Abstract
Purpose
The clinical importance of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas (IPMN) has been increasing with a large number of newly diagnosed IPMN. This study was designed to explore the characteristics of resected IPMN and to determine the predictive factors for malignant and invasive IPMN.
Methods
Retrospective review of a prospectively collected database was performed on 187 consecutive patients following IPMN surgery between 1994 and 2008 at a tertiary institute. The main duct type IPMN was radiologically defined as main pancreatic duct dilation >5 mm rather than previously defined ≥10 mm.
Results
The morphologic types of IPMN included 28 main duct (IPMN-M, 15.0%), 118 branch duct (IPMN-Br, 63.1%), and 41 mixed (IPMN-Mixed, 21.9%) IPMNs. There were 23 patients with adenoma, 106 borderline atypia, 15 carcinoma in situ, and 43 invasive carcinoma. Sixty-nine extrapancreatic malignancies were diagnosed in 61 (32.6%) patients. Based on multivariate analysis, IPMN-M was statistically significant predictor of malignancy/invasiveness (p = 0.013/p = 0.028). In patients with IPMN-Br, the presence of mural nodule was a predictive factor for malignancy/invasiveness (p = 0.005/p = 0.002). In patients with IPMN-Mixed, mural nodule (p = 0.038/p = 0.047) and wall thickening (>2 mm, p = 0.015/p = 0.046) were risk factor for malignancy/invasiveness and elevated CA19-9 (p = 0.046) for invasiveness.
Conclusions
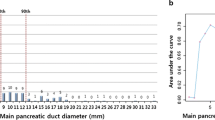
The main pancreatic duct diameter (>5 mm) is a significant predictor for malignancy and invasiveness. Therefore, IPMN patients with main pancreatic duct dilatation (>5 mm) should be considered surgical resection. Mural nodule is the indicator of surgery in IPMN-Br and IPMN-Mixed. In case of IPMN-Mixed with wall thickening or elevated serum CA19-9, surgical resection is recommended.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodriguez JR, Salvia R, Crippa S et al (2007) Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations in 145 patients who underwent resection. Gastroenterology 133(1):72–79, quiz 309-10
Longnecker DS, Adsay NV, Fernandez-del Castillo C et al (2005) Histopathological diagnosis of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms: interobserver agreement. Pancreas 31(4):344–349
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V et al (2006) International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 6(1–2):17–32
Levy P, Jouannaud V, O’Toole D et al (2006) Natural history of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas: actuarial risk of malignancy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4(4):460–468
Schmidt CM, White PB, Waters JA et al (2007) Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: predictors of malignant and invasive pathology. Ann Surg 246(4):644–651, discussion 651-4
Song SJ, Lee JM, Kim YJ et al (2007) Differentiation of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms from other pancreatic cystic masses: comparison of multirow-detector CT and MR imaging using ROC analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(1):86–93
Waters JA, Schmidt CM, Pinchot JW et al (2008) CT vs MRCP: optimal classification of IPMN type and extent. J Gastrointest Surg 12(1):101–109
Sahani DV, Kadavigere R, Blake M et al (2006) Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of pancreas: multi-detector row CT with 2D curved reformations–correlation with MRCP. Radiology 238(2):560–569
Chiu SS, Lim JH, Lee WJ et al (2006) Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour of the pancreas: differentiation of malignancy and benignancy by CT. Clin Radiol 61(9):776–783
Jang JY, Kim SW, Lee SE et al (2008) Treatment guidelines for branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: when can we operate or observe? Ann Surg Oncol 15(1):199–205
Jang JY, Kim SW, Ahn YJ et al (2005) Multicenter analysis of clinicopathologic features of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the pancreas: is it possible to predict the malignancy before surgery? Ann Surg Oncol 12(2):124–132
Kuroki T, Tajima Y, Tsutsumi R et al (2006) Inferior branch-preserving superior head resection of the pancreas with gastric wall-covering method for intraductal papillary mucinous adenoma. Am J Surg 191(6):823–826
Yamao K, Ohashi K, Nakamura T et al (2000) The prognosis of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Hepatogastroenterology 47(34):1129–1134
Bernard P, Scoazec JY, Joubert M et al (2002) Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas: predictive criteria of malignancy according to pathological examination of 53 cases. Arch Surg 137(11):1274–1278
Kobari M, Egawa S, Shibuya K et al (1999) Intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas comprise 2 clinical subtypes: differences in clinical characteristics and surgical management. Arch Surg 134(10):1131–1136
Yang AD, Melstrom LG, Bentrem DJ et al (2007) Outcomes after pancreatectomy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an institutional experience. Surgery 142(4):529–534, discussion 534-7
Kawai M, Uchiyama K, Tani M et al (2004) Clinicopathological features of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas: the differential diagnosis from benign entities. Arch Surg 139(2):188–192
Lee SE, Jang JY, Yang SH, Kim SW (2007) Intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma with atypical manifestations: report of two cases. World J Gastroenterol 13(10):1622–1625
Stelow EB, Stanley MW, Bardales RH et al (2003) Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. The findings and limitations of cytologic samples obtained by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. Am J Clin Pathol 120(3):398–404
Emerson RE, Randolph ML, Cramer HM (2006) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas is highly predictive of pancreatic neoplasia. Diagn Cytopathol 34(7):457–462
Choi MG, Kim SW, Han SS et al (2006) High incidence of extrapancreatic neoplasms in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Arch Surg 141(1):51–56, discussion 56
Kamisawa T, Tu Y, Egawa N et al (2005) Malignancies associated with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. World J Gastroenterol 11(36):5688–5690
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant No. 0820030).
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dae Wook Hwang and Jin-Young Jang are contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, D.W., Jang, JY., Lee, S.E. et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of surgically proven intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas in SNUH: a 15-year experience at a single academic institution. Langenbecks Arch Surg 397, 93–102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0674-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0674-6