Abstract
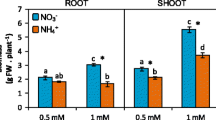
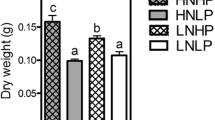
Oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) needs very high nitrogen fertilizer inputs. Significant amounts of this nitrogen are lost during early leaf shedding and are a source of environmental and economic concern. The objective of this study was to investigate whether the remobilization of leaf amino acids could be limiting for nitrogen use efficiency. Therefore, amino acid concentrations were analyzed in subcellular compartments of leaf mesophyll cells of plants grown under low (0.5 mM NO −3 ) and high (4 mM NO −3 ) nitrogen supply. With high nitrogen supply, young leaves showed an elevated amino acid content, mainly in vacuoles. In old leaves, however, subcellular concentrations were similar under high and low nitrogen conditions, showing that the excess nitrogen had been exported during leaf development. The phloem sap contained up to 650 mM amino acids, more than four times as much than the cytosol of mesophyll cells, indicating a very efficient phloem-loading process. Three amino acid permeases, BnAAP1, BnAAP2, and BnAAP6, were identified and characterized. BnAAP1 and BnAAP6 mediated uptake of neutral and acidic amino acids into Xenopus laevis oocytes at the actual apoplastic substrate concentrations. All three transporters were expressed in leaves and the expression was still detectable during leaf senescence, with BnAAP1 and BnAAP2 mRNA levels increasing from mature to old leaves. We conclude that phloem loading of amino acids is not limiting for nitrogen remobilization from senescing leaves in oilseed rape.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAP:
-
Amino acid permease
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
References
Aniol H (1994) Stickstoffverteilung in erntereifen Rapsbestaenden. Raps 3:144–146
Bhalerao R, Keskitalo J, Sterky F, Erlandsson R, Björkbacka H, Birve SJ, Karlsson J, Gardeström P, Gustafsson P, Lundeberg J, Jansson S (2003) Gene expression in autumn leaves. Plant Physiol 131:430–442
Boorer KJ, Fischer W-N (1997) Specificity and stoichiometry of the Arabidopsis H+/amino acid transporter AAP5. J Biol Chem 272:13040–13046
Buchanan-Wollaston V (1997) The molecular biology of leaf senescence. J Exp Bot 48:181–199
Bullock WO, Fernandez JM, Short JM (1987) XL1-Blue: a high efficiency plasmid transforming recA E. Coli strain with β-galactosidase selection. BioTechniques 5:376–378
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Dietrich D, Hammes U, Thor K, Suter-Grotemeyer M, Flückiger R, Slusarenko AJ, Ward JM, Rentsch D (2004) AtPTR1 a plasma membrane peptide transporter expressed during seed germination and in vascular tissue of Arabidopsis. Plant J. DOI 10.1111/j.1365–313X.2004.02224.x
Feller U, Keist M (1986) Senescence and nitrogen metabolism in annual plants. In: Lambers H, Neeterson JJ, Stulen I (eds) Fundamental ecological and agricultural aspects of nitrogen metabolism in higher plants. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 219–234
Fischer W-N, Kwart M, Hummel S, Frommer WB (1995) Substrate specificity and expression profile of amino acid transporters (AAPs) in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 270:16315–16320
Fischer W-N, Andre B, Rentsch D, Krolkiewicz S, Tegeder M, Breitkreuz K, Frommer WB (1998) Amino acid transport in plants. Trends Plant Sci 3:188–195
Fischer W-N, Loo DDF, Koch W, Ludewig U, Boorer KJ, Tegeder M, Rentsch D, Wright EM, Frommer WB (2002) Low and high affinity amino acid H+-cotransporters for cellular import of neutral and charged amino acids. Plant J 29:717–731
Frohman MA, Dush MK, Martin GR (1988) Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8998–9002
Frommer WB, Hummel S, Riesmeier JW (1993) Expression cloning in yeast of a cDNA encoding a broad specificity amino acid permease from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5944–5948
Gan S, Amasino RM (1995) Inhibition of leaf senescence by autoregulated production of cytokinin. Science 270:1986–1988
Gepstein G, Sabehi G, Carp M-J, Hajouj T, Nesher MFO, Yariv I, Dor C, Bassani M (2003) Large-scale identification of leaf senescence-associated genes. Plant J 36:629–642
Gerhardt R, Heldt HW (1984) Measurement of subcellular metabolite levels in leaves by fractionation of freeze-stopped material in nonaqueous media. Plant Physiol 75:542–547
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on the transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166:557–580
Handa H (2003) The complete nucleotide sequence and RNA editing content of the mitochondrial genome of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genomes of rapeseed and Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 31:5907–5916
Haritatos E, Medville R, Turgeon R (2000) Minor vein structure and sugar transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 211:105–111
Hirner B, Fischer WN, Rentsch D, Kwart M, Frommer WB (1998) Developmental control of H+/amino acid permease gene expression during seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 14:535–544
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hookema A (1993) New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res 2:208–218
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MV (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3908
Kwart M, Hirner B, Hummel S, Frommer WB (1993) Differential expression of two related amino acid transporters with differing substrate specificity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 4:993–1002
Leidreiter K, Kruse A, Heineke D, Robinson DG, Heldt HW (1995) Subcellular volumes and metabolite concentrations in potato (Solanum tuberosum cv. Desiree) leaves. Bot Acta 108:439–444
Lohaus G, Möllers C (2000) Phloem transport of amino acids ain two Brassica napus L. genotypes and one B. carinata genotype in relation to their seed protein content. Planta 211:833–840
Lohaus G, Burba M, Heldt HW (1994) Comparison of the contents of sucrose and amino acids in the leaves, phloem sap and taproots of high and low sugar-producing hybrids of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J Exp Bot 45:1097–1101
Lohaus G, Winter H, Riens B, Heldt HW (1995) Further studies of the phloem loading process in the leaves of barley and spinach. The comparison of metabolite concentrations in the apoplastic compartment with those in the cytosolic compartment and in the sieve tubes. Bot Acta 108:270–275
Lohaus G, Bueker M, Hussmann M, Soave C, Heldt HW (1998) Transport of amino acids with special emphasis on the synthesis and transport of asparagine in the Illinois low protein and Illinois high protein strains in maize. Planta 205:181–188
Lohaus G, Pennewiss K, Sattelmacher B, Hussmann M, Muehling HK (2001) Is the infiltration-centrifugation technique appropriate for the isolation of apoplastic fluid? A critical evaluation with different plant species. Physiol Plant 111:457–465
Miller AJ, Zhou JJ (2000) Xenopus oocytes as an expression system for plant transporters. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:343–358
Miranda M, Borisjuk L, Tewes A, Heim U, Sauer N, Wobus U, Weber H (2001) Amino acid permeases in developing seed of Vicia faba L.: expression precedes storage protein synthesis and is regulated by amino acid supply. Plant J 28:1–71
Möllers C (2002) Qualitätsentwicklungen in der Rapszüchtung. In: Proceedings, XXXVII Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Qualitätsforschung (DGQ) Qualität und Pflanzenzüchtung. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Qualitätsforschung, Frankfurt am Main, pp 107–110
Noh Y-S, Amasino RM (1999) Regulation of developmental senescence is conserved between Arabidopsis and Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol 41:195–206
Okumoto S, Schmidt R, Tegeder M, Fischer WN, Rentsch D, Frommer WB, Koch W (2002) High affinity amino acid transporters specifically expressed in xylem parenchyma and developing seed of Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:45338–45346
Ortiz-Lopez A, Chang H-C, Bush DR (2000) Amino acid transporters in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:275–280
Rathgeber J, Capesius I (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer and the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from mustard (Sinapis alba). Nucleic Acids Res 18:1288
Rentsch D, Hirner B, Schmelzer E, Frommer WB (1996) Salt stress-induced proline transporters and salt stress-repressed broad specificity amino acid permeases identified by suppression of a yeast amino acid permease-targeting mutant. Plant Cell 8:1437–1446
Riens B, Lohaus G, Heineke D, Heldt HW (1991) Amino acid and sucrose content determined in the cytosolic, chloroplastic, and vacuolar compartments and in the phloem sap of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol 97:227–233
Rolletscheck H, Borisjuk L, Miranda M, Radschuk R, Golombek S, Wobus U, Weber H (2003) Functional characterization of nitrogen transport and protein accumulation in crop seeds. In: Proceedings, Phloem 2003—international conference on phloem transport, Bayreuth, p 76
Rossato L, Laine P, Ourry A (2001) Nitrogen storage and remobilization in Brassica napus L. during the growth cycle: nitrogen fluxes within the plant and changes in soluble protein patterns. J Exp Bot 52:1655–1663
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sieling K, Christen O (1999) Yield, N uptake and N-use efficiency of and N-leaching after oilseed rape grown in different crop management systems in Northern Germany. In: Proceedings, 10th International Rapeseed Congress, Canberra, http://www.regional.org.au/au/gcirc/2/95.htm.
Stacey G, Koh S, Granger C, Becker JM (2002) Peptide transport in plants. Trends Plant Sci 7:257–263
Struck C, Mueller E, Martin H, Lohaus G (2004) The Uromyces fabae AfAAT3 gene encodes a general amino acid permease that prefers uptake of in planta scarce amino acids. Mol Plant Pathol 5:183–189
Tegeder M, Offler CE, Frommer WB, Patrick JW (2000) Amino acid transporters are localized to transfer cells of developing pea seeds. Plant Physiol 122:319–325
Unfried I, Stocker U, Gruendler P (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the 18S rRNA gene from Arabidopsis thaliana Co10. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7513
Winter H, Robinson DG, Heldt HW (1993) Subcellular volumes and metabolite concentrations in barley leaves. Planta 191:180–190
Winter H, Robinson DG, Heldt HW (1994) Subcellular volumes and metabolite concentrations in spinach leaves. Planta 193:530–535
Wipf D, Ludewig U, Tegeder M, Rentsch D, Koch W, Frommer WB (2002) Conservation of amino acid transporters in fungi, plants and animals. Trends Biochem Sci 27:139–147
Acknowledgements
We thank Christian Möllers of the Institut für Pflanzenbau und Pflanzenzüchtung, Universität Göttingen, for providing the vernalized rapeseed seedlings and valuable advice. We are grateful to Melanie Klenke and Marion Taube for sample preparation and the nonaqueous fractionation and W. Frommer, Tübingen, for providing the pBF1 vector. The suggestions of the two anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged. This work was funded by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft to G.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tilsner, J., Kassner, N., Struck, C. et al. Amino acid contents and transport in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) under different nitrogen conditions. Planta 221, 328–338 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1446-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1446-8