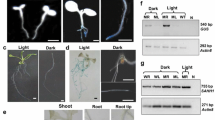
Abstract
Genetic engineering plays a unique role in fundamental plant biology studies and in improving crop traits. These efforts often necessitate introduction and expression of multiple genes using promoters from a very limited repertoire. Current common practice of expressing multiple genes is the repeated use of the same or similar promoters. This practice causes more frequent transgene silencing due to a high degree of sequence homology and a greater chance of rearrangement among repeatedly used promoter sequences. Therefore, availability and use of natural bidirectional promoters to minimize gene silencing and achieve desirable expression pattern of transgenes is a critical issue in the field of plant genetic engineering. Here we describe the use of a single natural bidirectional promoter to drive the expression of two reporter genes in onion epidermal cells and in transgenic tobacco plants. We show that (1) the promoter drives the simultaneous expression of GUS and GFP reporter genes after transient expression and stable transformation, (2) the transcription is equally strong in both directions, (3) immediate upstream regions in each direction control transcription independently from each other, and (4) the reporter genes are expressed in leaves and stems but not in roots, as expected from the fact that the endogenous promoter controls the expression of two photosynthetic genes in Arabidopsis. Hence, use of bidirectional promoters in heterologous background provides a means to express multiple genes in transgenic plants and aids genetic engineering-based crop improvement.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cab :
-
Chlorophyll a/b-binding protein
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- GFP:
-
Green-fluorescent protein
- URE:
-
Upstream regulatory elements
References
Adachi N, Lieber MR (2002) Bidirectional gene organization: a common architectural feature of the human genome. Cell 109:807–809
An G (1987) Integrated regulation of the photosynthetic gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana in transformed tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 207:210–216
An G, Ebert PR, Mitra A, Ha SB (1988) Binary vectors. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RA (eds) Plant molecular biology manual. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 1–19
Aoyama T, Chua NH (1997) A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J 11:605–612
Arguello-Astorga G, Herrera-Estrella L (1998) Evolution of light-regulated plant promoters. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:525–555
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Benfey PN, Chua NH (1990) The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter: combinatorial regulation of transcription in plants. Science 250:959–966
Carre IA, Kay SA (1995) Multiple DNA–protein complexes at a circadian-regulated promoter element. Plant Cell 7:2039–2051
Casadaban MJ, Cohen SN (1980) Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 138:179–207
Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward W, Prasher D (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263:802–805
Chaturvedi CP, Sawant SV, Kiran K, Mehrotra R, Lodhi N, Ansari SA, Tuli R (2006) Analysis of polarity in the expression from a multifactorial bidirectional promoter designed for high-level expression of transgenes in plants. J Biotechnol 123:1–12
Cho TJ, Davies CS, Nielsen NC (1989) Inheritance and organization of glycinin genes in soybean. Plant Cell 1:329–337
Christensen AH, Sharrock RA, Quail PH (1992) Maize polyubiquitin genes: structure, thermal perturbation of expression and transcript splicing, and promoter activity following transfer to protoplasts by electroporation. Plant Mol Biol 18:675–689
Colbert JT, Held BM, Wurtele ES, Dietrich PS (1997) Root preferential promoter. United States Patent 5(633):363
Conner TW (1997) TFM7 and TFM9, promoters for expression of a gene of choice in fruits such as tomato; DNA molecules, plant cells and plants containing them. United States Patent 5(608):150
Deveaux Y, Peaucelle A, Roberts GR, Coen E, Simon R, Mizukami Y, Traas J, Murray JAH, Doonan JH, Laufs P (2003) The ethanol switch: a tool for tissue-specific gene induction during plant development. Plant J 36:818–930
Fagard M, Vaucheret H (2000) Transgene silencing in plants: how many mechanisms? Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:167–194
Frey PM, Scharer-Hernandez NG, Futterer J, Potrykus I, Puonti-Kaerlas J (2001) Simultaneous analysis of the bidirectional African cassava mosaic virus promoter activity using two different luciferase genes. Virus Genes 22:231–242
Gallagher SR (1992) GUS protocols: using the GUS gene as a reporter of gene expression. Academic Press, San Diego
Gidoni D, Bond-Nutter D, Brosio P, Jones J, Bedbrook J, Dunsmuir P (1988) Coordinated expression between two photosynthetic petunia genes in transgenic plants. Mol Gen Genet 211:507–514
Ha SB, An G (1988) Identification of upstream regulatory elements involved in the developmental expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana cab1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8017–8021
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir and T region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. Nature 303:179–181
Jefferson A, Kavanagh TA, Bevan M (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Keddie JS, Tsiantis M, Piffanelli P, Cella R, Hatzopoulos P, Murphy DJ (1994) A seed-specific Brassica napus oleosin promoter interacts with a G-box-specific protein and may be bi-directional. Plant Mol Biol 24:327–340
Krom N, Ramakrishna W (2008) Comparative analysis of divergent and convergent gene pairs and their expression patters in rice, Arabidopsis, and Populus. Plant Physiol 147:1763–1773
Lam E, Benfey PN, Gilmartin PM, Fang RX, Chua NH (1989) Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7890–7894
Langridge WHR, Fitzgerald KJ, Koncz C, Schell J, Szalay AA (1989) Dual promoter of Agrobacterium tumefaciens mannopine synthase genes is regulated by plant growth hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3219–3223
Leutwiler LS, Meyerowitz EM, Tobin EM (1986) Structure and expression of three light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4051–4064
Li ZT, Jayasankar S, Gray DJ (2004) Bi-directional duplex promoters with duplicated enhancers significantly increase transgene expression in grape and tobacco. Transgenic Res 13:143–154
McElroy D, Zhang W, Cao J, Wu R (1990) Isolation of an efficient actin promoter for use in rice transformation. Plant Cell 2:163–171
Mette MF, Aufsatz W, Winden JVD, Matzke MA, Matzke AJM (2000) Transcriptional silencing and promoter methylation triggered by double-stranded RNA. EMBO J 19:5194–5201
Meyer P (1996) Homology-dependent gene silencing in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:23–48
Mitra A, An G (1989) Three distinct regulatory elements comprise the upstream promoter region of the nopaline synthase gene. Mol Gen Genet 215:294–299
Mitra A, Choi HK, An G (1989) Structural and functional analyses of Arabidopsis thaliana chlorophyll a/b-binding (cab) promoters. Plant Mol Biol 12:169–179
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–479
Ni M, Cui D, Einstein J, Narasimhulu S, Vergara CE, Gelvin SB (1995) Strength and tissue specificity of chimeric promoters derived from the octopine and mannopine synthase genes. Plant J 7:661–676
Peach C, Velten J (1991) Transgene expression variability (position effect) of CAT and GUS reporter genes driven by linked divergent T-DNA promoters. Plant Mol Biol 17:49–60
Roslan HA, Salter MG, Wood CD (2001) Characterization of the ethanol-inducible alc gene-expression system in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 28:225–235
Shaw CH, Carter GH, Watson MD, Shaw CH (1984) A functional map of the nopaline synthase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7831–7846
Shinshi H, Usami S, Ohme-Takagi M (1995) Identification of an ethylene-responsive region in the promoter of a tobacco class I chitinase gene. Plant Mol Biol 27:923–932
Sims TL, Goldberg RB (1989) The glycinin Gy1 gene from soybean. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4386
Trinklein ND, Aldred SF, Hartman SJ, Schroeder DI, Otillar RP, Myers RM (2004) An abundance of bidirectional promoters in the human genome. Genome Res 14:62–66
Velten J, Velten R, Hain R, Schell J (1984) Isolation of a dual plant promoter fragment from the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J 3:2723–2730
Williams EJB, Bowles DJ (2004) Coexpression of neighboring genes in the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 14:1060–1067
Xie M, He Y, Gan S (2001) Bidirectionalization of polar promoters in plants. Nat Biotechnol 19:677–679
Yang MQ, Taylor J, Elnitski L (2008) Comparative analyses of bidirectional promoters in vertebrates. BMC Bioinformatics 9(Suppl 6):S9
Zhang C, Gai Y, Wang W, Zhu Y, Chen X, Jiang X (2008) Construction and analysis of a plant transformation binary vector pBDGG harboring a bi-directional promoter fusing dual visible reporter genes. J Genet Genomics 35:245–249
Acknowledgments
We thank Amber Davis and Heather Janzen for expert technical assistance. Anish Mitra was an undergraduate summer research intern. This work was supported in part by grants from USDA-NRI and NSF to AM, a contribution of the University of Nebraska Agricultural Research Division.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitra, A., Han, J., Zhang, Z.J. et al. The intergenic region of Arabidopsis thaliana cab1 and cab2 divergent genes functions as a bidirectional promoter. Planta 229, 1015–1022 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0859-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0859-1