Abstract
Purpose
Acute mental stress (MS) causes an elevation in pulse wave velocity (PWV), an index of arterial stiffness. In contrast, aerobic exercise acutely decreases arterial stiffness, even in the short term. The present study aimed to examine whether acute MS-caused arterial stiffening can be counteracted by brief aerobic exercise.
Methods
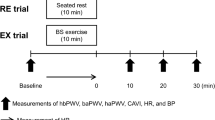
Thirteen young healthy men (mean age, 20 ± 1 years) participated in two randomized experimental visits where they were subjected to acute MS followed by seated rest (RE) or cycling exercise (EX) trials. Following a 5-min MS task, the participants in the RE trial rested on a chair for 10 min (from 10 to 20 min after the cessation of the task), whereas those in the EX trial cycled at 35% of heart rate reserve for the same duration. Heart-brachial PWV (hbPWV), brachial-ankle PWV (baPWV), heart-ankle PWV (haPWV), and the cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) were simultaneously measured at baseline and 5, 30, and 45 min after the task.
Results
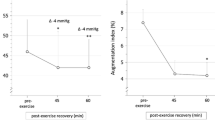
Both trials caused significant elevations (P < 0.05) in hbPWV, haPWV, and CAVI at 5 min after the task; subsequently, this persisted until 45 min after the task in the RE trial, whereas the elevations in the EX trial were eliminated. In the RE trial, baPWV significantly increased (P < 0.05) at 30 and 45 min after the task, whereas such an increase was not observed in the EX trial.
Conclusion
The findings of the present study reveal that brief aerobic exercise counteracts arterial stiffening caused by acute MS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- baPWV:
-
Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CAVI:
-
Cardio-ankle vascular index
- cfPWV:
-
Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- EX:
-
Acute mental stress followed by cycling exercise
- haPWV:
-
Heart-ankle pulse wave velocity
- hbPWV:
-
Heart-brachial pulse wave velocity
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HRR:
-
Heart rate reserve
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- MS:
-
Mental stress
- NS:
-
Not significant
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- RE:
-
Acute mental stress followed by seated rest
References
Brellenthin AG, Crombie KM, Hillard CJ, Koltyn KF (2017) Endocannabinoid and mood responses to exercise in adults with varying activity levels. Med Sci Sports Exerc 49:1688–1696. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000001276
Callister R, Suwarno NO, Seals DR (1992) Sympathetic activity is influenced by task difficulty and stress perception during mental challenge in humans. J Physiol 454:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019269
Carter JR, Kupiers NT, Ray CA (2005) Neurovascular responses to mental stress. J Physiol 564:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.079665
Chida Y, Steptoe A (2010) Greater cardiovascular responses to laboratory mental stress are associated with poor subsequent cardiovascular risk status: a meta-analysis of prospective evidence. Hypertension 55:1026–1032. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.109.146621
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, Nieman DC, Swain DP (2011) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1334–1359. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e318213fefb
Goto C, Nishioka K, Umemura T, Jitsuiki D, Sakagutchi A, Kawamura M, Chayama K, Yoshizumi M, Higashi Y (2010) Acute moderate-intensity exercise induces vasodilation through an increase in nitric oxide bioavailiability in humans. Am J Hypertens 20:825–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2007.02.014
Ghiadoni L, Donald AE, Cropley M, Mullen MJ, Oakley G, Taylor M, O’Connor G, Betteridge J, Klein N, Steptoe A, Deanfield JE (2000) Mental stress induces transient endothelial dysfunction in humans. Circulation 102:2473–2478. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.102.20.2473
Hayashi N, Someya N, Endo MY, Miura A, Fukuba Y (2006) Vasoconstriction and blood flow responses in visceral arteries to mental task in humans. Exp Physiol 91:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2005.031971
Heffernan KS, Edwards DG, Rossow L, Jae SY, Fernhall B (2007) External mechanical compression reduces regional arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:735–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0550-4
Kaewboonchoo O, Sembajwe G, Li J (2018) Associations between job strain and arterial stiffness: A large survey among enterprise employees from Thailand. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040659
Kingwell BA, Berry KL, Cameron JD, Jennings GL, Dart AM (1997) Arterial compliance increases after moderate-intensity cycling. Am J Physiol 273:H2186–H2191. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1997.273.5.h2186
Kume D, Nishiwaki M, Hotta N, Endoh H (2020) Impact of acute mental stress on segmental arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 120:2247–2257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04448-9
Kuipers NT, Sauder CL, Carter JR, Ray CA (2008) Neurovascular responses to mental stress in the supine and upright postures. J Appl Physiol 104:1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01285.2007
Matthews KA, Katholi CR, McCreath H, Whooley MA, Williams DR, Zhu S, Markovitz JH (2004) Blood pressure reactivity to psychological stress predicts hypertension in the CARDIA study. Circulation 110:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000133415.37578.E4
McEniery CM, Wallace S, Mackenzie IS, McDonnell B, DE Yasmin N, Cockcroft JR, Wilkinson IB (2006) Endothelial function is associated with pulse pressure, pulse wave velocity, and augmentation index in healthy humans. Hypertension 48:602–608. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000239206.64270.5f
Miller M, Mangano C, Park Y, Goel R, Plotnick GD, Vogel RA (2006) Impact of cinematic viewing on endothelial function. Heart 92:261–262. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2005.061424
Mitchell GF, Hwang SJ, Vasan RS, Larson MG, Pencina MJ, Hamburg NM, Vita JA, Levy D, Benjamin EJ (2010) Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 121:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.886655
Morishima T, Iemitsu M, Ochi E (2019) Short-term cycling restores endothelial dysfunction after resistance exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 29:1115–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13434
Morishima T, Padilla J, Tsuchiya Y, Ochi E (2020) Maintenance of endothelial function following acute resistance exercise in females is associated with a tempered blood pressure response. J Appl Physiol 129:792–799. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00378.2020
Nishiwaki M, Takahara K, Matsumoto N (2017) Arterial stiffness in young adult swimmers. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3505-9
Nishiwaki M, Yamaguchi T, Nishida R, Matsumoto N (2020) Dose of alcohol from beer required for acute reduction in arterial stiffness. Front Physiol 11:1033. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.01033
Okamoto T, Min SK, Sakamaki-Sunaga M (2018) Acute effect of interval walking on arterial stiffness in healthy young adults. Int J Sports Med 39:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0608-4476
Restaino RM, Holwerda SW, Credeur DP, Fadel PJ, Padilla J (2015) Impact of prolonged sitting on lower and upper limb micro- and macrovascular dilator function. Exp Physiol 100:829–838. https://doi.org/10.1113/ep085238
Sales AR, Fernandes IA, Rocha NG, Costa LS, Rocha HN, Mattos JD, Vianna LC, Silva BM, Nóbrega AC (2014) Aerobic exercise acutely prevents the endothelial dysfunction induced by mental stress among subjects with metabolic syndrome: the role of shear rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306:H963–H971. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00811.2013
Shirai K, Hiruta N, Song M, Kurosu T, Suzuki J, Tomaru T, Miyashita Y, Saiki A, Takahashi M, Suzuki K, Takata M (2011) Cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) as a novel indicator of arterial stiffness: theory, evidence and perspectives. J Atheroscler Thromb 18:924–938. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.7716
Spieker LE, Hürlimann D, Ruschitzka F, Corti R, Enseleit F, Shaw S, Hayoz D, Deanfield JE, Lüscher TF, Noll G (2002) Mental stress induces prolonged endothelial dysfunction via endothelin-A receptors. Circulation 105:2817–2820. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000021598.15895.34
Sugawara J, Tarumi T, Tanaka H (2010) Effect of mirthful laughter on vascular function. Am J Cardiol 106:856–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.05.011
Sugawara J, Tomoto T, Tanaka H (2019) Heart-to-brachium pulse wave velocity as a measure of proximal aortic stiffness: MRI and longitudinal studies. Am J Hypertens 32:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpy166
Takaishi T, Imaeda K, Tanaka T, Moritani T, Hayashi T (2012) A short bout of stair climbing-descending exercise attenuates postprandial hyperglycemia in middle-aged males with impaired glucose tolerance. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37:193–196. https://doi.org/10.1139/h11-140
Tinken TM, Thijssen DH, Black MA, Cable NT, Green DJ (2008) Time course of change in vasodilator function and capacity in response to exercise training in humans. J Physiol 586:5003–5012. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.158014
Tomoto T, Maeda S, Sugawara J (2017) Relation between arterial stiffness and aerobic capacity: Importance of proximal aortic stiffness. Eur J Sport Sci 17:571–575. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2016.1277787
Totosy de Zepetnek JO, Au JS, Ditor DS, MacDonald MJ (2015) Lower limb conduit artery endothelial responses to acute upper limb exercise in spinal cord injured and able-bodied men. Physiol Rep 3:e12367. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12367
Utsugi M, Saijo Y, Yoshioka E, Sato T, Horikawa N, Gong Y, Kishi R (2009) Relationship between two alternative occupational stress models and arterial stiffness: a cross-sectional study among Japanese workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0319-z
van Sloten TT, Schram MT, van den Hurk K, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Henry RM, Stehouwer CD (2014) Local stiffness of the carotid and femoral artery is associated with incident cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality: the Hoorn study. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:1739–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.12.041
Vlachopoulos C, Kosmopoulou F, Alexopoulos N, Ioakeimidis N, Siasos G, Stefanadis C (2006) Acute mental stress has a prolonged unfavourable effect on arterial stiffness and wave reflections. Psychosom Med 68:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.psy.0000203171.33348.72
Vlachopoulos C, Xaplanteris P, Alexopoulos N, Aznaouridis K, Vasiliadou C, Baou K, Stefanadi E, Stefanadis C (2009) Divergent effects of laughter and mental stress on arterial stiffness and central hemodynamics. Psychosom Med 71:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e318198dcd4
Wang H, Zhang T, Zhu W, Wu H, Yan S (2014) Acute effects of continuous and interval low-intensity exercise on arterial stiffness in healthy young men. Eur J Appl Physiol 114:1385–1392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2869-y
Yang H, Drummer TD, Carter JR (2013) Sex differences in sympathetic neural and limb vascular reactivity to mental stress in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304:H435–H443. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00688.2012
Zhou Z, He Z, Yuan M, Yin Z, Dang X, Zhu J, Zhu W (2015) Longer rest intervals do not attenuate the superior effects of accumulated exercise on arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 115:2149–2157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3195-8
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the study participants for their cooperation.
Funding
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, and Science (#20K11480 to DK) and a Grant-in-Aid of the Uruma Fund for the Promotion of Science (to DK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DK conceived and designed the study. DK performed the experiments. DK analyzed the data. All authors interpreted the results of the experiments. DK and MN drafted the manuscript. DK edited and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo pagani.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kume, D., Nishiwaki, M., Hotta, N. et al. Acute mental stress-caused arterial stiffening can be counteracted by brief aerobic exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 121, 1359–1366 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04618-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04618-3