Abstract
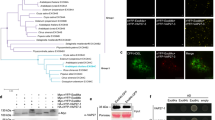
In cardoon pistils, while cardosin A is detected in the vacuoles of stigmatic papillae, cardosin B accumulates in the extracellular matrix of the transmitting tissue. Given cardosins’ high homology and yet different cellular localisation, cardosins represent a potentially useful model to understand and study the structural and functional plasticity of plant secretory pathways. The vacuolar targeting of cardosin A was replicated in heterologous species so the targeting of cardosin B was examined in these systems. Inducible expression in transgenic Arabidopsis and transient expression in tobacco epidermal cells were used in parallel to study cardosin B intracellular trafficking and localisation. Cardosin B was successfully expressed in both systems where it accumulated mainly in the vacuole but it was also detected in the cell wall. The glycosylation pattern of cardosin B in these systems was in accordance with that observed in cardoon high-mannose-type glycans, suggesting that either the glycans are inaccessible to the Golgi processing enzymes due to cardosin B conformation or the protein leaves the Golgi in an early step before Golgi-modifying enzymes are able to modify the glycans. Concerning cardosin B trafficking pathway, it is transported through the Golgi in a RAB-D2a-dependent route, and is delivered to the vacuole via the prevacuolar compartment in a RAB-F2b-dependent pathway. Since cardosin B is secreted in cardoon pistils, its localisation in the vacuoles in cardoon ovary and in heterologous systems, suggests that the differential targeting of cardosins A and B in cardoon pistils results principally from differences in the cells in which these two proteins are expressed.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP:
-
Aspartic proteinases
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- PSI:
-
Plant-specific insert
References
Batoko H, Zheng H, Hawes C, Moore I (2000) A rab1 GTPase is required for transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus and for normal Golgi movement in plants. Plant Cell 12:2201–2218
Craft J, Samalova M, Baroux C, Townley H, Martinez A, Jepson I, Tsiantis M, Moore I (2005) New pOp/LhG4 vectors for stringent glucocorticoid dependent transgene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant J 41:899–918
Di Sansebastiano GP, Paris N, Marc-Martin S, Neuhaus JM (1998) Specific accumulation of GFP in a non-acidic vacuolar compartment via a C-terminal propeptide-mediated sorting pathway. Plant J 15:449–457
Duarte P (2005) Biogenesis of cardosin A: expression and biosynthetic pathways. PhD thesis, Faculty of Sciences, University of Porto, Portugal. Available at http://hdl.handle.net/10216/14338
Duarte P, Pissarra J, Moore I (2008) Processing and trafficking of a single isoform of the aspartic proteinase cardosin A on the vacuolar pathway. Planta 227:1255–1268
Egas C, Lavoura N, Resende R, Brito R, Pires E, Pedroso de Lima M, Faro C (2000) The saposin-like domain of the plant aspartic proteinase precursor is a potent inducer of vesicle leakage. J Biol Chem 275:38190–38196
Faro C, Ramalho-Santos M, Vieira M, Mendes A, Simões I, Andrade R, Veríssimo P, Lin X, Tang J, Pires E (1999) Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding cardosin A, an RGD-containing plant aspartic proteinase. J Biol Chem 274:28724–28729
Figueiredo R, Duarte P, Pereira S, Pissarra J (2006) The embryo sac of Cynara cardunculus—ultrastructure of the development and localisation of the aspartic proteinase cardosin B. Sex Plant Reprod 19:93–101
Frazão C, Bento I, Costa J, Soares CM, Verissimo P, Faro C, Pires E, Cooper J, Carrondo MA (1999) Crystal structure of cardosin A, a glycosylated and Arg-Gly-Asp-containing aspartic proteinase from the flowers of Cynara cardunculus. J Biol Chem 274:27694–27701
Hadlington J, Denecke J (2001) Transient expression, a tool to address questions in plant cell biology. In: Hawes C, Satiat-Jeunemaitre B (eds) Plant cell biology: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 107–126
Humair D, Felipe DH, Neuhaus J-M, Paris N (2001) Demonstration in yeast of the function of BP-80, a putative plant vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Cell 13:781–792
Kotzer AM, Brandizzi F, Neumann U, Paris N, Moore I, Hawes C (2004) AtRabF2b (Ara7) acts on the vacuolar trafficking pathway in tobacco leaf epidermal cells. J Cell Sci 117:6377–6389
Lerouge P, Cabanes-Macheteau M, Rayon C, Fischette-Lainé A, Gomord V, Faye L (1998) N-Glycoprotein biosynthesis in plants: recent developments and future trends. Plant Mol Biol 38:31–48
Oliveira A (2009) Cardosin B expression during seed development—comparison between the native and heterologous systems. Master thesis. Faculty of Sciences, University of Porto, Portugal
Park M, Lee D, Lee G, Hwang I (2005) AtRMR1 functions as a cargo receptor for protein trafficking to the protein storage vacuole. J Cell Biol 170:757–767
Pereira C (2008) Cardosin A vacuolar determinants. Master thesis, Faculty of Sciences, University of Porto, Portugal
Pereira C, Soares da Costa D, Pereira S, Nogueira F, Albuquerque P, Teixeira J, Faro C, Pissarra J (2008) Cardosins in post-embryonic development of cardoon: towards an elucidation of biological function of plant aspartic proteinases. Protoplasma 232:203–213
Pissarra J, Pereira C, Soares da Costa D, Figueiredo R, Duarte P, Teixeira J, Pereira S (2007) From flower to seed germination in Cynara cardunculus: a role for aspartic proteinases. Int J Plant Dev Biol 2:274–281
Ramalho-Santos M, Pissarra J, Veríssimo P, Pereira S, Salema R, Pires E, Faro C (1997) Cardosin A, an abundant aspartic proteinase, accumulates in protein storage vacuoles in the stigmatic papillae of Cynara cardunculus L. Planta 203:204–212
Ramalho-Santos M, Veríssimo P, Cortes L, Samyn B, Van Beeumen J, Pires E, Faro C (1998) Identification and proteolytic processing of procardosin A. Eur J Biochem 255:133–138
Rayon C, Lerouge P, Faye L (1998) The protein N-glycosylation in plants. J Exp Bot 49:1463–1472
Rettinger J, Aschrafi A, Schmalzing G (2000) Roles of individual N-glycans for ATP potency and expression of the rat P2X1 receptor. J Biol Chem 275:33542–33547
Robinson D, Langhans M, Saint-Jore-Dupas C, Hawes C (2008) BFA effects are tissue and not just plant specific. Trends Plant Sci 13:405–408
Shaner N, Campbell R, Steinbach P, Giepmans B, Palmer A, Tsien R (2004) Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 12:1567–1572
Simões I, Faro C (2004) Structure and function of plant aspartic proteinases. Eur J Biochem 271:2067–2075
Simões I, Mueller EC, Otto A, Bur D, Cheung AY, Faro C, Pires E (2005) Molecular analysis of the interaction between cardosin A and phospholipase Dα. FEBS J 272:5786–5798
Teh O-K, Moore I (2007) An ARF-GEF acting at the Golgi and in selective endocytosis in polarized plant cells. Nature 448:493–496
Vieira M, Pissarra J, Veríssimo P, Castanheira P, Costa Y, Pires E, Faro C (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding cardosin B, an aspartic proteinase accumulating extracellularly in the transmitting tissue of Cynara cardunculus L. Plant Mol Biol 45:529–539
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), PhD grant SFRH/BD/2004/17272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Costa, D.S., Pereira, S., Moore, I. et al. Dissecting cardosin B trafficking pathways in heterologous systems. Planta 232, 1517–1530 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1276-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1276-9