Abstract.
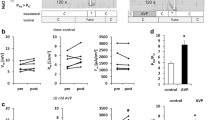
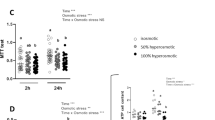
Minute-by-minute net water fluxes (J w) were measured across the isolated rectal epithelium in rats and rabbits. Five minutes after a serosal (but not mucosal) hypertonic challenge (plus 200 mosmol/l) a significant increase in the basal J w was recorded in both species [ΔJ w, µl min–1 cm–2: 0.40±0.06 (rats); 0.45±0.10 (rabbits)]. At the same time, most epithelial cells shrank markedly while the intercellular spaces were wide open (electron microscopy studies). In freeze-fracture studies multi-strand tight-junction structures (only slightly modified by serosal hypertonicity in rabbits) were observed in control conditions. No structural changes were observed after mucosal hypertonicity (both in rats and rabbits). Immunohistochemical studies showed the expression of aquaporin 3 (AQP3) at the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells in the rat. A first conclusion is that the epithelium of the mammalian rectum is a highly polarized, aquaporin-3-containing, water permeability structure. The J w increase induced by serosal hypertonicity was sensitive to mercurial agents in both species and no changes in unidirectional [14C]mannitol fluxes (P s) or transepithelial resistance (R T) were observed during this J w increase. These observations suggest a transcellular route for the osmotically induced increase in water fluxes. In the rabbit rectum the initial J w response, associated with serosal hypertonicity, was a transient one. It was followed by a second, slow and HgCl2-sensitive J w increase (a transient peak in paracellular mannitol permeability was also observed). A second conclusion is that serosal hypertonicy induces an increase in transcellular water permeability in both rat and rabbit rectum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 6 March 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kierbel, A., Capurro, C., Pisam, M. et al. Effects of medium hypertonicity on water permeability in the mammalian rectum: ultrastructural and molecular correlates. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 440, 609–618 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240000308
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240000308