Abstract
Translation of nucleus-encoded messages in plants is conducted by the cytoplasmic ribosome, an enzyme that is comprised of two RNA/protein subunits. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the 81 different ribosomal proteins (r-proteins) of the cytosolic ribosome belong to gene families with multiple expressed members. Given that ribosomes generally contain only one copy of each r-protein, regulatory mechanisms must exist to ensure their stoichiometric accumulation. These mechanisms must be dynamic, allowing for adjustments to ribosome biogenesis to fulfill biological requirements for protein synthesis during development, and following stress induction of global changes in gene expression. In this study, we investigated whether r-protein paralogs are feedback regulated at the transcript level by obtaining a T-DNA knockout of one member, RPL23aB, from the two-member RPL23a family. Expression of the lone functional paralog in this line, RPL23aA, was compared to the expression of both paralogs in wildtype plants under non-stressed, low temperature-, and high light stresses. RPL23aA expression was not upregulated in RPL23aB knockouts to compensate for paralog-loss, and consequently knockouts showed reduced total abundance of RPL23a transcripts. However, no phenotype developed in RPL23aB knockouts, suggesting that this paralog is dispensable under experimental conditions examined, or that compensation by RPL23aA may occur post-transcriptionally. Patterns of RPL23aA and RPL23aB transcript accumulation in wildtype plants suggest that paralogs respond coordinately to developmental and stress stimuli.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- r-protein:
-
Ribosomal protein
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- SSU:
-
Small subunit
- LSU:
-
Large subunit
- RNP:
-
Ribonucleoprotein
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- BKO:
-
RPL23aB knockout
- WT:
-
Wildtype
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- CBF:
-
CRT/DRE binding factor
References
Abovich N, Gritz L, Tung L, Rosbash M (1985) Effect of RP51 gene dosage alterations on ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 5:3429–3435
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Aro EM, Virgin I, Andersson B (1993) Photoinhibition of photosystem II - Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta 1143:113–134
Bachand F, Lackner DH, Bahler J, Silver PA (2006) Autoregulation of ribosome biosynthesis by a translational response in fission yeast. Mol Cell Biol 26:1731–1742
Bailey S, Walters RG, Jansson S, Horton P (2001) Acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to the light environment: the existence of separate low light and high light responses. Planta 213:794–801
Bailey S, Horton P, Walters RG (2004) Acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to the light environment: the relationship between photosynthetic function and chloroplast composition. Planta 218:793–802
Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 289:905–920
Barakat A, Szick-Miranda K, Chang IF, Guyot R, Blanc G, Cooke R, Delseny M, Bailey-Serres J (2001) The organization of cytoplasmic ribosomal protein genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant Physiol 127:398–415
Beckmann R, Bubeck D, Grassucci R, Penczek P, Verschoor A, Blobel G, Frank J (1997) Alignment of conduits for the nascent polypeptide chain in the ribosome-Sec61 complex. Science 278:2123–2126
Branco-Price C, Kawaguchi R, Ferreira RB, Bailey-Serres J (2005) Genome-wide analysis of transcript abundance and translation in Arabidopsis seedlings subjected to oxygen deprivation. Ann Bot 96:647–660
Carroll AJ, Heazlewood JL, Ito J, Millar AH (2008) Analysis of the Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosome proteome provides detailed insights into its components and their post-translational modification. Mol Cell Proteomic 7:347–369
Chang I-F, Szick-Miranda K, Pan S, Bailey-Serres J (2005) Proteomic characterization of evolutionarily conserved and variable proteins of Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosomes. Plant Physiol 137:848–862
Chen J-G, Ullah H, Temple B, Liang J, Guo J, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Jones AM (2006) RACK1 mediates multiple hormone responsiveness and developmental processes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 57:2697–2708
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Cook D, Fowler S, Fiehn O, Thomashow MF (2004) A prominent role for the CBF cold response pathway in configuring the low-temperature metabolome of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15243–15248
Darbinian N, Gallia GL, Khalili K (2001) Helix-destabilizing properties of the human single-stranded DNA- and RNA-binding protein Pur alpha. J Cell Biochem 80:589–595
Degenhardt RF, Bonham-Smith PC (2008) Arabidopsis ribosomal proteins RPL23aA and RPL23aB are differentially targeted to the nucleolus and are disparately required for normal development. Plant Physiol 147:128–142
Desikan R, Neill SJ, Hancock JT (2000) Hydrogen peroxide-induced gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Free Radic Biol Med 28:773–778
Ditt RF, Kerr KF, de Figueiredo P, Delrow J, Comai L, Nester EW (2006) The Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome in response to Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:665–681
Fernandez P, Di Rienzo J, Fernandez L, Hopp HE, Paniego N, Heinz RA (2008) Transcriptomic identification of candidate genes involved in sunflower responses to chilling and salt stresses based on cDNA microarray analysis. BMC Plant Biol 8:11
Fowler S, Thomashow MF (2002) Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14:1675–1690
Giannino D, Grugis G, Ticconi C, Florio S, Mele G, Santini L, Cozza R, Bitonti MB, Innocenti A, Mariotti D (2000) Isolation and molecular characterization of the gene encoding the cytoplasmic ribosomal protein S28 in Prunus persica (L.) Batsch. Mol Gen Genet 263:201–212
Gilmour SJ, Zarka DG, Stockinger EJ, Salazar MP, Houghton JM, Thomashow MF (1998) Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J 16:433–442
Gray GR, Savitch LV, Ivanov AC, Huner NPA (1996) Photosystem II excitation pressure and development of resistance to photoinhibition. II. Adjustment of photosynthetic capacity in winter wheat and winter rye. Plant Physiol 110:61–71
Gray GR, Hope BJ, Qin XQ, Taylor BG, Whitehead CL (2003) The characterization of photoinhibition and recovery during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana using chlorophyll fluorescence imaging. Physiol Plant 119:365–375
Guarinos E, Santos C, Sánchez A, Qiu D-Y, Remacha M, Ballesta JPG (2003) Tag-mediated fractionation of yeast ribosome populations proves the monomeric organization of the eukaryotic ribosomal stalk structure. Mol Microbiol 50:703–712
Hanson CL, Videler H, Santos C, Ballesta JPG, Robinson CV (2004) Mass spectrometry of ribosomes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Implications for assembly of the stalk complex. J Biol Chem 279:42750–42757
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Ho LHM, Giraud E, Lister R, Thirkettle-Watts D, Low J, Clifton R, Howell KA, Carrie C, Donald T, Whelan J (2007) Characterization of the regulatory and expression context of an alternative oxidase gene provides insights into cyanide-insensitive respiration during growth and development. Plant Physiol 143:1519–1533
Huner NPA, Oquist G, Hurry VM, Krol M, Falk S, Griffith M (1993) Photosynthesis, photoinhibition and low-temperature acclimation in cold tolerant plants. Photosynth Res 37:19–39
Huner NPA, Oquist G, Sarhan F (1998) Energy balance and acclimation to light and cold. Trends Plant Sci 3:224–230
Ito T, Kim GT, Shinozaki K (2000) Disruption of an Arabidopsis cytoplasmic ribosomal protein S13-homologous gene by transposon-mediated mutagenesis causes aberrant growth and development. Plant J 22:257–264
Ivanov AV, Malygin AA, Karpova GG (2006) Eukaryotic ribosomal proteins: Interaction with their own pre-mRNAs and involvement in regulation of their splicing. Mol Biol 40:640–649
Jung SH, Lee JY, Lee DH (2003) Use of SAGE technology to reveal changes in gene expression in Arabidopsis leaves undergoing cold stress. Plant Mol Biol 52:553–567
Kawaguchi R, Girke T, Bray EA, Bailey-Serres J (2004) Differential mRNA translation contributes to gene regulation under non-stress and dehydration stress conditions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 38:823–839
Kenward MG, Roger JH (1997) Small sample inference for fixed effects from restricted maximum likelihood. Biometrics 53:983–997
Kim J (2007) Perception, transduction, and networks in cold signaling. J Plant Biol 50:139–147
Kim CH, Warner JR (1983) Messenger-RNA for ribosomal-proteins in yeast. J Mol Biol 165:79–89
Kim KY, Park SW, Chung YS, Chung CH, Kim JI, Lee JH (2004) Molecular cloning of low-temperature-inducible ribosomal proteins from soybean. J Exp Bot 55:1153–1155
Kimura M, Yamamoto YY, Seki M, Sakurai T, Sato M, Abe T, Yoshida S, Manabe K, Shinozaki K, Matsui M (2003) Identification of Arabidopsis genes regulated by high light-stress using cDNA microarray. Photochem Photobiol 77:226–233
Kodama Y, Nagaya S, Shinmyo A, Kato K (2007) Mapping and characterization of DNase I hypersensitive sites in Arabidopsis chromatin. Plant Cell Physiol 48:459–470
Kosugi S, Ohashi Y (1997) PCF1 and PCF2 specifically bind to cis elements in the rice proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Plant Cell 9:1607–1619
Kosugi S, Ohashi Y (2002) DNA binding and dimerization specificity and potential targets for the TCP protein family. Plant J 30:337–348
Kultz D (2005) Molecular and evolutionary basis of the cellular stress response. Annu Rev Physiol 67:225–257
Lecompte O, Ripp R, Thierry J-C, Moras D, Poch O (2002) Comparative analysis of ribosomal proteins in complete genomes: an example of reductive evolution at the domain scale. Nucleic Acids Res 30:5382–5390
Lin CT, Thomashow MF (1992) DNA-sequence analysis of a complementary-DNA for cold-regulated Arabidopsis gene COR15 and characterization of the COR15 polypeptide. Plant Physiol 99:519–525
Li CX, Potuschak T, Colon-Carmona A, Gutierrez RA, Doerner P (2005) Arabidopsis TCP20 links regulation of growth and cell division control pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12978–12983
Manevski A, Bertoni G, Bardet C, Tremousaygue D, Lescure B (2000) In synergy with various cis-acting elements, plant insterstitial telomere motifs regulate gene expression in Arabidopsis root meristems. FEBS Lett 483:43–46
McIntosh KB, Bonham-Smith PC (2005) The two ribosomal protein L23A genes are differentially transcribed in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome 48:443–454
McIntosh KB, Bonham-Smith PC (2006) Ribosomal protein gene regulation: what about plants? Can J Bot 84:342–362
Menetret JF, Hegde RS, Heinrich SU, Chandramouli P, Ludtke SJ, Rapoport TA, Akey CW (2005) Architecture of the ribosome-channel complex derived from native membranes. J Mol Biol 348:445–457
Morgan DG, Menetret JF, Neuhof A, Rapoport TA, Akey CW (2002) Structure of the mammalian ribosome-channel complex at 17 angstrom resolution. J Mol Biol 324:871–886
Nicolai M, Roncato MA, Canoy AS, Rouquie D, Sarda X, Freyssinet G, Robaglia C (2006) Large-scale analysis of mRNA translation states during sucrose starvation in Arabidopsis cells identifies cell proliferation and chromatin structure as targets of translational control. Plant Physiol 141:663–673
Nishimura T, Wada T, Okada K (2004) A key factor of translation reinitiation, ribosomal protein L24, is involved in gynoecium development in Arabidopsis. Biochem Soc Trans 32:611–613
Nishimura T, Wada T, Yamamoto KT, Okada K (2005) The Arabidopsis STV1 protein, responsible for translation reinitiation, is required for auxin-mediated gynoecium patterning. Plant Cell 17:2940–2953
Nissen P, Hansen J, Ban N, Moore PB, Steitz TA (2000) The structural basis of ribosome activity in peptide bond synthesis. Science 289:920–930
Oono Y, Seki M, Nanjo T, Narusaka M, Fujita M, Satoh R, Satou M, Sakurai T, Ishida J, Akiyama K, Iida K, Maruyama K, Satoh S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of Arabidopsis gene expression during rehydration process after dehydration using ca. 7000 full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 34:868–887
Oono Y, Seki M, Satou M, Iida K, Akiyama K, Sakurai T, Fujita M, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Monitoring expression profiles of Arabidopsis genes during cold acclimation and deacclimation using DNA microarrays. Funct Integr Genomics 6:212–234
Oquist G, Chow WS, Anderson JM (1992) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis represents a mechanism for the long-term regulation of photosystem-II. Planta 186:450–460
Pinon V, Etchells JP, Rossignol P, Collier SA, Arroyo JM, Martienssen RA, Byrne ME (2008) Three PIGGYBACK genes that specifically influence leaf patterning encode ribosomal proteins. Development 135:1315–1324
Planta RJ, Mager WH (1998) The list of cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 14:471–477
Pnueli L, Liang H, Rozenberg M, Mittler R (2003) Growth suppression, altered stomatal responses, and augmented induction of heat shock proteins in cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (Apx1)-deficient Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 34:185–201
Pool MR, Stumm J, Fulga TA, Sinning I, Dobberstein B (2002) Distinct modes of signal recognition particle interaction with the ribosome. Science 297:1345–1348
Popescu SC, Tumer NE (2004) Silencing of ribosomal protein L3 genes in N. tabacum reveals coordinate expression and significant alterations in plant growth, development and ribosome biogenesis. Plant J 39:29–44
Revenkova E, Masson J, Koncz C, Afsar K, Jakovleva L, Paszkowski J (1999) Involvement of Arabidopsis thaliana ribosomal protein S27 in mRNA degradation triggered by genotoxic stress. EMBO J 18:490–499
Rossel JB, Wilson IW, Pogson BJ (2002) Global changes in gene expression in response to high light in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 130:1109–1120
Saez-Vasquez J, Raynal M, Mezabasso L, Delseny M (1993) Two related, low-temperature-induced genes from Brassica napus are homologous to the human tumor BBC1 (Breast Basic Conserved) gene. Plant Mol Biol 23:1211–1221
Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Osakabe Y, Qin F, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Functional analysis of an Arabidopsis transcription factor, DREB2A, involved in drought-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 18:1292–1309
Scarpeci TE, Valle EM (2008) Rearrangement of carbon metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana subjected to oxidative stress condition: an emergency survival strategy. Plant Growth Regul 54:133–142
Scarpeci TE, Zanor MI, Carrillo N, Mueller-Roeber B, Valle EM (2008) Generation of superoxide anion in chloroplasts of Arabidopsis thaliana during active photosynthesis: a focus on rapidly induced genes. Plant Mol Biol 66:361–378
Schuwirth BS, Borovinskaya MA, Hau CW, Zhang W, Vila-Sanjurjo A, Holton JM, Cate JHD (2005) Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 A resolution. Science 310:827–834
Seki M, Narusaka M, Kamiya A, Ishida J, Satou M, Sakurai T, Nakajima M, Enju A, Akiyama K, Oono Y, Muramatsu M, Hayashizaki Y, Kawai J, Carninci P, Itoh M, Ishii Y, Arakawa T, Shibata K, Shinagawa A, Shinozaki K (2002) Functional annotation of a full-length Arabidopsis cDNA collection. Science 296:141–145
Sessions A, Burke E, Presting G, Aux G, McElver J, Patton D, Dietrich B, Ho P, Bacwaden J, Ko C, Clarke JD, Cotton D, Bullis D, Snell J, Miguel T, Hutchison D, Kimmerly B, Mitzel T, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J, Law M, Goff SA (2002) A high-throughput Arabidopsis reverse genetics system. Plant Cell 14:2985–2994
Shor B, Calaycay J, Rushbrook J, McLeod M (2003) Cpc2/RACK1 is a ribosome-associated protein that promotes efficient translation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 278:49119–49128
Spahn CMT, Beckmann R, Eswar N, Penczek PA, Sali A, Blobel G, Frank J (2001) Structure of the 80S ribosome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae- tRNA-ribosome and subunit-subunit interactions. Cell 107:373–386
Steponkus PL, Uemura M, Joseph RA, Gilmour SJ, Thomashow MF (1998) Mode of action of the COR15a gene on the freezing tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14570–14575
Tatematsu K, Nakabayashi K, Kamiya Y, Nambara E (2008) Transcription factor AtTCP14 regulates embryonic growth potential during seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 53:42–52
Thomashow MF (1999) Plant cold acclimation: Freezing tolerance genes and regulatory mechanisms. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:571–599
Tremousaygue D, Manevski A, Bardet C, Lescure N, Lescure B (1999) Plant interstitial telomere motifs participate in the control of gene expression in root meristems. Plant J 20:553–561
Tremousaygue D, Garnier L, Bardet C, Dabos P, Herve C, Lescure B (2003) Internal telomeric repeats and ‘TCP domain’ protein-binding sites co-operate to regulate gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana cycling cells. Plant J 33:957–966
Vandenabeele S, Van Der Kelen K, Dat J, Gadjev I, Boonefaes T, Morsa S, Rottiers P, Slooten L, Van Montagu M, Zabeau M, Inze D, Van Breusegem F (2003) A comprehensive analysis of hydrogen peroxide-induced gene expression in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:16113–16118
Vanderauwera S, Zimmermann P, Rombauts S, Vandenabeele S, Langebartels C, Gruissem W, Inze D, Van Breusegem F (2005) Genome-wide analysis of hydrogen peroxide-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis reveals a high light-induced transcriptional cluster involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 139:806–821
Vanderhaeghen R, De Clercq R, Karimi M, Van Montagu M, Hilson P, Van Lijsebettens M (2006) Leader sequence of a plant ribosomal protein gene with complementarity to the 18S rRNA triggers in vitro cap-independent translation. FEBS Lett 580:2630–2636
Van Lijsebettens M, Vanderhaeghen R, De Block M, Bauw G, Villarroel R, Van Montagu M (1994) An S18 ribosomal protein gene copy at the Arabidopsis PFL locus affects plant development by its specific expression in meristems. EMBO J 13:3378–3388
Warner JR, Mitra G, Schwindinger WF, Studeny M, Fried HM (1985) Saccharomyces cerevisiae coordinates accumulation of yeast ribosomal proteins by modulating messenger-RNA splicing, translational initiation, and protein-turnover. Mol Cell Biol 5:1512–1521
Weijers D, Franke-van Dijk M, Vencken RJ, Quint A, Hookaas P, Offringa R (2001) An Arabidopsis Minute-like phenotype caused by a semi-dominant mutation in a ribosomal protein S5 gene. Development 128:4289–4299
Wilkosz R, Schlappi M (2000) A gene expression screen identifies EARLI1 as a novel vernalization-responsive gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 44:777–787
Wimberly BT, Brodersen DE, Clemons WM Jr, Morgan-Warren RJ, Carter AP, Vonrhein C, Hartsch T, Ramakrishnan V (2000) Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature 407:327–339
Xiong LM, Lee BH, Ishitani M, Lee H, Zhang CQ, Zhu JK (2001) FIERY1 encoding an inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase is a negative regulator of abscisic acid and stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 15:1971–1984
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yao Y, Ling Q, Wang H, Huang H (2008) Ribosomal proteins promote leaf adaxial identity. Development 135:1325–1334
Zhang CK, Lang P, Dane F, Ebel RC, Singh NK, Locy RD, Dozier WA (2005) Cold acclimation induced genes of trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata). Plant Cell Rep 23:764–769
Acknowledgments
We thank Jacqueline Hulm, Donna Lindsay and Heather Wakely for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
425_2008_765_MOESM2_ESM.tif
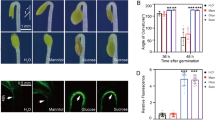
MOESM2 Fig. S1 supplementary RT-PCR analysis of homozygous T-DNA insertion lines. Gene specific primers were used to amplify RPL23aA or RPL23aB (Supplemental Table 1; RPL23A1F and RPL23A1R for RPL23aA, RPL23A2F and RPL23A2R for RPL23aB) from total RNA extracts of wildtype plants (WT), putative RPL23aA T-DNA knockout lines SAIL-258-C12 (A1) and SALK-091329.46.50 (A2), and putative RPL23aB T-DNA knockout line SAIL-597-B08 (BKO). For the SAIL-258-C12 image, intervening lanes have been removed. Thirty cycles were used for PCR and amplicons were 437 and 535 bp for RPL23aA and RPL23aB, respectively. Agarose gels were stained with EtBr. (TIFF 845 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Degenhardt, R.F., Bonham-Smith, P.C. Transcript profiling demonstrates absence of dosage compensation in Arabidopsis following loss of a single RPL23a paralog. Planta 228, 627–640 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0765-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0765-6