Abstract
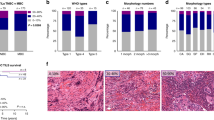
Both stromal tumor–infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) affect responses to immunotherapy; however, the extent of sTIL and PD-L1 expression within various metaplastic components in metaplastic breast carcinoma (MBC), which are critical for the characterization of immune microenvironments, remains unreported. We profiled sTIL infiltration and PD-L1 expression in different metaplastic components of specimens from 82 MBC patients. The overall positivity for high or intermediate (H/I) sTIL, immune cell-PD-L1 (IcPD-L1), and tumor cell-PD-L1 (TcPD-L1) was 34.1%, 47.6%, and 17.1%, respectively, but differences specific to MBC subtypes and each metaplastic component existed. Squamous cell carcinoma exhibited the highest positivity rates of sTIL(H/I) (50.0%) and IcPD-L1 (66.7%), while matrix-producing carcinoma had the lowest respective rates (14.3% and 28.6%). The positivity rates of sTIL(H/I) and IcPD-L1 were the highest in squamous component (Sq) and the lowest in chondroid component (Ch). All cases that had discordant sTIL categories between carcinoma of no special type (NST) and metaplastic components showed sTIL(H/I) positivity higher in Sq, but lower in spindled component (Sp) and Ch. While there was no pattern of higher IcPD-L1-positivity in Sp, six of the seven cases that were TcPD-L1-discordant between NST and Sp were TcPD-L1-positive in Sp, suggesting a trend for higher TcPD-L1 in Sp. The diagnostic predictability of total tumor IcPD-L1 positivity based on IcPD-L1 positivity in Sq and Ch was 95.2% and 33.3%, respectively. Multivariate analysis showed that sTIL(H/I) positivity, but not PD-L1 positivity, correlated with better survival. Our data implicate distinct immune microenvironments in different metaplastic components in MBC, which may have immunopathologic, diagnostic, and therapeutic significance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pezzi CM, Patel-Parekh L, Cole K, Franko J, Klimberg VS, Bland K (2007) Characteristics and treatment of metaplastic breast cancer: analysis of 892 cases from the National Cancer Data Base. Ann Surg Oncol 14:166–173
Aydiner A, Sen F, Tambas M, Ciftci R, Eralp Y, Saip P, Karanlik H, Fayda M, Kucucuk S, onder S, Yavuz E, Muslumanoglu M, Igci A (2015) Metaplastic breast carcinoma versus triple-negative breast cancer: survival and response to treatment. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e2341
Rayson D, Adjei AA, Suman VJ, Wold LE, Ingle JN (1999) Metaplastic breast cancer: prognosis and response to systemic therapy. Ann Oncol 10:413–419
Stanton SE, Adams S, Disis ML (2016) Variation in the incidence and magnitude of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer subtypes: a systematic review. JAMA Oncol 2:1354–1360
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Darb-Esfahani S, Lederer B, Heppner BI, Weber KE, Budczies J, Huober J, Klauschen F, Furlanetto J, Schmitt WD, Blohmer JU, Karn T, Pfitzner BM, Kümmel S, Engels K, Schneeweiss A, Hartmann A, Noske A, Fasching PA, Jackisch C, van Mackelenbergh M, Sinn P, Schem C, Hanusch C, Untch M, Loibl S (2018) Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: a pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol 19:40–50
Loibl S, Untch M, Burchardi N, Huober J, Sinn BV, Blohmer JU, Grischke EM, Furlanetto J, Tesch H, Hanusch C, Engels K, Rezai M, Jackisch C, Schmitt WD, von Minckwitz G, Thomalla J, Kümmel S, Rautenberg B, Fasching PA, Weber K, Rhiem K, Denkert C, Schneeweiss A (2019) A randomised phase II study investigating durvalumab in addition to an anthracycline taxane-based neoadjuvant therapy in early triple-negative breast cancer: clinical results and biomarker analysis of GeparNuevo study. Ann Oncol 30:1279–1288
Gonzalez-Ericsson PI, Stovgaard ES, Sua LF, Reisenbichler E, Kos Z, Carter JM, Michiels S, le Quesne J, Nielsen TO, Lænkholm AV, Fox SB, Adam J, Bartlett JMS, Rimm DL, Quinn C, Peeters D, Dieci MV, Vincent-Salomon A, Cree I, Hida AI, Balko JM, Haynes HR, Frahm I, Acosta-Haab G, Balancin M, Bellolio E, Yang W, Kirtani P, Sugie T, Ehinger A, Castaneda CA, Kok M, McArthur H, Siziopikou K, Badve S, Fineberg S, Gown A, Viale G, Schnitt SJ, Pruneri G, Penault-Llorca F, Hewitt S, Thompson EA, Allison KH, Symmans WF, Bellizzi AM, Brogi E, Moore DA, Larsimont D, Dillon DA, Lazar A, Lien H, Goetz MP, Broeckx G, el Bairi K, Harbeck N, Cimino-Mathews A, Sotiriou C, Adams S, Liu SW, Loibl S, Chen IC, Lakhani SR, Juco JW, Denkert C, Blackley EF, Demaria S, Leon-Ferre R, Gluz O, Zardavas D, Emancipator K, Ely S, Loi S, Salgado R, Sanders M, International Immuno‐Oncology Biomarker Working Group (2020) The path to a better biomarker: application of a risk management framework for the implementation of PD-L1 and TILs as immuno-oncology biomarkers into breast cancer clinical trials and daily practice. J Pathol 250:667–684
Schmid P, Chui SY, Emens LA (2019) Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. Reply. N Engl J Med 380:987–988
Joneja U, Vranic S, Swensen J, Feldman R, Chen W, Kimbrough J, Xiao N, Reddy S, Palazzo J, Gatalica Z (2017) Comprehensive profiling of metaplastic breast carcinomas reveals frequent overexpression of programmed death-ligand 1. J Clin Pathol 70:255–259
Gonzalez-Martinez S, Perez-Mies B, Carretero-Barrio I, Palacios-Berraquero ML, Perez-Garcia J, Cortes J, Palacios J (2020) Molecular features of metaplastic breast carcinoma: an infrequent subtype of triple negative breast carcinoma. Cancers (Basel):12(7)
Tray N, Taff J, Singh B, Suh J, Ngo N, Kwa M, Troxel AB, Chae YK, Kurzrock R, Patel SP, Sharon E, Denkert C, Ross JS, Adams S (2019) Metaplastic breast cancers: genomic profiling, mutational burden and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Breast 44:29–32
Alsuliman A, Colak D, Al-Harazi O, Fitwi H, Tulbah A, Al-Tweigeri T, Al-Alwan M, Ghebeh H (2015) Bidirectional crosstalk between PD-L1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition: significance in claudin-low breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 14:149
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, Wienert S, van den Eynden G, Baehner FL, Penault-Llorca F, Perez EA, Thompson EA, Symmans WF, Richardson AL, Brock J, Criscitiello C, Bailey H, Ignatiadis M, Floris G, Sparano J, Kos Z, Nielsen T, Rimm DL, Allison KH, Reis-Filho JS, Loibl S, Sotiriou C, Viale G, Badve S, Adams S, Willard-Gallo K, Loi S, International TILs Working Group 2014 (2015) The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann Oncol 26:259–271
Dill EA, Gru AA, Atkins KA, Friedman LA, Moore ME, Bullock TN, Cross JV, Dillon PM, Mills AM (2017) PD-L1 expression and Intratumoral heterogeneity across breast cancer subtypes and stages: an assessment of 245 primary and 40 metastatic tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 41:334–342
Afkhami M, Schmolze D, Yost SE, Frankel PH, Dagis A, Amanam IU, Telatar M, Nguyen K, Yu KW, Luu T, Pillai R, Aoun PA, Mortimer J, Yuan Y (2019) Mutation and immune profiling of metaplastic breast cancer: correlation with survival. PLoS One 14:e0224726
Chao X, Liu L, Sun P, Yang X, Li M, Luo R, Huang Y, He J, Yun J (2020) Immune parameters associated with survival in metaplastic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 22:92
Kalaw E, Lim M, Kutasovic JR, Sokolova A, Taege L, Johnstone K, Bennett J, Saunus JM, Niland C, Ferguson K, Gresshoff I, Bettington M, Pathmanathan N, Tse GM, Papadimos D, Pathmanathan R, Harris G, Yamaguchi R, Tan PH, Fox S, O’Toole SA, Simpson PT, Lakhani SR, McCart Reed AE (2020) Metaplastic breast cancers frequently express immune checkpoint markers FOXP3 and PD-L1. Br J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01065-3
Hendry S, Salgado R, Gevaert T et al (2017) Assessing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in solid tumors: a practical review for pathologists and proposal for a standardized method from the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 2: TILs in Melanoma, Gastrointestinal Tract Carcinomas, Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Mesothelioma, Endometrial and Ovarian Carcinomas, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Genitourinary Carcinomas, and Primary Brain Tumors. Adv Anat Pathol 24:311–335
Adams S, Othus M, Patel SP et al (2020) Dual anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 blockade in metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: Dart (SWOG S1609, Cohort
Allison KHBE, Ellis IO, Fox SB, Lakhani SR, Lax SF, Sahin A, Salgado R, Sapino A, Sasano H, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, Thompson LDR, van Diest PJ (2019) Epithelial tumours of the breast. In: WHO Classification of Tumours Breast Tumours, 5th edn. IRAC, Lyon, p 136
Krings G, Chen YY (2018) Genomic profiling of metaplastic breast carcinomas reveals genetic heterogeneity and relationship to ductal carcinoma. Mod Pathol 31:1661–1674
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Kawakami F, Sircar K, Rodriguez-Canales J, Fellman BM, Urbauer DL, Tamboli P, Tannir NM, Jonasch E, Wistuba II, Wood CG, Karam JA (2017) Programmed cell death ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte status in patients with renal cell carcinoma and sarcomatoid dedifferentiation. Cancer 123:4823–4831
Kim S, Kim MY, Koh J, Go H, Lee DS, Jeon YK, Chung DH (2015) Programmed death-1 ligand 1 and 2 are highly expressed in pleomorphic carcinomas of the lung: comparison of sarcomatous and carcinomatous areas. Eur J Cancer 51:2698–2707
Vranic S, Stafford P, Palazzo J, Skenderi F, Swensen J, Xiu J, Spetzler D, Gatalica Z (2020) Molecular profiling of the metaplastic spindle cell carcinoma of the breast reveals potentially targetable biomarkers. Clin Breast Cancer 20(326–331):e321
Loi S, Drubay D, Adams S, Pruneri G, Francis PA, Lacroix-Triki M, Joensuu H, Dieci MV, Badve S, Demaria S, Gray R, Munzone E, Lemonnier J, Sotiriou C, Piccart MJ, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Vingiani A, Gray K, Andre F, Denkert C, Salgado R, Michiels S (2019) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis: a pooled individual patient analysis of early-stage triple-negative breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 37:559–569
Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN, Martino S, Wang M, Jones VE, Saphner TJ, Wolff AC, Wood WC, Davidson NE, Sledge GW, Sparano JA, Badve SS (2014) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J Clin Oncol 32:2959–2966
Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R, Viale G, van Eenoo F, Rouas G, Francis P, Crown JPA, Hitre E, de Azambuja E, Quinaux E, di Leo A, Michiels S, Piccart MJ, Sotiriou C (2013) Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J Clin Oncol 31:860–867
Mori H, Kubo M, Yamaguchi R, Nishimura R, Osako T, Arima N, Okumura Y, Okido M, Yamada M, Kai M, Kishimoto J, Oda Y, Nakamura M (2017) The combination of PD-L1 expression and decreased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with a poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 8:15584–15592
Tomioka N, Azuma M, Ikarashi M, Yamamoto M, Sato M, Watanabe KI, Yamashiro K, Takahashi M (2018) The therapeutic candidate for immune checkpoint inhibitors elucidated by the status of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Breast Cancer 25:34–42
Chen IC, Lin CH, Huang CS, Lien HC, Hsu C, Kuo WH, Lu YS, Cheng AL (2011) Lack of efficacy to systemic chemotherapy for treatment of metaplastic carcinoma of the breast in the modern era. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130:345–351
Adams S (2017) Dramatic response of metaplastic breast cancer to chemo-immunotherapy. NPJ Breast Cancer 3:8
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science Council Grant NSC 108-2320-B-002-061.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HCL and YSL: conception and design of the work, analysis and interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript. HCL, YHL, and YTL: interpretation of sections. ICC, CHL, TWWC, and YSL: collection and evaluation of clinical data. HCL, YHL, ICC, CHL, TWWC, YTL, and YSL read, edited, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the institutional review board of the National Taiwan University Hospital (202004007RIN). Samples were used in accordance with ethical guidelines for the use of retrospective tissue samples provided by the institutional review board of the National Taiwan University Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lien, HC., Lee, YH., Chen, IC. et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte abundance and programmed death-ligand 1 expression in metaplastic breast carcinoma: implications for distinct immune microenvironments in different metaplastic components. Virchows Arch 478, 669–678 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-020-02954-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-020-02954-x