Abstract
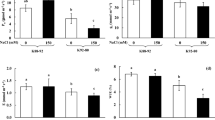
3′,5′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is an important second messenger in plants. In the present study, roles of cGMP in salt resistance in Arabidopsis roots were investigated. Arabidopsis roots were sensitive to 100 mM NaCl treatment, displaying a great increase in electrolyte leakage and Na+/K+ ratio and a decrease in gene expression of the plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase. However, application of exogenous 8Br-cGMP (an analog of cGMP), H2O2 or CaCl2 alleviated the NaCl-induced injury by maintaining a lower Na+/K+ ratio and increasing the PM H+-ATPase gene expression. In addition, the inhibition of root elongation and seed germination under salt stress was removed by 8Br-cGMP. Further study indicated that 8Br-cGMP-induced higher NADPH levels for PM NADPH oxidase to generate H2O2 by regulating glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) activity. The effect of 8Br-cGMP and H2O2 on ionic homeostasis was abolished when Ca2+ was eliminated by glycol-bis-(2-amino ethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA, a Ca2+ chelator) in Arabidopsis roots under salt stress. Taken together, cGMP could regulate H2O2 accumulation in salt stress, and Ca2+ was necessary in the cGMP-mediated signaling pathway. H2O2, as the downstream component of cGMP signaling pathway, stimulated PM H+-ATPase gene expression. Thus, ion homeostasis was modulated for salt tolerance.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 8Br-cGMP:
-
8Bromo-3,5-cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- DPI:
-
Diphenylene iodonium
- DTT:
-
1,4-Dithiothreitol
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- EGTA:
-
Glycol-bis-(2-amino ethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- EL:
-
Electrolyte leakage
- G6PDH:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- Ly83583:
-
6-Anilino-5,8-quinolinedione
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
References
Arango M, Gevaudant F, Oufattole M, Boutry M (2003) The plasma membrane proton pump ATPase: the significance of gene subfamilies. Planta 216:355–365
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bright J, Desikan R, Hancock JT, Weir IS, Neill SJ (2006) ABA-induced NO generation and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis are dependent on H2O2 synthesis. Plant J 45:113–122
Coelho SM, Taylor AR, Ryan KP, Sousa-Pinto I, Brown MT, Brownlee C (2002) Spatiotemporal patterning of reactive oxygen production and Ca2+ wave propagation in Fucus rhizoid cells. Plant Cell 14:2369–2381
Cramer GR, Lynch J, Läuchli A, Epstein E (1987) Influx of Na+, K+, and Ca2+ into roots of salt-stressed cotton seedlings. Plant Physiol 83:510–516
Davies JM, Poole PJ, Rea PA, Sander D (1992) Potassium transport into plant vacuoles energized directly by a proton-pumping inorganic pyrophosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1–5
Demidchik V, Tester M (2002) Sodium fluxes through nonselective cation channels in the plasma membrane of protoplasts from Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 128:379–387
DeWitt ND, Sussman MR (1995) Immunological localization of an epitope-tagged plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase) in phloem companion cells. Plant Cell 7:2053–2067
Donaldson L, Ludidi N, Knight MR, Gehring C, Denby K (2004) Salt and osmotic stress cause rapid increases in Arabidopsis thaliana cGMP levels. FEBS Lett 569:317–320
Esposito S, Carfagna S, Massaro G, Vona V, Di MRV (2001) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in barley roots: kinetic properties and localization of the isoforms. Planta 212:627–634
Gévaudant F, Duby G, Stedingk EV, Zhao RM, Morsomme P, Boutry M (2007) Expression of a constitutively activated plasma membrane H+-ATPase alters plant development and increases salt tolerance. Plant Physiol 144:1763–1776
Harper JF, Manney L, DeWitt ND, Yoo MH, Sussman MR (1990) The Arabidopsis thaliana plasma membrane H+-ATPase multigene family. Genomic sequence and expression of a third isoform. J Biol Chem 265:13601–13608
Harper JF, Breton G, Harmon A (2004) Decoding Ca2+ signals through plant protein kinases. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:263–288
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Rev Plant Biol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Houlne G, Boutry M (1994) Identification of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene encoding a plasma membrane H+-ATPase whose expression is restricted to anther tissues. Plant J 5:311–317
Hung KT, Hsu YT, Kao CH (2006) Hydrogen peroxide is involved in methyl jasmonate-induced senescence of rice leaves. Plant Physiol 127:293–303
Kerkeb L, Donaire JP, Rodriguez-Rosales MP (2001) Plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity is involved in adaptation of tomato calli to NaCl. Plant Physiol 111:483–490
Knight H (2000) Calcium signaling during abiotic stress in plants. Int Rev Cytol 195:269–324
Knight H, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1997) Calcium signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana responding to drought and salinity. Plant J 12:1067–1078
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Levine A, Tenhaken R, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1994) H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive response. Cell 79:583–593
Li SW, Xue LG (2010) The interaction between H2O2 and NO, Ca2+, cGMP, and MAPKs during adventitious rooting in mung bean seedlings. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 10:1007–1014
Li SW, Xue LG, Xu SJ, Feng HY, An LZ (2009) Hydrogen peroxide acts as a signal molecule in the adventitious root formation of mung bean seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 65:63–71
Ludidi N, Gehring C (2003) Identification of a novel protein with guanylyl cyclase activity in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 278:6490–6494
Maathuis FJM (2006) cGMP modulates gene transcription and cation transport in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 45:700–711
Maffei ME, Mithofer A, Arimura G, Uchtenhagen H, Bossi S, Bertea CM, Cucuzza LS, Novero M, Volpe V, Quadro S, Boland W (2006) Effects of feeding Spodoptera littoralis on Lima bean leaves. III. Membrane depolarization and involvement of hydrogen peroxide. Plant Physiol 140:1022–1035
Matsumura H, Miyachi S (1980) Cycling assay for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides. Methods Enzymol 69:465–470
McAinsh MR, Clayton H, Mansfield TA, Hetherington AM (1996) Changes in stomatal behaviour and guard cell cytosolic free calcium in response to oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 111:1031–1042
Melillo MT, Leonetti P, Bongiovanni M, Castagnone-Sereno P, Bleve ZT (2006) Modulation of reactive oxygen species activities and H2O2 accumulation during compatible and incompatible tomato-root-knot nematode interactions. New Phytol 170:501–512
Michelet B, Boutry M (1995) The plasma membrane H+-ATPase: a highly regulated enzyme with multiple physiological functions. Plant Physiol 108:1–6
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) The reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Morsomme P, Boutry M (2000) The plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase, structure, function and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:1–16
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Neill SJ, Desikan R, Hancock JT (2002) Hydrogen peroxide signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:388–395
Neill SJ, Desikan R, Hancock JT (2003) Nitric oxide signalling in plants. New Phytol 159:11–35
Neuhaus G, Bowler C, Hiratsuka K, Yamagata H, Chua NH (1997) Phytochrome-regulated repression of gene expression requires calcium and cGMP. EMBO J 16:2554–2564
Niu X, Narasimhan ML, Salzman RA, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1993) NaCl regulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase gene expression in a glycophyte and a halophyte. Plant Physiol 103:713–718
Niu X, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (1995) Ion homeostasis in NaCl stress environments. Plant Physiol 109:735–742
Palmgren MG (2001) Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPases: powerhouses for nutrient uptake. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:817–845
Pastori GM, Foyer CH (2002) Common components, networks, and pathways of cross-tolerance to stress. The central role of ‘redox’ and abscisic acid-mediated controls. Plant Physiol 129:460–468
Polisensky DH, Braam J (1996) Cold-shock regulation of the Arabidopsis TCH genes and the effects of modulating intracellular calcium levels. Plant Physiol 111:1271–1279
Rausch T, Kirsh M, Löw R, Lehr A, Vierck R, Zhigang A (1996) Salt stress responses of higher plants, the role of proton pumps and Na+/H+ antiporters. J Plant Physiol 148:425–433
Rea P, Griffith CJ, Sander D (1987) Purification of the N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteolipid of a higher plant tonoplast H+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 262:14745–14752
Reddy VS, Reddy ASN (2004) Proteomics of calcium-signaling components in plants. Phytochem 65:1745–1776
Rubio F, Flores P, Navarro JM, Martinez V (2003) Effects of Ca2+, K+ and cGMP on Na+ uptake in pepper plants. Plant Sci 165:1043–1049
Sagi M, Fluhr R (2006) Production of reactive oxygen species by plant NADPH oxidases. Plant Physiol 141:336–340
Sairam RK, Srivastava GC (2002) Changes in antioxidant activity in sub-cellular fractions of tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to long term salt stress. Plant Sci 162:897–904
Serrano R (1989) Structure and function of plasma membrane ATPase. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40:61–94
Shabala S, Shabala L, Volkenburgh EV, Newman I (2005) Effect of divalent cations on ion fluxes and leaf photochemistry in salinised barley leaves. J Exp Bot 56:1369–1378
Teng Y, Xu WZ, Ma M (2010) cGMP is required for seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 167:885–889
Tian WN, Braunstein LD, Pang J, Stuhlmeier KM, Xi QC, Tian X, Stanton RC (1998) Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity for cell growth. J Biol Chem 273:10609–10617
Van Gestelen P, Asard H, Caubergs RJ (1997) Solubilization and separation of a plant plasma membrane NADPH-O2 − synthase from other NAD(P)H oxidoreductases. Plant Physiol 115:543–550
Vitart V, Baxter I, Doerner P, Harper JF (2001) Evidence for a role in growth and salt resistance of a plasma membrane H+-ATPase in the root endodermis. Plant J 27:191–201
Wang XM, Ma YY, Huang CH, Wan Q, Li N, Bi YR (2008) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase plays a central role in modulating reduced glutathione levels in reed callus under salt stress. Planta 227:611–623
Wang HH, Liang XL, Wan Q, Wang XM, Bi YR (2009) Ethylene and nitric oxide are involved in maintaining ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis callus under salt stress. Planta 230:293–307
Wang XM, Li JS, Liu J, He WL, Bi YR (2010) Nitric oxide increases mitochondrial respiration in a cGMP-dependent manner in the callus from Arabidopsis thaliana. Nitric Oxide 23:242–250
Young JC, DeWitt ND, Sussman MR (1998) A transgene encoding a plasma membrane H+-ATPase that confers acid resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 149:501–507
Yu LJ, Lan WZ, Chen C, Yang Y (2004) Glutathione levels control glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity during elicitor induced oxidative stress in cell suspension cultures of Taxus chinensis. Plant Sci 167:329–335
Zhang YY, Wang LL, Liu YL, Zhang Q, Wei QP, Zhang WH (2006) Nitric oxide enhances salt tolerance in maize seedlings through increasing activities of proton-pump and Na+/H+ antiport in the tonoplast. Planta 224:545–555
Zhang F, Wang YP, Yang YL, Wu H, Wang D, Liu JQ (2007) Involvement of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in salt resistance in the calluses from Populus euphratica. Plant Cell Environ 30:775–785
Zhao LQ, Zhang F, Guo JK, Yang YL, Li BB, Zhang LX (2004) Nitric oxide functions as a signal in salt resistance in the calluses from two ecotypes of reed. Plant Physiol 134:849–857
Zhao MG, Tian QY, Zhang WH (2007) Nitric oxide synthase-dependent nitric oxide production is associated with salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 144:206–217
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (2007AA021401), the Major Project of Cultivating New Varieties of Transgenic Organisms (2009ZX08009-029B), the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Ratification No. 20100211110009) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 90917019). The Arabidopsis seeds used in this study were kindly provided by Dr. Ning Li (Department of Biology, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Li and X. Wang contributed equally to the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, X., Zhang, Y. et al. cGMP regulates hydrogen peroxide accumulation in calcium-dependent salt resistance pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana roots. Planta 234, 709–722 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1439-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1439-3