Abstract
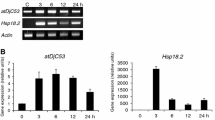
The glycine-rich protein AtGRP2 is one of the four members of the cold-shock domain (CSD) protein family in Arabidopsis. It is characterized by the presence of a nucleic acid-binding CSD domain, two glycine-rich domains and two CCHC zinc-fingers present in nucleic acid-binding proteins. In an attempt to further understand the role of CSD/GRP proteins in plants, we have proceeded to the functional characterization of the AtGRP2 gene. Here, we demonstrate that AtGRP2 is a nucleo-cytoplasmic protein involved in Arabidopsis development with a possible function in cold-response. Expression analysis revealed that the AtGRP2 gene is active in meristematic tissues, being modulated during flower development. Down-regulation of AtGRP2 gene, using gene-silencing techniques resulted in early flowering, altered stamen number and affected seed development. A possible role of AtGRP2 as an RNA chaperone is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDS:
-
Cold-shock domain
- CSP:
-
Cold-shock protein
- CCHC:
-
Knuckle zinc finger
- GRP:
-
Glycine-rich protein
- GUS:
-
β-glucuronidase
- MBP:
-
Maltose-binding protein
- RRM:
-
RNA recognition motif
References
Bocca SN, Magioli C, Mangeon A, Junqueira RM, Cardeal V, Margis R, Sachetto-Martins G (2005) Survey of glycine-rich proteins (GRPs) in the Eucalyptus expressed sequence tag database (ForEST). Gen Mol Biol 23:608–624
Bowman JL, Drews GN, Meyerowitz EM (1991) Expression of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene AGAMOUS is restricted to specific cell types late in flower development. Plant Cell 3:749–758
Burd CG, Dreyfuss G (1994) Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science 269:23074–23078
Carpenter CD, Kreps JA, Simon AE (1994) Genes enconding gycine-rich Arabidopsis thaliana proteins with RNA-binding motifs are influenced by cold treatment and an endogenous circadian rhythm. Plant Physiol 104:1015–1025
Cheng Y, Kato N, Wang W, Li J, Chen X (2003) Two RNA binding proteins, HEN4 and HUA1, act in the processing of AGAMOUS pre-mRNA in Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev Cell 4:53–66
Clarke MC, Wei W, Lindsey K (1992) High-frequency transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Mol Biol Rep 10:178–189
de Almeida Engler J, De Groodt R, Van Montagu M, Engler G (2001) In situ hybridization to mRNA of Arabidopsis tissue sections. Methods 23:325–334
de Oliveira DE, Seurinck J, Inzé D, Van Montagu M, Botterman J (1990) Differential expression of five Arabidopsis genes encoding glycine-rich proteins. Plant Cell 2:427–436
Dreyfuss G, Kim VN, Kataoka N (2002) Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:195–205
Evdokimova V, Ruzanov P, Imataka H, Raught B, Svitkin Y, Ovchinnikov LP, Sonenberg N (2001) The major mRNA-associated protein YB-1 is a potent 5’ cap-dependent mRNA stabilizer. EMBO J 20:5491–5502
Fusaro A, Mangeon A, Rocha C, Junqueira R, Coutinho T, Margis R, Sachetto-Martins G (2001) Classification, expression pattern and comparative analysis of sugarcane expressed sequences tags (ESTs) encoding glycine-rich proteins (GRPs). Gen Mol Biol 24:263–273
Gendra E, Moreno A, Albà MM, Pagès M (2004) Interaction of the plant glycine-rich RNA-binding protein MA16 with a novel nucleolar DEAD box RNA helicase protein from Zea mays. Plant J 38:875–886
Graumann P, Marahiel M (1998) A superfamily of proteins that contain the cold-shock domain. Trends Biochem Sci 23:286–290
Hanano S, Sugita M, Sugiura M (1996) Isolation of a novel RNA-binding protein and its association with a large ribonucleoprotein particle present in the nucleoplasm of tobacco cells. Plant Mol Biol 31:57–68
Haseloff J, Siemering KR, Prasher DC, Hodge S (1997) Removal of a cryptic intron and subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein are required to mark transgenic Arabidopsis plants brightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2122–2127
Heintzen C, Melzer S, Fischer R, Kappeler S, Apel K, Staiger D (1994) A light- and temperature-entrained circadian clock controls expression of transcripts encoding nuclear proteins with homology to RNA-binding proteins in meristematic tissue. Plant J 5:799–813
Heintzen C, Nater M, Apel K, Staiger D (1997) AtGRP7, a nuclear RNA-binding protein as a component of a circadian-regulated negative feedback loop in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8515–8520
Hirose T, Sugita M, Sugiura M (1993) cDNA structure, expression and nucleic-acid binding properties of three RNA-binding proteins in tobacco: ocurrence of tissue alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3981–3987
Jiang C, Iu B, Singh J (1996) Requirement of a CCGAC cis-acting element for cold induction of the BN115 gene from B. napus. Plant Mol Biol 30:679–684
Karlson D, Imai R (2003) Conservation of the cold shock domain protein family in plants. Plant Physiol 131:12–15
Karlson D, Nakaminami K, Toyomasu T, Imai R (2002) A cold-regulated nucleic acid-binding protein of winter wheat shares a domain with bacterial cold-shock proteins. J Biol Chem 20:35248–35256
Kim YO, Kim JS, Kang H (2005) Cold-inducible zinc finger-containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein contributes to the enhancement of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 42:890–900
Kingsley PD, Palis J (1994) GRP-2 proteins contain both CCHC zinc-fingers and a cold shock domain. Plant Cell 6:1522–1523
Kwak KJ, Kim YO, Kang H (2005). Characterization of transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing GR-RBP4 under high salinity, dehydration, or cold stress. J Exp Bot 56:3007–3016
Li J, Jia D, Chen X (2001) HUA1, a regulator of stamen and carpel identities in Arabidopsis, codes for a nuclear RNA binding protein. Plant Cell 13:2269–2281
Lim MH, Kim J, Kim YS, Chung KS, Seo YH, Lee I, Kim J, Hong CB, Kim HJ, Park CM (2004) A new Arabidopsis gene, FLK, encodes an RNA binding protein with K homology motifs and regulates flowering time via FLOWERING LOCUS C. Plant Cell 16:731–740
Macknight R, Bancroft I, Page T, Lister C, Schmidt R, Love K, Westphal L, Murphy G, Sherson S, Cobbett C, Dean C (1997) FCA, a gene controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis, encodes a protein containing RNA-binding domains. Cell 89:737–745
Magioli C, Barrôco RMP, Benicio CA, de Santiago-Fernandes LD, Mansur E, Engler G, Margis-Pinheiro M, Sachetto-Martins G (2001) Somatic embryo formation in Arabidopsis and eggplant is associated with expression of a glycine-rich protein gene (Atgrp-5). Plant Sci 161:573–581
Mockler TC, Yu X, Shalitin D, Parikh D, Michael TP, Liou J, Huang J, Smith Z, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Chory J, Lin C (2004) Regulation of flowering time in Arabidopsis by K homology domain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12759–12764
Moriguchi K, Sugita M, Sugiura M (1997) Structure and subcellular localization of a small RNA-binding protein from tobacco. Plant J 12:215–221
Moss EG, Lee RC, Ambros V (1997) The cold shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C. elegans and is regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell 88:637–646
Moss EG, Tang L (2003) Conservation of the heterochronic regulator Lin-28, its developmental expression and microRNA complementary sites. Dev Biol 258:432–442
Mouradov A, Cremer F, Coupland G (2002) Control of flowering time: interacting pathways as a basis for diversity. Plant Cell 14:S111–S130
Nakaminami K, Karlson DT, Imai R (2006) Functional conservation of cold shock domains in bacteria and higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10122–10127
Nishiyama H, Itoh K, Kaneko Y, Kishishita M, Yoshida O, Fujita J (1997) A glycine-rich RNA-binding protein mediating cold-inducible suppression of mammalian cell growth. J Cell Biol 137:899–908
Ossareh-Nazari B, Gwizdek C, Dargemont C (2001) Protein export from the nucleus. Traffic 2:684–689
Sachetto-Martins G, Fernandes LD, Félix DB, de Oliveira DE (1995) Preferential transcriptional activity of a glycine-rich protein gene from Arabidopsis thaliana in protoderm derived cells. Int J Plant Sci 156:460–470
Sachetto-Martins G, Franco L, de Oliveira D (2000) Plant glycine-rich proteins: a family or just proteins with a common motif? Bioch Biophys Acta 1492:1–14
Sato N (1994) A cold-regulated cyanobacterial gene cluster encodes a RNA-binding protein and ribosomal protein S21. Plant Mol Biol 24:819–823
Schomburg FM, Patton DA, Meinke DW, Amasino RM (2001) FPA, a gene involved in floral induction in Arabidopsis, encodes a protein containing RNA-recognition motifs. Plant Cell 13:1427–1436
Simpson GG, Dean C (2002) Arabidopsis, the rosetta stone of flowering time? Science 296:285–289
Simpson GG, Quesada V, Henderson IR, Dijkwel PP, Macknight R, Dean C (2004) RNA processing and Arabidopsis flowering time control. Bioch Soc Trans 32:565–566
Wilhelm JE, Mansfield J, Hom-Booher N, Wang S, Turck CW, Hazelrigg T, Vale RD (2000) Isolation of a ribonucleoprotein complex involved in mRNA localization in Drosophila oocytes. J Cell Biol 148:427–440
Wilkinson MF, Shyu AB (2001) Multifunctional regulatory proteins that control gene expression in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Bioessays 23:775–787
Zchut S, Weiss M, Pick U (2003) Temperature-regulated expression of a glycine-rich RNA-binding protein in the halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina. J Plant Physiol 160:1375–1384
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank D. E. de Oliveira (Institute of Plant Biotechnology for Developing Countries, Gent, Belgium) for critical reading of the manuscript. A.F.F. was supported by a Ph.D. fellowship from CAPES. S.N.B. and C.M. were supported by CNPq post-doctoral and CAPES-ProDoc fellowships, respectively. V.C.J., T.C.C. and C.M.R.L. were recipient of PIBIC fellowship from CNPq. This work was supported by grants from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and the Fundação Carlos Chagas de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ) to G.S.M. and by Interuniversity Poles of Attraction Programme-Belgian Science Policy (P5/13) to D.I.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fusaro, A.F., Bocca, S.N., Ramos, R.L.B. et al. AtGRP2, a cold-induced nucleo-cytoplasmic RNA-binding protein, has a role in flower and seed development. Planta 225, 1339–1351 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0444-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0444-4