Abstract.
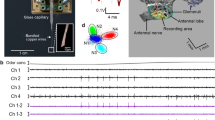
Responses to single pheromone molecules, elementary receptor currents (ERC), recorded from antennal olfactory receptor neurones of the moth Bombyx mori were studied in situ, at the opened sensilla, using the voltage-clamp technique in transepithelial recordings. The amplitude parameters of the ERCs eliciting one action potential in the bombykol and bombykal receptor neurones were analysed. The ERC amplitude varied largely within a range of 0.5–5.5 pA. The amplitude histograms of the ERCs exhibited a series of peaks and shoulders. Quantal analysis of the amplitude distributions based on spectral methods revealed that a quantum event underlies the ERCs. Deconvolution of the ERC amplitude distributions using the distribution of baseline noise indicates that the ERCs exhibit discrete amplitude levels. The weighted average interval between the levels indicates that the quantal size is 0.6–0.7 pA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 29 April 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Redkozubov, A. Elementary receptor currents elicited by a single pheromone molecule exhibit quantal composition. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 440, 896–901 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240000345
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240000345