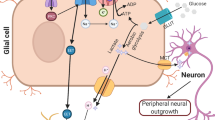
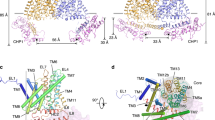
Abstract
NCX proteins explore the electrochemical gradient of Na+ to mediate Ca2+-fluxes in exchange with Na+ either in the Ca2+-efflux (forward) or Ca2+-influx (reverse) mode, whereas the directionality depends on ionic concentrations and membrane potential. Mammalian NCX variants (NCX1-3) and their splice variants are expressed in a tissue-specific manner to modulate the heartbeat rate and contractile force, the brain’s long-term potentiation and learning, blood pressure, renal Ca2+ reabsorption, the immune response, neurotransmitter and insulin secretion, apoptosis and proliferation, mitochondrial bioenergetics, etc. Although the forward mode of NCX represents a major physiological module, a transient reversal of NCX may contribute to EC-coupling, vascular constriction, and synaptic transmission. Notably, the reverse mode of NCX becomes predominant in pathological settings. Since the expression levels of NCX variants are disease-related, the selective pharmacological targeting of tissue-specific NCX variants could be beneficial, thereby representing a challenge. Recent structural and biophysical studies revealed a common module for decoding the Ca2+-induced allosteric signal in eukaryotic NCX variants, although the phenotype variances in response to regulatory Ca2+ remain unclear. The breakthrough discovery of the archaebacterial NCX structure may serve as a template for eukaryotic NCX, although the turnover rates of the transport cycle may differ ∼103-fold among NCX variants to fulfill the physiological demands for the Ca2+ flux rates. Further elucidation of ion-transport and regulatory mechanisms may lead to selective pharmacological targeting of NCX variants under disease conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CALX:
-
Drosophila melanogaster NCX ortholog
- CAX:
-
Ca2+/anion exchanger
- CBD:
-
Ca2+ binding domain
- E Ca :
-
Equilibrium potential of Ca2+
- E NCX :
-
Equilibrium potential of NCX
- FRCRCFa:
-
NCX inhibitory cyclic hexapeptide
- FRET:
-
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer.
- I1-inactivation:
-
Na+-dependent inactivation of NCX
- I2-inactivation:
-
Ca2+-dependent inactivation of NCX
- NCLX:
-
Mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
- NCKX:
-
Na+/Ca2+-K+ exchanger
- NCX:
-
Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
- n H :
-
Hill coefficient
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- SAXS:
-
Small-angle X-ray scattering
- SLC8:
-
Solute carrier 8 gene family
- SLC24:
-
Solute carrier 24 gene family
- SR:
-
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- TM:
-
Trans-membrane segment
- VCX:
-
Vacuolar Ca2+/H+ exchanger
- LTCC:
-
L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel
- XIP:
-
NCX inhibitory peptide
References
Ago Y, Kawasaki T, Nashida T, Ota Y, Cong Y, Kitamoto M et al (2011) SEA0400, a specific Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitor, prevents dopaminergic neurotoxicity in an MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 61:1441–1451
Altimimi HF, Fung EH, Winkfein RJ, Schnetkamp PP (2010) Residues contributing to the Na+-binding pocket of the SLC24 Na+/Ca2+-K+ exchanger NCKX2. J Biol Chem 285:15245–15255
Andrikopoulos P, Baba A, Matsuda T, Djamgoz MBA, Yaqoob MM, Eccles SA (2011) Ca2+ influx through reverse mode Na+/Ca2+ exchange is critical for vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 activation and angiogenic functions of human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 286:37919–37931
Annunziato L, Pignataro G, Di Renzo GF (2004) Pharmacology of brain Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: From molecular biology to therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol Rev 56:633–654
Antoons G, Willems R, Sipido KR (2012) Alternative strategies in arrhythmia therapy: Evaluation of Na/Ca exchange as an anti-arrhythmic target. Pharmacol Ther 134:26–42
Baazov D, Wang X, Khananshvili D (1999) Time-resolved monitoring of electrogenic Na+-Ca2+ exchange in the isolated cardiac sarcolemma vesicles by using a rapid-response fluorescent probe. Biochemistry 38:1435–1445
Berberián G, Forcato D, Beaugé L (2009) Key role of a PtdIns-4,5P2 micro domain in ionic regulation of the mammalian heart Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Cell Calcium 45:546–553
Bers DM (2000) In: Excitation-contraction coupling and cardiac contractile force, 2nd edit., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 133–333
Bers DM (2002) Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature 415:198–205
Bers DM (2008) Calcium cycling and signaling in cardiac myocytes. Annu Rev Physiol 70:23–49
Bers DM, Grandi E (2011) Human atrial fibrillation: insights from computational electrophysiological models. Trends Cardiovasc Med 21:145–150
Besserer GM, Ottolia M, Nicoll DA, Chaptal V, Cascio D, Philipson KD, Abramson J (2007) The second Ca2+-binding domain of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger is essential for regulation: Crystal structures and mutational analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18467–18472
Besserer GM, Nicoll DA, Abramson J, Philipson (2012) Characterization and purification of a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger from an archaebacterium. J Biol Chem 287:8652–8659
Biesmans L, Macquaide N, Heinzel FR, Bito V, Smith GL, Sipido KR (2011) Subcellular heterogeneity of ryanodine receptor properties in ventricular myocytes with low T-tubule density. PLoS One 6(10):e25100
Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ (1999) Sodium/calcium exchange: Its physiological implications. Physiol Rev 79:763–854
Blaustein MP, Leenen FH, Chen L, Golovina VA et al (2012) How NaCl raises blood pressure: A new paradigm for the pathogenesis of salt-dependent hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H1031–H1049
Boscia F, D’Avanzo C, Pannaccione A, Secondo A, Casamassa A, Formisano L, Guida N, Annunziato L (2011) Silencing or knocking out the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-3 (NCX3) impairs oligodendrocyte differentiation. Cell Death Differ. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.125
Boscia F, Gala R, Pignataro G, de Bartolomeis A, Cicale M et al (2006) Permanent focal brain ischemia induces isoform-dependent changes in the pattern of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger gene expression in the ischemic core, periinfarct area, and intact brain regions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:502–517
Boscia F, Gala R, Pannaccione A, Secondo A, Scorziello A, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (2009) NCX1 expression and functional activity increase in microglia invading the infarct core. Stroke 40:3608–3617
Bourgonje VJ, Vos MA, Ozdemir S, Doisne N, Acsai K, Varro A et al (2013) Combined Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and L-type calcium channel block as a potential strategy to suppress arrhythmias and maintain ventricular function. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 6:371–379
Boyman L, Hagen BM, Giladi M, Hiller R, Lederer WJ, Khananshvili D (2011) Proton-sensing Ca2+ binding domains regulate the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem 286:28811–28820
Boyman L, Hiller R, Lederer WJ, Khananshvili D (2008) Direct loading of the purified endogenous inhibitor into the cytoplasm of patched cardiomyocytes blocks the ion currents and calcium transport through the NCX1 protein. Biochemistry 47:6602–6611
Boyman L, Mikhasenko H, Hiller R, Khananshvili D (2009) Kinetic and equilibrium properties of regulatory calcium sensors of NCX1 protein. J Biol Chem 284:6185–6193
Boyman L, Williams GSB, Khananshvili D, Sekler I, Lederer WJ (2013) NCLX: The mitochondrial sodium calcium exchanger. J Mol Cell Cardiol 59:205–213
Breukels V, Konijnenberg A, Nabuurs SM, Touw WG, Vuister GW (2011) The second Ca2+-binding domain of NCX1 binds Mg2+ with high affinity. Biochemistry 50:8804–8812
Cai X, Lytton J (2004) The cation/Ca2+ exchanger superfamily: phylogenetic analysis and structural implications. Mol Biol Evol 21:1692–1703
Chaptal V, Besserer GM, Ottolia M, Nicoll DA, Cascio D, Philipson KD, Abramson J (2007) How does regulatory Ca2+ regulate the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger? Channels 1:397–403
Chaptal V, Ottolia M, Mercado-Besserer G, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD, Abramson J (2009) Structure and functional analysis of a Ca2+ sensor mutant of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem 284:14688–14692
Chen L, Koh DS, Hille B (2003) Dynamics of calcium clearance in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 52:1723–1731
Cheung JY, Rothblum LI, Moorman JR, Tucker AL, Song J, Ahlers BA, Carl LL, Wang J, Zhang XQ (2007) N Y Acad Sci 1099:119–134
Cheung JY, Zhang XQ, Song J, Gao E, Chan TO, Rabinowitz JE, Koch WJ, Feldman AM, Wang J (2013) Coordinated regulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and Na+-K+-ATPase by phospholemman (FXYD1). Adv Exp Med Biol 961:175–190
Cheung JY, Zhang XQ, Song J, Gao E, Rabinowitz JE, Chan TO, Wang J (2010) Phospholemman: A novel cardiac stress protein. Clin Transl Sci 4:189–196
Cook NJ, Kaupp UB (1988) Solubilization, purification and functional reconstitution of the sodium-calcium exchanger from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem 263:11382–11388
Cross JL, Meloni BP, Bakker AJ, Lee S, Knuckey NW (2010) Modes of neuronal calcium entry and homeostasis following cerebral ischemia. Stroke Res Treat 2010:316862
DiPolo R, Beauge L (2006) Sodium/calcium exchanger: Influence of metabolic regulation on ion carrier interactions. Physiol Rev 86:155–203
Doering AE, Eisner DA, Lederer WJ (1996) Cardiac Na-Ca exchange and pH. Ann N Y Acad Sci 779:182–198
Doering AE, Lederer WJ (1994) The action of Na+ as a cofactor in the inhibition by cytoplasmic protons of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in the guinea-pig. J Physiol 480:9–20
Dunn J, Elias CL, Le HD, Omelchenko A, Hryshko LV, Lytton J (2002) The molecular determinants of ionic regulatory differences between brain and kidney Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1) isoforms. J Biol Chem 277:33957–33962
Dyck C, Omelchenko A, Elias CL, Quednau BD, Philipson KD, Hnatowich M, Hryshko LV (1999) Ionic regulatory properties of brain and kidney splice variants of the NCX1 Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Gen Physiol 114:701–711
Eisner D, Sipido K (2004) Sodium calcium exchange in the heart—Necessity or luxury? Circ Res 95:549–551
Forrest LR, Krämer R, Ziegler C (2011) The structural basis of secondary active transport mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Acta 1807:167–188
Gao Z, Rasmussen TP, Li Y, Kutschke W, Koval OM, Wu Y et al (2013) Genetic inhibition of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger current disables fight or flight sinoatrial node activity without affecting resting heart rate. Circ Res 112:309–317
Giladi M, Bohbot H, Buki T, Schulze DH, Hiller R, Khananshvili D (2012) Dynamic features of allosteric Ca2+ sensor in tissue-specific NCX variants. Cell Calcium 51:478–485
Giladi M, Boyman L, Mikhasenko H, Hiller R, Khananshvili D (2010) Essential role of the CBD1-CBD2 linker in slow dissociation of Ca2+ from the regulatory two-domain tandem of NCX1. J Biol Chem 285:28117–28125
Giladi M, Friedberg I, Fang X, Hiller R, Wang YX, Khananshvili D (2012) G503 is obligatory for coupling of regulatory domains in NCX proteins. Biochemistry 51:7313–7320
Giladi M, Hiller R, Hirsch JA, Khananshvili D (2013) Population shift underlies Ca2+-induced regulatory transitions in the sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX). J Biol Chem 288:23141–23149
Giladi M, Khananshvili D (2013) Molecular determinants of allosteric regulation in NCX proteins. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:35–48
Giladi M, Sasson Y, Fang X, Hiller R, Buki T, Wang Y-X, Hirsch JA, Khananshvili D (2012) A common Ca2+-driven interdomain module governs eukaryotic NCX regulation. PloS One 7(6):e39985
Ginsburg KS, Weber CR, Bers DM (2013) Cardiac Na+–Ca2+ exchanger: Dynamics of Ca2+-dependent activation and deactivation in intact myocytes. J Physiol 591:2067–2086
Goldhaber JI, Philipson KD (2013) Cardiac sodium-calcium exchange and efficient excitation-contraction coupling: Implications for heart disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:355–364
Greiser M, Lederer WJ, Schotten U (2011) Alterations of atrial Ca2+ handling as cause and consequence of atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 89:722–733
Guo K, Wang X, Gao G, Huang C, Elmslie KS, Peterson BZ (2010) Amino acid substitutions in the FXYD motif enhance phospholemman-induced modulation of cardiac L-type calcium channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 99:C1203–C1211
Herchuelz A, Kamagate A, Ximenes H, Van Eylen F (2007) Role of Na/Ca exchange and the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in beta cell function and death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1099:456–467
Herchuelz A, Nguidjoe E, Jiang L, Pachera N (2012) β-Cell preservation and regeneration in diabetes by modulation of β-cell Ca2+ homeostasis. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(Suppl 3):136–142
Herchuelz A, Nguidjoe E, Jiang L, Pachera N (2013) Na+/Ca2+ exchange and the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in β-cell function and diabetes. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:385–394
Herrmann S, Lipp P, Wiesen K, Stieber J, Nguyen H, Kaiser E, Ludwig A (2013) The cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger NCX1 is a key player in the initiation and maintenance of a stable heart rhythm. Cardiovasc Res 99(4):780–788. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvt154
Hilge M, Aelen J, Vuister GW (2006) Ca2+ regulation in the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger involves two markedly different Ca2+ sensors. Mol Cell 22:15–25
Hilge M, Aelen J, Foarce A, Perrakis A, Vuister GW (2009) Ca2+ regulation in the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger features a dual electrostatic switch mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14333–14331
Hilgemann DW (1990) Regulation and deregulation of cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange in giant excised sarcolemmal membrane patches. Nature 344:242–245
Hilgemann DW, Ball R (1996) Regulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchange and MgATP potassium channels by PIP2. Science 273:956–959
Hilgemann DW, Collins A, Matsuoka S (1992) Steady-state and dynamic properties of cardiac Na/Ca. Secondary modulation by cytoplasmic calcium and ATP. J Gen Physiol 100:933–961
Hilgemann DW, Matsuoka S, Nagel GA, Collins A (1992) Steady-state and dynamic properties of cardiac sodium-calcium exchange. Sodium-dependent inactivation. J Gen Physiol 100:905–932
Hilgemann DW, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD (1991) Charge movement during Na+-translocation by native and cloned Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Nature 352:715–718
Hobai IA, Khananshvili D, Levi AJ (1997) The peptide ‘FRCRCFa’, dialyzed intracellularly, inhibits the Na/Ca exchange with high affinity in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Plugers Arch 433:455–463
Hryshko L (2008) What regulates Na+/Ca2+ exchange? Focus on “sodium-dependent inactivation of sodium/calcium exchange in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295:C869-871
Hryshko LV, Matsuoka S, Nicoll DA, Weiss JN, Schwarz EM et al (1996) Anomalous regulation of the Drosophila Na+-Ca2+ exchanger by Ca2+. J Gen Physiol 108:67–74
Imahashi K, Pott C, Goldhaber JI, Steenbergen C, Philipson KD, Murphy E (2005) Cardiac-specific ablation of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger confers protection against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res 97:916–921
Iwamoto T, Kita S, Zhang J, Blaustein MP, Arai Y, Yoshida S, Wakimoto K, Komuro I, Katsuragi T (2004) Salt-sensitive hypertension is triggered by Ca2+ entry via Na+/Ca2+ exchanger type-1 in vascular smooth muscle. Nat Med 10:1193–1199
Iwamoto T, Watanabe Y, Kita S, Blaustein MP (2007) Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitors: a new class of calcium regulators. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets 3:188–198
Iwamoto T, Watano T, Shigekawa M (1996) A novel isothiourea derivative selectively inhibits the reverse mode of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in cells expressing NCX1. J Biol Chem 271:22391–22397
Jayasinghe ID, Baddeley D, Kong CH, Wehrens XH, Cannell MB, Soeller C (2012) Nanoscale organization of junctophilin-2 and ryanodine receptors within peripheral couplings of rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. Biophys J 102:L19–L21
Jayasinghe I, Dj C, Soeller C, Cannell M (2012) Comparison of the organization of T-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum and ryanodine receptors in rat and human ventricular myocardium. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 39:469–476
Jeffs GJ, Meloni BP, Sokolow S, Herchuelz A, Schurmans S, Knuckey NW (2008) NCX3 knockout mice exhibit increased hippocampal CA1 and CA2 neuronal damage compared to wild-type mice following global cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 210:268–273
Jeon D, Yang YM, Jeong MJ, Philipson KD, Rhim H, Shin HS (2003) Enhanced learning and memory in mice lacking Na+-Ca2+ exchanger 2. Neuron 38:965–976
John SA, Liao J, Jiang Y, Ottolia M (2013) The cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger has two cytoplasmic ion permeation pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:7500–7505
John SA, Ribalet B, Weiss JN, Philipson KD, Ottolia M (2011) Ca2+-dependent structural rearrangements within Na+-Ca2+ exchanger dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:1699–1704
Kemeny LV, Schnur A, Czepan M, et al (2013) Na+/Ca2+ exchangers regulate the migration and proliferation of human gastric myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 305:G552-G563
Khananshvili D (2013) The SLC8 gene family of sodium-calcium exchangers (NCX)—Structure, function, and regulation in health and disease. Mol Aspects Med 34:220–235
Khananshvili D (1998) Structure, mechanism and regulation of the cardiac sarcolemma Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Mol Cell Biol 23B:309–356
Khananshvili D (1990) Distinction between the two basic mechanisms of cation transport in the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange system. Biochemistry 29:2437–2442
Khananshvili D (1991) Voltage-dependent modulation of ion binding and translocation in the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange system. J Biol Chem 266:13764–13769
Khananshvili D (1991) Mechanism of partial reactions in the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Ann N Y Acad Sci 639:85–98
Khananshvili D, Shaulov G, Weil-Maslansky E (1995) Rate-limiting mechanisms of exchange reactions in the cardiac sarcolemma Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Biochemistry 34:10290–10297
Khananshvili D, Shaulov G, Weil-Maslansky E, Baazov D (1995) Positively charged cyclic hexapeptides, novel blockers for the cardiac sarcolemma Na+-Ca2+ exchange. J Biol Chem 270:16182–16188
Khananshvili D, Weil-Maslansky E, Baazov D (1996) Kinetics and mechanism: modulation of ion transport in the cardiac sarcolemma sodium-calcium exchanger by protons, monovalent, ions, and temperature. Ann N Y Acad Sci 779:217–235
Kofuji P, Lederer WJ, Schulze DH (1994) Mutually exclusive and cassette exons underlie alternatively spliced isoforms of the Na/Ca exchanger. J Biol Chem 269:5145–5149
Lakatta EG, DiFrancesco D (2009) What keeps us ticking: A funny current, a calcium clock, or both? J Mol Cell Cardiol 47:157–170
Laüger P (1987) Voltage dependence of sodium-calcium exchange: Predictions from kinetic models. J Membr Biol 99:1–11
Lee SL, Yu AS, Lytton J (1994) Tissue-specific expression of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger isoforms. J Biol Chem 269:14849–14852
Li Z, Nicoll DA, Collins A, Hilgemann DW et al (1991) Identification of a peptide inhibitor of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem 266:1014–1020
Liao J, Li H, Zeng W, Sauer DB, Belmares R, Jiang Y (2012) Structural insight into the ion-exchange mechanism of the sodium/calcium exchanger. Science 335:686–690
Linck B, Bokník P, Huke S, Kirchhefer U et al (2000) Functional properties of transgenic mouse hearts overexpressing both calsequestrin and the Na+/Ca2+exchanger. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:648–657
Linck B, Qiu Z, He Z, Tong Q, Hilgemann DW, Philipson KD (1998) Functional comparison of the three isoforms of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1, NCX2, NCX3). Am J Physiol 274:C415–C423
Lytton J (2007) Na+/Ca2+ exchangers: Three mammalian gene families control Ca2+-transport. Biochem J 406:365–382
Maack C, Ganesan A, Sidor A, O’Rourke B (2005) Cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger is regulated by allosteric calcium and exchanger inhibitory peptide at distinct sites. Circ Res 96:91–99
Ma B, Tsai C-J, Haliloğlu T, Nussinov R (2011) Dynamic allostery: Linkers are not merely flexible. Structure 19:907–917
Mangoni ME, Nargeot J (2008) Genesis and regulation of the heart automaticity. Physiol Rev 88:919–982
Matsuda T, Arakawa N, Takuma K, Kishida Y, Kawasaki Y et al (2001) SEA0400, a novel and selective inhibitor of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, attenuates reperfusion injury in the in vitro and in vivo cerebral ischemic models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:249–256
Matsuoka S, Nicoll DA, Hryshko LV, Levitsky DO, Weiss JN, Philipson KD (1995) Regulation of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger by Ca2+. Mutational analysis of the Ca2+-binding domain. J Gen Physiol 105:403–420
Matsuoka S, Nicoll DA, Reilly RF, Hilgemann DW, Philipson KD (1993) Initial localization of regulatory regions of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:3870–3874
Matsuoka S, Nicoll DA, He Z, Philipson KD (1997) Regulation of cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger by the endogenous XIP region. J Gen Physiol 109:273–286
Meszaros J, Khananshvili D, Hart G (2001) Mechanisms underlying delayed afterdepolarizations in hypertrophied left ventricular myocytes of rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H903–H914
Milberg P, Pott C, Frommeyer G, Fink M, Ruhe M, Matsuda T, Baba A et al (2012) Acute inhibition of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger reduces proarrhythmia in an experimental model of chronic heart failure. Heart Rhythm 9:570–578
Nagy ZA, Virág L, Tóth A, Biliczki P, Acsai K, Bányász T, Nánási P, Papp JG, Varró A (2004) Selective inhibition of sodium-calcium exchanger by SEA-0400 decreases early and delayed after depolarization in canine heart. Br J Pharmacol 143:827–831
Neco P, Rose B, Huynh N, Zhang R, Bridge JH, Philipson KD, Goldhaber JI (2010) Sodium-calcium exchange is essential for effective triggering of calcium release in mouse heart. Biophys J 99:755–764
Nicoll DA, Applebury ML (1989) Purification of the bovine rod outer segment Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem 264:16207–16213
Nicoll DA, Longoni S, Philipson KD (1990) Molecular cloning and functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Science 250:562–565
Nicoll DA, Sawaya MR, Kwon S, Cascio D, Philipson KD, Abramson J (2006) The crystal structure of the primary Ca2+ sensor of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger reveals a novel Ca2+ binding motif. J Biol Chem 281:21577–21581
Niggli E, Lederer WJ (1991) Molecular operations of the sodium-calcium exchanger revealed by conformational currents. Nature 349:621–624
Nishizawa T, Kita S, Maturana AD, Furuya N, Hirata K, Kasuya G, Ogasawara S, Dohmae N, Iwamoto T, Ishitani R and Nureki O. (2013). Structural basis for the counter-transport mechanism of a H+/Ca2+ exchanger. Science www.sciencemag.org/content/early/recent
Nita II, Hershfinkel M, Fishman D, Ozeri E, Rutter GA, Sensi SL, Khananshvili D, Lewis EC, Sekler I. The mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger upregulates glucose dependent Ca2+ signaling linked to insulin secretion. PloS One 7(10):e46649
Noda M, Ifuku M, Mori Y, Verkhratsky A (2013) Calcium influx through reversed NCX controls migration of microglia. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:289–294
Ohtsuka M, Takano H, Suzuki M, Zou Y, Akazawa H et al (2004) Role of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Evaluation using a heterozygous Na+-Ca2+ exchanger knockout mouse model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:849–853
Omelchenko A, Dyck C, Hnatowich M, Buchko J, Nicoll DA et al (1998) Functional differences in ionic regulation between alternatively spliced isoforms of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger from Drosophila melanogaster. J Gen Physiol 111:691–702
On C, Marshall CR, Chen N, Moyes CD, Tibbits GF (2008) Gene structure evolution of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) family. BMC Evol Biol 8:127–142
On C, Marshall CR, Perry SF, Le HD, Yurkov V, Omelchenko A, Hnatowich M, Hryshko LV, Tibbits GF (2009) Characterization of zebrafish (Danio rerio) NCX4: A novel NCX with distinct electrophysiological properties. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C173–C181
Ota Y, Kawanai T, Watanabe R, Nishimura A, Ago Y, Takuma K, Matsuda T (2013) Effect of overexpression of the brain-specific Na+/Ca2+ exchanger splice variant NCX1.5 on NO cytotoxicity in HEK293 cells. J Pharmacol Sci 121:351–354
Ottolia M, Nicoll DA, John S, Philipson KD (2010) Interactions between Ca2+ binding domains of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger and secondary regulation. Channels 4:1–4
Ottolia M, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD (2009) Roles of two Ca2+-binding domains in regulation of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem 284:32735–32741
Ottolia M, Torres N, Bridge JH, Philipson KD, Goldhaber JI (2013) Na/Ca exchange and contraction of the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 61:28–33
Palty R, Hershfinkel M, Sekler I (2012) Molecular identity and functional properties of the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem 287:31650–31657
Palty R, Silverman WF, Hershfinkel M, Caporale T, Sensi SL, Parnis J, Nolte C, Fishman D, Shoshan-Barmatz V, Herrmann S, Khananshvili D, Sekler I (2010) NCLX is an essential component of mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:436–441
Parnis J, Montana V, Delgado-Martinez I, Matyash V, Parpura V, Kettenmann H, Sekler I, Nolte CJ (2013) Mitochondrial exchanger NCLX plays a major role in the intracellular Ca2+ signaling, gliotransmission, and proliferation of astrocytes. J Neurosci 33:7206–7219
Pavlovic D, Fuller W, Shattock MJ (2013) Novel regulation of cardiac Na pump via phospholemman. J Mol Cell Cardiol 61:83–93
Philipson KD, Nicoll DA (2000) Sodium-calcium exchange: A molecular perspective. Annu Rev Physiol 62:111–133
Pobarko D, Fameli N, Kuo KH, van Breemen C (2008) Ca2+ signaling in smooth muscle: TRPC6, NCX and Na+ in nanodomains. Channels 2:10–12
Pott C, Eckardt L, Goldhaber JI (2011) Triple threat: the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in the pathophysiology of cardiac arrhythmia, ischemia and heart failure. Curr Drug Targets 12:737–747
Pott C, Philipson KD, Goldhaber JI (2005) Excitation-contraction coupling in Na+-Ca2+ exchanger knockout mice: Reduced transsarcolemmal Ca2+ flux. Circ Res 97:1288–1295
Puglisi JL, Negroni JA, Chen-Izu Y, Bers DM (2013) The force-frequency relationship: Insights from mathematical modeling. Adv Physiol Educ 37:28–34
Reeves JP, Hale CC (1984) The stoichiometry of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchange system. J Biol Chem 259:7733–7739
Reeves JP, Condrescu M (2008) Ionic regulation of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger. Channels 2:322–328
Ren X, Philipson K (2013) The topology of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, NCX1. J Mol Cell Cardiol 57:68–71
Reuter H, Henderson SA, Han T, Matsuda T, Baba A, Ross RS, Goldhaber JI, Philipson KD (2002) Knockout mice for pharmacological screening: testing the specificity of Na+-Ca2+ exchange inhibitors. Circ Res 91:90–92
Reuter H, Henderson SA, Han T, Mottino GA, Frank JS, Ross RS, Goldhaber JI, Philipson KD (2003) Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in the absence of Na+-Ca2+ exchange. Cell Calcium 34:19–26
Reyes RC, Verkhratsky A, Parpura V (2012) Plasmalemmal Na+/Ca2+ exchanger modulates Ca2+-dependent exocytotic release of glutamate from rat cortical astrocytes. ASN Neurol 4(1):e00075
Rispoli G, Navangione A, Vellani V (1995) Transport of K + by Na + -Ca2+, K + exchanger in isolated rods of lizard retina. Biophys J 69:74–81
Roome CJ, Power EM, Empson RM (2013) Transient reversal of the sodium/calcium exchanger boosts presynaptic calcium and synaptic transmission at a cerebellar synapse. J Neurophysiol 109:1669–1680
Rose CR, Karus C (2013) Two sides of the same coin: Sodium homeostasis and signaling in astrocytes under physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Glia 61:1191–1205
Salinas PK, Brüschweiler-Li L, Johnson E, Brüschweiler R (2011) Ca2+ binding alters the inter-domain flexibility between the cytoplasmic Ca-binding domains in the Na/Ca exchanger. J Biol Chem 286:32123–32131
Schnetkamp PP (2013) The SLC24 gene family of Na+/Ca2+-K+ exchangers: From sight and smell to memory consolidation and skin pigmentation. Mol Asp Med 34:455–464
Sirabella R, Secondo A, Pannaccione A, Molinaro P, Formisano L, Guida N, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L, Cataldi M (2012) ERK1/2, p38, and JNK regulate the expression and the activity of the three isoforms of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3, in neuronal PC12 cells. J Neurochem 122:911–922
Sobie EA, Song LS, Lederer WJ (2002) Termination of cardiac Ca2+ sparks: An investigative mathematical model of calcium-induced calcium release. Biophys J 83:59–78
Stein WD (1986) Transport and diffusion across cell membranes. Acad. Press, NY, pp 55–120
Svensson KJ, Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC et al (2011) Hypoxia triggers a proangiogenic pathway involving cancer cell microvesicles and PAR-2-mediated heparin-binding EGF signaling in endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:13147–13152
Takuma K, Ago Y, Matsuda T (2013) The glial sodium-calcium exchanger: A new target for nitric oxide-mediated cellular toxicity. Curr Protein Pept Sci 14:43–50
Takuma K, Tanaka T, Takahashi T, Hiramatsu N, Ota Y, Ago Y, Matsuda T (2012) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition attenuates the development of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemi-Parkinsonian rats. Eur J Pharmacol 683:166–173
Tóth A, Kiss L, Varró A, Nánási PP (2009) Potential therapeutic effects of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibition in cardiac diseases. Curr Med Chem 16:3294–3321
Tsai CJ, del Sol A, Nussinov R (2008) Allostery: Absence of a change in shape does not imply that allostery is not at play. J Mol Biol 378:1–11
Valsecchi V, Pignataro G, Del Prete A, Sirabella R et al (2011) NCX1 is a novel target gene for hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in ischemic brain preconditioning. Stroke 42:754–763
Voigt N, Li N, Wang Q, Wang W, Trafford AW et al (2012) Enhanced sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak and increased Na+-Ca2+ exchanger function underlie delayed afterdepolarizations in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation 125:2059–2070
Waight AB, Pedersen BP, Schlessinger A, Bonomi M, Chau BH, Roe-Zurz Z, Risenmay AJ, Sali A, Stroud RM (2013) Structural basis for alternating access of a eukaryotic calcium/proton exchanger. Nature 499:107–110
Weisbrod D, Peretz A, Ziskind A, Menaker N, Oz S, Barad L, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Dascal N, Khananshvili D, Binah O, Attali B (2013) The Ca2+-activated K+ channel IKCa/SK4: A critical new player in human embryonic cardiac pacemaker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:1685–1694
Wu M, Tong S, Gonzalez J, Jayaraman V, Spudich JL, Zheng L (2011) Structural basis of the Ca2+ inhibitory mechanism of Drosophila Na/Ca exchanger CALX and its modification by alternative splicing. Structure 19:1509–1517
Wu M, Tonga S, Walterspergerb S, Diederichsc K, Wang M and Zheng L (2013) Crystal structure of Ca2+/H+ antiporter protein YfkE reveals the mechanisms of Ca2+ efflux and its pH regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302515110
Zhang J (2013) New insights into the contribution of arterial NCX to the regulation of myogenic tone and blood pressure. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:329–343
Zhang S, Dong H, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2007) Upregulation of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger contributes to the enhanced Ca2+ entry in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C2297–C2305
Zhang J, Ren C, Chen L, Navedo MF, Antos LK et al (2010) Knockout of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in smooth muscle attenuates vasoconstriction and L-type Ca2+ channel current and lowers blood pressure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298:H1472–H1483
Zhang J, Ren C, Chen L, Navedo MF et al (2010) Knockout of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in smooth muscle attenuates vasoconstriction and L-type Ca2+ channel current and lowers blood pressure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298:H1472–H1483
Zulian A, Baryshnikov SG, Linde CI, Hamlyn JM, Ferrari P, Golovina VA (2010) Upregulation of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and TRPC6 contributes to abnormal Ca2+ homeostasis in arterial smooth muscle cells from Milan hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299:H624–H633
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Israeli Ministry of Health grant #2010-3-6266, the USA-Israeli Binational Research grant # 2009-334, and the Israel Science Foundation grant #23/10. Financial support from the Fields Foundation is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memoriam John Reeves
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khananshvili, D. Sodium-calcium exchangers (NCX): molecular hallmarks underlying the tissue-specific and systemic functions. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 43–60 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1405-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1405-y