Abstract
Purpose
It has been reported that acute brief episodes of mental stress (MS) result in a prolonged increase in carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV), an index of aortic stiffness. However, whether acute MS also impacts arterial stiffness in other segments is unclear. The present study aimed to examine the impact of acute MS on segmental arterial stiffness.
Methods
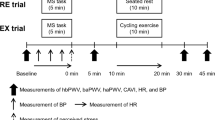
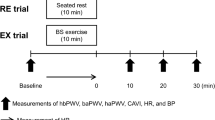
In the main experiment, 17 young male subjects (mean age, 20.1 ± 0.7 years) performed a 5-min MS and control (CON) task in a random order. Pulse wave velocity (PWV) from the heart to the brachium (hbPWV) and the ankle (haPWV), PWV between the brachial artery and the ankle (baPWV), and the cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) were simultaneously measured at baseline and 5, 15, and 30 min after the task.
Results
Compared to baseline values, hbPWV, baPWV, haPWV, and CAVI significantly increased until 30 min after the MS task, whereas these variables did not significantly change following the CON task. At 5 and 30 min after the MS task, percentage changes from baseline were significantly higher in hbPWV (+ 5.2 ± 4.4 and 6.6 ± 4.9%) than in baPWV (+ 2.2 ± 2.1 and 2.2 ± 2.0%) or haPWV (+ 3.6 ± 2.6 and 4.3 ± 2.9%) and were also significantly lower in baPWV than in haPWV.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that acute MS elicits an increase in arterial stiffness in various segments and this arterial stiffening is not uniform among the segments.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- baPWV:
-
Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CAVI:
-
Cardio-ankle vascular index
- cfPWV:
-
Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity
- CON:
-
Control
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- haPWV:
-
Heart-ankle pulse wave velocity
- hbPWV:
-
Heart-brachial pulse wave velocity
- MS:
-
Mental stress
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- SNS:
-
Sympathetic nervous system
- VAS:
-
Visual analogue scale
References
Benetos A, Laurent S, Hoeks AP, Boutouyrie PH, Safar ME (1993) Arterial alterations with aging and high blood pressure. A noninvasive study of carotid and femoral arteries. Arterioscler Thromb 13:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.13.1.90
Broadley AJ, Korszun A, Abdelaal E, Moskvina V, Jones CJ, Nash GB, Ray C, Deanfield J, Frenneaux MP (2005) Inhibition of cortisol production with metyrapone prevents mental stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and baroreflex impairment. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.068
Calcaterra V, Vandoni M, Correale L, Larizza D, DeBarbieri G, Albertini R, Tinelli C, Arpesella M, Bernardi L (2014) Deep breathing acutely improves arterial dysfunction in obese children: evidence of functional impairment? Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 24:1301–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2014.06.011
Callister R, Suwarno NO, Seals DR (1992) Sympathetic activity is influenced by task difficulty and stress perception during mental challenge in humans. J Physiol 454:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019269
Carroll D, Ginty AT, Der G, Hunt K, Benzeval M, Phillips AC (2012) Increased blood pressure reactions to acute mental stress are associated with 16-year cardiovascular disease mortality. Psychophysiology 49:1444–1448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2012.01463.x
Carter JR, Kupiers NT, Ray CA (2005) Neurovascular responses to mental stress. J Physiol 564:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.079665
Caslin HL, Franco RL, Crabb EB, Huang CJ, Bowen MK, Acevedo EO (2016) The effect of obesity on inflammatory cytokine and leptin production following acute mental stress. Psychophysiology 53:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12568
Eriksson M, Johansson K, Sarabi M, Lind L (2007) Mental stress impairs endothelial vasodilatory function by a beta-adrenergic mechanism. Endothelium 14:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/10623320701421420
Esler M (2017) Mental stress and human cardiovascular disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 74:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.10.011
Fonkoue IT, Marvar PJ, Norrholm SD, Kankam ML, Li Y, DaCosta D, Rothbaum BO, Park J (2018) Acute effects of device-guided slow breathing on sympathetic nerve activity and baroreflex sensitivity in posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 315:H141–H149. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00098.2018
Ghiadoni L, Donald AE, Cropley M, Mullen MJ, Oakley G, Taylor M, O'Connor G, Betteridge J, Klein N, Steptoe A, Deanfield JE (2000) Mental stress induces transient endothelial dysfunction in humans. Circulation 102:2473–2478. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.102.20.2473
Goswami N, Roessler A, Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Montani JP, Steptoe A (2012) Delaying orthostatic syncope with mental challenge: a pilot study. Physiol Behav 106:569–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.02.022
Goswami N, Blaber AP, Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Convertino VA (2019) Lower body negative pressure: physiological effects, applications, and implementation. Physiol Rev 99:807–851. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00006.2018
Hayashi K, Miyachi M, Seno N, Takahashi K, Yamazaki K, Sugawara J, Yokoi T, Onodera S, Mesaki N (2006a) Variations in carotid arterial compliance during the menstrual cycle in young women. Exp Physiol 91:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2005.032011
Hayashi N, Someya N, Endo MY, Miura A, Fukuba Y (2006b) Vasoconstriction and blood flow responses in visceral arteries to mental task in humans. Exp Physiol 91:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2005.031971
Heffernan KS, Edwards DG, Rossow L, Jae SY, Fernhall B (2007) External mechanical compression reduces regional arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:735–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0550-4
Hijmering ML, Stroes ES, Olijhoek J, Hutten BA, Blankestijn PJ, Rabelink TJ (2002) Sympathetic activation markedly reduces endothelium-dependent, flow-mediated vasodilation. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:683–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01786-7
Holwerda SW, Luehrs RE, DuBose L, Collins MT, Wooldridge NA, Stroud AK, Fadel PJ, Abboud FM, Pierce GL (2019) Elevated muscle sympathetic nerve activity contributes to central artery stiffness in young and middle-age/older adults. Hypertension 73:1025–1035. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12462
Horváth IG, Németh A, Lenkey Z, Alessandri N, Tufano F, Kis P, Gaszner B, Cziráki A (2010) Invasive validation of a new oscillometric device (Arteriograph) for measuring augmentation index, central blood pressure and aortic pulse wave velocity. J Hypertens 28:2068–2075. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32833c8a1a
Hsiao JK, Lynch JJ, Foreman PJ, Gross HS (1987) Cardiovascular response to speaking in schizophrenics. Psychiatry Res 22:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(87)90052-7
Kaewboonchoo O, Sembajwe G, Li J (2018) Associations between job strain and arterial stiffness: a large survey among enterprise employees from Thailand. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:E659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040659
Kamiya A, Iwase S, Michikami D, Fu Q, Mano T (2000) Head-down bed rest alters sympathetic and cardiovascular responses to mental stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R440–R447
Kobayashi R, Yoshida S, Okamoto T (2015) Arterial stiffness after glucose ingestion in exercise-trained versus untrained men. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 40:1151–1156. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2015-0131
Kobayashi R, Sato K, Takahashi T, Asaki K, Iwanuma S, Ohashi N, Hashiguchi T (2019) Arterial stiffness during hyperglycemia in older adults with high physical activity vs low physical activity. J Clin Biochem Nutr 65:146–152. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.19-32
Kuipers NT, Sauder CL, Carter JR, Ray CA (2008) Neurovascular responses to mental stress in the supine and upright postures. J Appl Physiol 104:1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01285.2007
Lackner HK, Goswami N, Papousek I, Roessler A, Grasser EK, Montani JP, Jezova D, Hinghofer-Szalkay H (2010a) Time course of cardiovascular responses induced by mental and orthostatic challenges. Int J Psychophysiol 75:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2009.11.003
Lackner HK, Goswami N, Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Papousek I, Scharfetter H, Furlan R, Schwaberger G (2010b) Effects of stimuli on cardiovascular reactivity occurring at regular intervals during mental stress. J Psychophysiol 24:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1027/0269-8803/a000006
Mangiafico RA, Malatino LS, Attinà T, Messina R, Fiore CE (2002) Exaggerated endothelin release in response to acute mental stress in patients with intermittent claudication. Angiology 53:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1177/000331970205300403
Matthews KA, Katholi CR, McCreath H, Whooley MA, Williams DR, Zhu S, Markovitz JH (2004) Blood pressure reactivity to psychological stress predicts hypertension in the CARDIA study. Circulation 110:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000133415.37578.E4
McEniery CM, Wallace S, Mackenzie IS, McDonnell B, DE Yasmin N, Cockcroft JR, Wilkinson IB (2006) Endothelial function is associated with pulse pressure, pulse wave velocity, and augmentation index in healthy humans. Hypertension 48:602–608
Mitchell GF, Hwang SJ, Vasan RS, Larson MG, Pencina MJ, Hamburg NM, Vita JA, Levy D, Benjamin EJ (2010) Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 121:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.886655
Nardone M, Incognito AV, Millar PJ (2018) Evidence for pressure-independent sympathetic modulation of central pulse wave velocity. J Am Heart Assoc 7:e007971. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.007971
Nishiwaki M, Kurobe K, Kiuchi A, Nakamura T, Matsumoto N (2014) Sex differences in flexibility-arterial stiffness relationship and its application for diagnosis of arterial stiffening: a cross-sectional observational study. PLoS ONE 9:e113646. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113646
Nishiwaki M, Takahara K, Matsumoto N (2017) Arterial stiffness in young adult swimmers. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3505-9
Nishiwaki M, Nakano Y, Matsumoto N (2019) Effects of regular high-cocoa chocolate intake on arterial stiffness and metabolic characteristics during exercise. Nutrition 60:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.09.021
Papousek I, Nauschnegg K, Paechter M, Lackner HK, Goswami N, Schulter G (2010) Trait and state positive affect and cardiovascular recovery from experimental academic stress. Biol Psychol 83:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.11.008
Reims HM, Sevre K, Fossum E, Høieggen A, Eide I, Kjeldsen SE (2004) Plasma catecholamines, blood pressure responses and perceived stress during mental arithmetic stress in young men. Blood Press 13:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1080/08037050410016474
Rimmele U, Zellweger BC, Marti B, Seiler R, Mohiyeddini C, Ehlert U, Heinrichs M (2007) Trained men show lower cortisol, heart rate and psychological responses to psychosocial stress compared with untrained men. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:627–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.04.005
Ring M, Eriksson MJ, Zierath JR, Caidahl K (2014) Arterial stiffness estimation in healthy subjects: a validation of oscillometric (Arteriograph) and tonometric (SphygmoCor) techniques. Hypertens Res 37:999–1007. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2014.115
Rozanski A, Blumenthal JA, Kaplan J (1999) Impact of psychological factors on the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and implications for therapy. Circulation 99:2192–2217. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.99.16.2192
Saitoh M, Yanagawa T, Kondoh T, Miyakoda H, Kotake H, Mashiba H (1995) Neurohumoral factor responses to mental (arithmetic) stress and dynamic exercise in normal subjects. Intern Med 34:618–622. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.34.618
Sales AR, Fernandes IA, Rocha NG, Costa LS, Rocha HN, Mattos JD, Vianna LC, Silva BM, Nóbrega AC (2014) Aerobic exercise acutely prevents the endothelial dysfunction induced by mental stress among subjects with metabolic syndrome: the role of shear rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306:H963–H971. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00811.2013
Shirai K, Hiruta N, Song M, Kurosu T, Suzuki J, Tomaru T, Miyashita Y, Saiki A, Takahashi M, Suzuki K, Takata M (2011) Cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) as a novel indicator of arterial stiffness: theory, evidence and perspectives. J Atheroscler Thromb 18:924–938. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.7716
Spieker LE, Hürlimann D, Ruschitzka F, Corti R, Enseleit F, Shaw S, Hayoz D, Deanfield JE, Lüscher TF, Noll G (2002) Mental stress induces prolonged endothelial dysfunction via endothelin-A receptors. Circulation 105:2817–2820. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000021598.15895.34
Sugawara J, Hayashi K, Yokoi T, Cortez-Cooper MY, DeVan AE, Anton MA, Tanaka H (2005) Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity: an index of central arterial stiffness? J Hum Hypertens 19:401–406. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001838
Sugawara J, Komine H, Hayashi K, Yoshizawa M, Otsuki T, Shimojo N, Miyauchi T, Yokoi T, Maeda S, Tanaka H (2009) Reduction in alpha-adrenergic receptor-mediated vascular tone contributes to improved arterial compliance with endurance training. Int J Cardiol 135:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.04.007
Sugawara J, Tomoto T, Tanaka H (2019) Heart-to-brachium pulse wave velocity as a measure of proximal aortic stiffness: MRI and longitudinal studies. Am J Hypertens 32:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpy166
Tanaka H, Munakata M, Kawano Y, Ohishi M, Shoji T, Sugawara J, Tomiyama H, Yamashina A, Yasuda H, Sawayama T, Ozawa T (2009) Comparison between carotid-femoral and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity as measures of arterial stiffness. J Hypertens 27:2022–2027. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832e94e7
Thijssen DH, Atkinson CL, Ono K, Sprung VS, Spence AL, Pugh CJ, Green DJ (2014) Sympathetic nervous system activation, arterial shear rate, and flow-mediated dilation. J Appl Physiol 116:1300–1307. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00110.2014
Tsubakimoto A, Saito I, Mannami T, Naito Y, Nakamura S, Dohi Y, Yonemasu K (2006) Impact of metabolic syndrome on brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in Japanese. Hypertens Res 29:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.29
Utsugi M, Saijo Y, Yoshioka E, Sato T, Horikawa N, Gong Y, Kishi R (2009) Relationship between two alternative occupational stress models and arterial stiffness: a cross-sectional study among Japanese workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0319-z
van Sloten TT, Schram MT, van den Hurk K, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Henry RM, Stehouwer CD (2014) Local stiffness of the carotid and femoral artery is associated with incident cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality: the Hoorn study. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:1739–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.12.041
Vlachopoulos C, Kosmopoulou F, Alexopoulos N, Ioakeimidis N, Siasos G, Stefanadis C (2006) Acute mental stress has a prolonged unfavorable effect on arterial stiffness and wave reflections. Psychosom Med 68:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.psy.0000203171.33348.72
Vlachopoulos C, Xaplanteris P, Alexopoulos N, Aznaouridis K, Vasiliadou C, Baou K, Stefanadi E, Stefanadis C (2009) Divergent effects of laughter and mental stress on arterial stiffness and central hemodynamics. Psychosom Med 71:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e318198dcd4
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1318–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.10.061
Wilkinson IB, MacCallum H, Hupperetz PC, van Thoor CJ, Cockcroft JR, Webb DJ (2001) Changes in the derived central pressure waveform and pulse pressure in response to angiotensin II and noradrenaline in man. J Physiol 530:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0541k
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all the subjects for their participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DK and MN conceived and designed the study. DK performed the experiments. DK and MN analysed the data. All authors interpreted the results of the experiments. DK prepared figures and tables. DK drafted the manuscript. All authors edited and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Fabio Fischetti.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kume, D., Nishiwaki, M., Hotta, N. et al. Impact of acute mental stress on segmental arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 120, 2247–2257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04448-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04448-9