Abstract
Objective
The body’s adaptation to physical exercise is modulated by sympathetic and parasympathetic (vagal) branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Heart rate variability (HRV), the beat-to-beat variation of the heart, is a proxy measure for ANS activity, whereas blood pressure (BP) is an indicator for cardiovascular function. Impaired vagal activity and lower BP is already described after exercise. However, inconsistent results exist about how long vagal recovery takes and how long post-exercise hypotension persists. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess HRV and BP 1 h after maximal cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET).
Patients and methods
HRV (Polar RS800CX), peripheral and central BP (Mobil-O-Graph®) were prospectively studied in 107 healthy volunteers (47 female, median age 29.0 years) in supine position, before and 60 min after maximal CPET.
Results
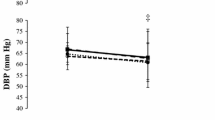
One hour after terminating CPET measures of HRV were still impaired and post-exercise BP was significantly reduced suggesting an improved vascular function compared to pre levels. HRV parameters post-exercise were 34.7% (RMSSD), 67.2% (pNN50), 57.2% (HF), and 42.7% (LF) lower compared to pre-exercise levels (for all p < 0.001). Median reduction in BP was 5 mmHg for systolic BP (p < 0.001), and 4 mmHg for diastolic BP (p = 0.016) and central systolic post-exercise (p = 0.005).
Conclusions
One hour after terminating strenuous exercise, autonomic nervous regulation seems to be postponed which is reflected in reduced HRV, whereas the early recovery of the vasculature, post-exercise hypotension, is still preserved over the recovery period of 1 h.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANS:
-
Autonomic nervous system
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CPET:
-
Cardiopulmonary exercise test
- DPB:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- HF:
-
High frequency
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- LF:
-
Low frequency
- NN:
-
Normal to normal
- RMSSD:
-
Root mean square of successive differences
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- VO:
-
Peak oxygen uptake
References
Abhishekh HA, Nisarga P, Kisan R, Meghana A, Chandran S, Trichur R, Sathyaprabha TN (2013) Influence of age and gender on autonomic regulation of heart. J Clin Monit Comput 27(3):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-012-9424-3
Arai Y, Saul JP, Albrecht P, Hartley LH, Lilly LS, Cohen RJ, Colucci WS (1989) Modulation of cardiac autonomic activity during and immediately after exercise. Am J Physiol 256(1 Pt 2):H132–H141
Aubert AE, Seps B, Beckers F (2003) Heart rate variability in athletes. Sports Med 33(12):889–919
Barak OF, Jakovljevic DG, Popadic Gacesa JZ, Ovcin ZB, Brodie DA, Grujic NG (2010) Heart rate variability before and after cycle exercise in relation to different body positions. J Sports Sci Med 9(2):176–182
Bellenger CR, Fuller JT, Thomson RL, Davison K, Robertson EY, Buckley JD (2016) Monitoring athletic training status through autonomic heart rate regulation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-016-0484-2
Borjesson M, Onerup A, Lundqvist S, Dahlof B (2016) Physical activity and exercise lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension: narrative review of 27 RCTs. Br J Sports Med 50(6):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-095786
Brownley KA, West SG, Hinderliter AL, Light KC (1996) Acute aerobic exercise reduces ambulatory blood pressure in borderline hypertensive men and women. Am J Hypertens 9(3):200–206
Buchheit M, Gindre C (2006) Cardiac parasympathetic regulation: respective associations with cardiorespiratory fitness and training load. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291(3):H451-H458. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00008.2006.-The
Coote JH (2010) Recovery of heart rate following intense dynamic exercise. Exp Physiol 95(3):431–440. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2009.047548
Cunha FA, Midgley AW, Goncalves T, Soares PP, Farinatti P (2015) Parasympathetic reactivation after maximal CPET depends on exercise modality and resting vagal activity in healthy men. SpringerPlus 4:100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-0882-1
Danieli A, Lusa L, Potocnik N, Meglic B, Grad A, Bajrovic FF (2014) Resting heart rate variability and heart rate recovery after submaximal exercise. Clin Autonom Res Off J Clin Autonom Res Soc 24(2):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-014-0225-2
de Oliveira TP, de Alvarenga Mattos R, da Silva RB, Rezende RA, de Lima JR (2013) Absence of parasympathetic reactivation after maximal exercise. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 33(2):143–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12009
Epstein S, Robinson BF, Kahler RL, Braunwald E (1965) Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on the cardiac response to maximal and submaximal exercise in man. J Clin Invest 44(11):1745–1753. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI105282
Esco MR, Flatt AA (2014) Ultra-short-term heart rate variability indexes at rest and post-exercise in athletes: evaluating the agreement with accepted recommendations. J Sports Sci Med 13(3):535–541
Esco MR, Williford HN (2013) Relationship between post-exercise heart rate variability and skinfold thickness. SpringerPlus 2:389. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-389
Furlan R, Piazza S, Dell’Orto S, Gentile E, Cerutti S, Pagani M, Malliani A (1993) Early and late effects of exercise and athletic training on neural mechanisms controlling heart rate. Cardiovasc Res 27(3):482–488
Gladwell VF, Sandercock GR, Birch SL (2010) Cardiac vagal activity following three intensities of exercise in humans. Clin Physiol Funct Imag 30(1):17–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-097X.2009.00899.x
Guilkey JP, Overstreet M, Mahon AD (2015) Heart rate recovery and parasympathetic modulation in boys and girls following maximal and submaximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 115(10):2125–2133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3192-y
Heart rate variability (1996) Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Eur Heart J 17(3):354–381
Henriquez OC, Baez SM, Von Oetinger A, Canas JR, Ramirez CR (2013) Autonomic control of heart rate after exercise in trained wrestlers. Biol Sport 30(2):111–115. https://doi.org/10.5604/20831862.1044429
Imai K, Sato H, Hori M, Kusuoka H, Ozaki H, Yokoyama H, Takeda H, Inoue M, Kamada T (1994) Vagally mediated heart rate recovery after exercise is accelerated in athletes but blunted in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 24(6):1529–1535
James DV, Barnes AJ, Lopes P, Wood DM (2002) Heart rate variability: response following a single bout of interval training. Int J Sports Med 23(4):247–251. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2002-29077
Joyner MJ, Casey DP (2014) Muscle blood flow, hypoxia, and hypoperfusion. J Appl Physiol 116(7):852–857. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00620.2013
Le VV, Mitiku T, Sungar G, Myers J, Froelicher V (2008) The blood pressure response to dynamic exercise testing: a systematic review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 51(2):135–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.07.001
Michael S, Jay O, Halaki M, Graham K, Davis GM (2016) Submaximal exercise intensity modulates acute post-exercise heart rate variability. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(4):697–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3327-9
Mourot L, Bouhaddi M, Tordi N, Rouillon JD, Regnard J (2004) Short- and long-term effects of a single bout of exercise on heart rate variability: comparison between constant and interval training exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol 92(4–5):508–517
Müller J, Wilms M, Oberhoffer R (2015) Acute effects of submaximal endurance training on arterial stiffness in healthy middle- and long-distance runners. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 17(5):371–374. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12530
Müller J, Meyer J, Elmenhorst J, Oberhoffer R (2016) Body weight and not exercise capacity determines central systolic blood pressure, a surrogate for arterial stiffness, in children and adolescents. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 18(8):762–765. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12754
Munir S, Jiang B, Guilcher A, Brett S, Redwood S, Marber M, Chowienczyk P (2008) Exercise reduces arterial pressure augmentation through vasodilation of muscular arteries in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294(4):H1645–H1650. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.01171.2007
Pecanha T, de Paula-Ribeiro M, Nasario-Junior O, de Lima JR (2013) Post-exercise heart rate variability recovery: a time-frequency analysis. Acta Cardiol 68(6):607–613. https://doi.org/10.2143/AC.68.6.8000008
Pecanha T, Prodel E, Bartels R, Nasario-Junior O, Paula RB, Silva LP, Laterza MC, Lima JR (2014) 24-h cardiac autonomic profile after exercise in sedentary subjects. Int J Sports Med 35(3):245–252. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1349873
Pober DM, Braun B, Freedson PS (2004) Effects of a single bout of exercise on resting heart rate variability. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(7):1140–1148
Rajendra Acharya U, Paul Joseph K, Kannathal N, Lim CM, Suri JS (2006) Heart rate variability: a review. Med Biol Eng Comput 44(12):1031–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-006-0119-0
Savin WM, Davidson DM, Haskell WL (1982) Autonomic contribution to heart rate recovery from exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exercise Physiol 53(6):1572–1575
Schultz MG, Sharman JE (2014) Exercise hypertension. Pulse (Basel) 1(3–4):161–176. https://doi.org/10.1159/000360975
Seiler S, Haugen O, Kuffel E (2007) Autonomic recovery after exercise in trained athletes: intensity and duration effects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(8):1366–1373. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e318060f17d
Terziotti P, Schena F, Gulli G, Cevese A (2001) Post-exercise recovery of autonomic cardiovascular control: a study by spectrum and cross-spectrum analysis in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 84(3):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210170003
Tsuji H, Larson MG, Venditti FJ Jr, Manders ES, Evans JC, Feldman CL, Levy D (1996) Impact of reduced heart rate variability on risk for cardiac events. Framingham Heart Study Circ 94(11):2850–2855
Weber T, Wassertheurer S, Rammer M, Maurer E, Hametner B, Mayer CC, Kropf J, Eber B (2011) Validation of a brachial cuff-based method for estimating central systolic blood pressure. Hypertension 58(5):825–832. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.176313
Acknowledgements
We thank our students Danja Schuster, Daniel Wieczorek and Lena Ziegler for their work and effort within the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
None.
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Pagani.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weberruss, H., Maucher, J., Oberhoffer, R. et al. Recovery of the cardiac autonomic nervous and vascular system after maximal cardiopulmonary exercise testing in recreational athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 205–211 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3762-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3762-2