. 31, 313–326 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hopkins, D.A., Holstege, G. Amygdaloid projections to the mesencephalon, pons and medulla oblongata in the cat. Exp Brain Res 32, 529–547 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239551
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239551