Abstract
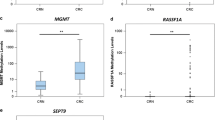
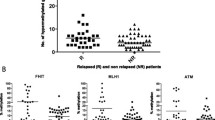
Methylation-specific multiple ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA) is a fast, new, inexpensive method that has rarely been exploited in DNA methylation profiling of colorectal cancers (CRCs). The aim of this study was to test the diagnostic utility of MS-MLPA to evaluate the methylation status of 34 genes in normal colonic mucosa samples and in a well-characterized series of 83 adenocarcinomas and 21 neuroendocrine carcinomas of colon–rectum. Two commercial MS-MLPA kits (SALSA MS-MLPA ME001-C1 Tumor suppressor-1 Kit and SALSA MS-MLPA ME002-B1 Tumor suppressor-2 Kit) were used to perform promoter methylation analysis on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues. MS-MLPA analysis was validated by bisulfite pyrosequencing, bisulfite cycle sequencing, and methylation-specific PCR. MS-MLPA analysis identified a subset of 27 CRCs (26 % of cases) showing high levels of gene methylation involving a mean percentage of 34 % of the promoters examined. These tumors exhibited all the main clinicopathological and genetic features described for CRCs with CpG island Methylator Phenotype-High. High levels of methylation were observed with similar frequency in adenocarcinomas and in neuroendocrine carcinomas (25 % versus 29 %, respectively), but different methylation profiles were observed in the two tumor types. In both groups, tumors with microsatellite instability and widespread methylation represented a homogeneous clinicopathological entity. MS-MLPA assay is an easy and reliable system for epigenetic characterization of tumor tissues and leads to a rapid identification of CRCs with the highest levels of gene methylation. Aberrant gene methylation is a common abnormality in CRC initiation and may be observed in tumors with very different genetic and clinicopathological profiles.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinoue T, Weisenberger DJ, Lange CP, Shen H, Byun HM, Van Den Berg D, Malik S, Pan F, Noushmehr H, van Dijk CM, Tollenaar RA, Laird PW (2012) Genome-scale analysis of aberrant DNA methylation in colorectal cancer. Genome Res 22:271–282
Xu Y, Hu B, Choi AJ, Gopalan B, Lee BH, Kalady MF, Church JM, Ting AH (2012) Unique DNA methylome profiles in CpG island methylator phenotype colon cancers. Genome Res 22:283–291
Curtin K, Slattery ML, Samowitz WS (2011) CpG island methylation in colorectal cancer: past, present and future. Patholog Res Int. doi:10.4061/2011/902674
Shen L, Catalano PJ, Benson AB 3rd, O’Dwyer P, Hamilton SR, Issa JP (2007) Association between DNA methylation and shortened survival in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with 5-fluorouracil based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:6093–6098
Barault L, Charon-Barra C, Jooste V, de la Vega MF, Martin L, Roignot P, Rat P, Bouvier AM, Laurent-Puig P, Faivre J, Chapusot C, Piard F (2008) Hypermethylator phenotype in sporadic colon cancer: study on a population-based series of 582 cases. Cancer Res 68:8541–8546
Lee S, Cho NY, Choi M, Yoo EJ, Kim JH, Kang GH (2008) Clinicopathological features of CpG island methylator phenotype-positive colorectal cancer and its adverse prognosis in relation to KRAS/BRAF mutation. Pathol Int 58:104–113
Kim JH, Shin SH, Kwon HJ, Cho NY, Kang GH (2009) Prognostic implications of CpG island hypermethylator phenotype in colorectal cancers. Virchows Arch 455:485–494
Ogino S, Nosho K, Kirkner GJ, Kawasaki T, Meyerhardt JA, Loda M, Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS (2009) CpG island methylator phenotype, microsatellite instability, BRAF mutation and clinical outcome in colon cancer. Gut 58:90–96
Nygren AO, Ameziane N, Duarte HM et al (2005) Methylation-specific MLPA (MS-MLPA): simultaneous detection of CpG methylation and copy number changes of up to 40 sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e128
Eberth S, Schneider B, Rosenwald A, Hartmann EM, Romani J, Zaborski M, Siebert R, Drexler HG, Quentmeier H (2010) Epigenetic regulation of CD44 in Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. BMC Cancer. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-517
Pavicic W, Perkiö E, Kaur S, Peltomäki P (2011) Altered methylation at microRNA-associated CpG islands in hereditary and sporadic carcinomas: a methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA)-based approach. Mol Med. doi:10.2119/molmed.2010.00239
Schwarzenbach H, Chun FK, Isbarn H, Huland H, Pantel K (2011) Genomic profiling of cell-free DNA in blood and bone marrow of prostate cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137:811–819
Hess CJ, Ameziane N, Schuurhuis GJ, Errami A, Denkers F, Kaspers GJ, Cloos J, Joenje H, Reinhardt D, Ossenkoppele GJ, Zwaan CM, Waisfisz Q (2008) Hypermethylation of the FANCC and FANCL promoter regions in sporadic acute leukaemia. Cell Oncol 30:299–306
Cabello MJ, Grau L, Franco N, Orenes E, Alvarez M, Blanca A, Heredero O, Palacios A, Urrutia M, Fernández JM, López-Beltrán A, Sánchez-Carbayo M (2011) Multiplexed methylation profiles of tumor suppressor genes in bladder cancer. J Mol Diagn 13:29–40
Castro M, Grau L, Puerta P, Gimenez L, Venditti J, Quadrelli S, Sánchez-Carbayo M (2010) Multiplexed methylation profiles of tumor suppressor genes and clinical outcome in lung cancer. J Transl Med. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-8-86
Livide G, Epistolato MC, Amenduni M, Disciglio V, Marozza A, Mencarelli MA, Toti P, Lazzi S, Hadjistilianou T, De Francesco S, D’Ambrosio A, Renieri A, Ariani F (2012) Epigenetic and copy number variation analysis in retinoblastoma by MS-MLPA. Pathol Oncol Res 18:703–712
Ewald C, Hofmann T, Kuhn SA, Deufel T, Beetz C, Kalff R (2008) Methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification in meningiomas. J Neurooncol 90:267–273
Moelans CB, Verschuur-Maes AH, van Diest PJ (2011) Frequent promoter hypermethylation of BRCA2, CDH13, MSH6, PAX5, PAX6 and WT1 in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer. J Pathol 225:222–231
Chen K, Sawhney R, Khan M, Benninger MS, Hou Z, Sethi S, Stephen JK, Worsham MJ (2007) Methylation of multiple genes as diagnostic and therapeutic markers in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:1131–1138
Shah N, Lin B, Sibenaller Z, Ryken T, Lee H, Yoon JG, Rostad S, Foltz G (2011) Comprehensive analysis of MGMT promoter methylation: correlation with MGMT expression and clinical response in GBM. PLoS One 6(1):e16146
Joensuu EI, Abdel-Rahman WM, Ollikainen M, Ruosaari S, Knuutila S, Peltomaki P (2008) Epigenetic signatures of familial cancer are characteristic of tumor type and family category. Cancer Res 68:4597–4605
Leong KJ, Wei W, Tannahill LA, Caldwell GM, Jones CE, Morton DG, Matthews GM, Bach SP (2011) Methylation profiling of rectal cancer identifies novel markers of early-stage disease. Br J Surg 98:724–734
Berginc G, Bracko M, Glavac D (2010) MS-MLPA reveals progressive age-dependent promoter methylation of tumor suppressor genes and possible role of IGSF4 gene in colorectal carcinogenesis of microsatellite instable tumors. Cancer Invest 28:94–102
Furlan D, Carnevali IW, Bernasconi B, Sahnane N, Milani K, Cerutti R, Bertolini V, Chiaravalli AM, Bertoni F, Kwee I, Pastorino R, Capella C (2010) Hierarchical clustering analysis of pathologic and molecular data identifies prognostically and biologically distinct groups of colorectal carcinomas. Mod Pathol 24:126–137
La Rosa S, Marando A, Furlan D, Sahnane N, Capella C (2012) Colorectal poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas and mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinomas: insights into the diagnostic immunophenotype, assessment of methylation profile and search for prognostic markers. Am J Surg Pathol 36:601–611
Klimstra DSAR, Capella C, Kloppel G, Komminoth P, Solcia E, Rindi G (2010) Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the colon and rectum. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban FH, Theise ND (eds) WHO classification of tumors of the digestive system. JARC, Lyon, pp 174–177
Hamilton SRBF, Boffetta P, Ilyas M (2010) Carcinoma of the colon and rectum. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban FH, Theise ND (eds) WHO classification of tumors of the digestive system. JARC, Lyon, pp 134–146
Edge SBBD, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A (2010) Colon and rectum. In: Edge SB (ed) TNM classification of malignant tumor, 7th edn. Springer, New York, pp 173–206
Edge SBBD, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A (2010) Neuroendocrine tumors. In: Edge SB (ed) TNM classification of malignant tumor, 7th edn. Springer, New York, pp 227–235
Furlan D, Cerutti R, Genasetti A, Pelosi G, Uccella S, La Rosa S, Capella C (2003) Microallelotyping defines the monoclonal or the polyclonal origin of mixed and collision endocrine-exocrine tumors of the gut. Lab Invest 83:963–971
van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL, Delabesse E, Davi F, Schuuring E, van Garcia-Sanz R, Krieken JH, Droese J, González D, Bastard C, White HE, Spaargaren M, González M, Parreira A, Smith JL, Morgan GJ, Kneba M, Macintyre EA (2003) Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 17:2257–2317
Herman JG, Umar A, Polyak K, Graff JR, Ahuja N, Issa JP, Markowitz S, Willson JK, Hamilton SR, Kinzler KW, Kane MF, Kolodner RD, Vogelstein B, Kunkel TA, Baylin SB (1998) Incidence and functional consequences of MLH1 promoter hypermethylation in colorectal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6870–6875
Doyle B, O’Riain C, Appleton K (2011) Pyrosequencing of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Methods Mol Biol 724:181–190
Clark SJ, Harrison J, Paul CL, Frommer M (1994) High sensitivity mapping of methylated cytosines. Nucl Acids Res 22:2990–2997
Furlan D, Carnevali I, Marcomini B, Cerutti R, Dainese E, Capella C, Riva C (2006) The high frequency of de novo promoter methylation in synchronous primary endometrial and ovarian carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 12:3329–3336
Dikow N, Nygren AO, Schouten JP, Hartmann C, Kramer N, Janssen B, Zschocke J (2007) Quantification of the methylation status of the PWS/AS imprinted region: comparison of two approaches based on bisulfite sequencing and methylation-sensitive MLPA. Mol Cell Probes 21:208–215
Priolo M, Sparago A, Mammi C, Cerrato F, Lagana C, Riccio A (2008) MS-MLPA is a specific and sensitive technique for detecting all chromosome 11p15.5 imprinting defects of BWS and SRS in a single-tube experiment. Eur J Hum Genet 16:565–571
Samowitz WS, Albertsen H, Herrick J, Levin TR, Sweeney C, Murtaugh MA, Wolff RK, Slattery ML (2005) Evaluation of a large, population-based sample supports a CpG island methylator phenotype in colon cancer. Gastroenterology 129:837–845
Hawkins N, Norrie M, Cheong K, Mokany E, Ku SL, Meagher A, O’Connor T, Ward R (2002) CpG island methylation in sporadic colorectal cancers and its relationship to microsatellite instability. Gastroenterology 122:1376–1387
Jass JR (2007) Classification of colorectal cancer based on correlation of clinical, morphological and molecular features. Histopathology 50:113–130
Walther A, Johnstone E, Swanton C, Midgley R, Tomlinson I, Kerr D (2009) Genetic prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:489–499
Limsui D, Vierkant RA, Tillmans LS, Wang AH, Weisenberger DJ, Laird PW, Lynch CF, Anderson KE, French AJ, Haile RW, Harnack LJ, Potter JD, Slager SL, Smyrk TC, Thibodeau SN, Cerhan JR, Limburg PJ (2010) Cigarette smoking and colorectal cancer risk by molecularly defined subtypes. J Natl Cancer Inst 102:1012–1022
Arnold CN, Nagasaka T, Goel A, Scharf I, Grabowski P, Sosnowski A, Schmitt-Graff A, Boland CR, Arnold R, Blum HE (2008) Molecular characteristics and predictors of survival in patients with malignant neuroendocrine tumors. Int J Cancer 123:1556–1564
Arnold CN, Sosnowski A, Schmitt-Graff A, Arnold R, Blum HE (2007) Analysis of molecular pathways in sporadic neuroendocrine tumors of the gastro-entero-pancreatic system. Int J Cancer 120:2157–2164
Baylin SB, Herman JG, Graff JR, Vertino PM, Issa JP (1998) Alterations in DNA methylation: a fundamental aspect of neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res 72:141–196
Chan AO, Broaddus RR, Houlihan PS et al (2002) CpG island methylation in aberrant crypt foci of the colorectum. Am J Pathol 160:1823–1830
Chan AO, Issa JP, Morris JS, Hamilton SR, Rashid A (2002) Concordant CpG island methylation in hyperplastic polyposis. Am J Pathol 160:529–536
Petko Z, Ghiassi M, Shuber A et al (2005) Aberrantly methylated CDKN2A, MGMT, and MLH1 in colon polyps and in fecal DNA from patients with colorectal polyps. Clin Cancer Res 11:1203–1209
Belshaw NJ, Pal N, Tapp HS et al (2010) Patterns of DNA methylation in individual colonic crypts reveal aging and cancer-related field defects in the morphologically normal mucosa. Carcinogenesis 31:1158–1163
Shen L, Kondo Y, Rosner GL et al (2005) MGMT promoter methylation and field defect in sporadic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1330–1338
House MG, Herman JG, Guo MZ, Hooker CM, Schulick RD, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Maitra A, Yeo CJ (2003) Aberrant hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes in pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Ann Surg 238:423–431
Liu L, Broaddus RR, Yao JC, Xie S, White JA, Wu TT, Hamilton SR, Rashid A (2005) Epigenetic alterations in neuroendocrine tumors: methylation of RAS-association domain family 1, isoform A and p16 genes are associated with metastasis. Mod Pathol 18:1632–1640
Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, Maruyama R, Virmani AK, Girard L, Miyajima K, Harada K, Ariyoshi Y, Takahashi T, Sugio K, Brambilla E, Gilcrease M, Minna JD, Gazdar AF (2001) DNA methylation profiles of lung tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 1:61–67
Virmani AK, Tsou JA, Siegmund KD, Shen LY, Long TI, Laird PW, Gazdar AF, Laird-Offringa IA (2002) Hierarchical clustering of lung cancer cell lines using DNA methylation markers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11:291–297
Belinsky SA (2004) Gene-promoter hypermethylation as a biomarker in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4:707–717
Carmona FJ, Esteller M (2010) Epigenomics of human colon cancer. Mutat Res 693:53–60
Acknowledgments
We thank Luisa Bernardinelli for helpful advice and discussions. This study has been carried out using equipment from the “Centro Grandi Strumenti” of the University of Insubria.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furlan, D., Sahnane, N., Mazzoni, M. et al. Diagnostic utility of MS-MLPA in DNA methylation profiling of adenocarcinomas and neuroendocrine carcinomas of the colon–rectum. Virchows Arch 462, 47–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1348-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1348-2