Abstract
Introduction
Many environmental and dietary influences can cause immune cells to produce biological mediators that increase airway inflammation. A high-fat meal (HFM) is one stimulus that increases airway inflammation in healthy individuals. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammation systemically and may be beneficial to the airways.
Purpose
To determine if omega-3 fatty acid supplementation via fish oil would mitigate the airway inflammatory response induced by a single HFM.
Methods
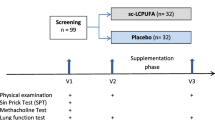
Seventeen non-asthmatic men (22 ± 2 years.) were supplemented with 3,000 mg × day−1 fish oil or a placebo for 3 weeks. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO; a marker of airway inflammation), impulse oscillometry (a measure of respiratory impedance), pulmonary function, and triglycerides were measured prior to and 2 h following a HFM.
Results
Following a HFM, triglycerides increased in both fish oil and placebo groups compared to pre-HFM (~59 and ~49 %, respectively, p < 0.05). The percent increase in FENO was greater in the placebo group compared to the fish oil group (25.7 ± 16.7 vs. −1.99 ± 10.5 %, respectively, p < 0.05). A significant correlation was observed between blood triglycerides and FENO in the placebo group (r = 0.61; p < 0.05), but not the fish oil group (p = 0.21).
Conclusion
A single HFM increases airway inflammation and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation via fish oil protects against HFM associated changes in airway health.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi F, McLaughlin T, Lamendola C, Kim HS, Tanaka A, Wang T, Nakajima K, Reaven GM (2000) High carbohydrate diets, triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, and coronary heart disease risk. Am J Cardiol 85(1):45–48 (pii: S0002-9149(99)00604-9)
Ahuja KD, Adams MJ, Robertson IK, Ball MJ (2009) Acute effect of a high-carbohydrate low-fat meal on platelet aggregation. Platelets 20(8):606–609. doi:10.3109/09537100903267517
Biltagi MA, Baset AA, Bassiouny M, Kasrawi MA, Attia M (2009) Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C and Zn supplementation in asthmatic children: a randomized self-controlled study. Acta Paediatr 98(4):737–742 (pii: APA1213)
Black PN, Sharpe S (1997) Dietary fat and asthma: is there a connection? Eur Respir J 10(1):6–12
Calder PC (2001) Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and immunity. Lipids 36(9):1007–1024
Calder PC (2003) N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammation: from molecular biology to the clinic. Lipids 38(4):343–352
Caughey GE, Mantzioris E, Gibson RA, Cleland LG, James MJ (1996) The effect on human tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 beta production of diets enriched in n-3 fatty acids from vegetable oil or fish oil. Am J Clin Nutr 63(1):116–122
De Caterina R, Cybulsky MI, Clinton SK, Gimbrone MA Jr, Libby P (1994) The omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoate reduces cytokine-induced expression of proatherogenic and proinflammatory proteins in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb 14(11):1829–1836
Endres S, Ghorbani R, Kelley VE, Georgilis K, Lonnemann G, van der Meer JW, Cannon JG, Rogers TS, Klempner MS, Weber PC et al (1989) The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med 320(5):265–271. doi:10.1056/NEJM198902023200501
Eriksson EE, Xie X, Werr J, Thoren P, Lindbom L (2001) Direct viewing of atherosclerosis in vivo: plaque invasion by leukocytes is initiated by the endothelial selectins. FASEB J 15(7):1149–1157
Foliaki S, Annesi-Maesano I, Tuuau-Potoi N, Waqatakirewa L, Cheng S, Douwes J, Pearce N (2008) Risk factors for symptoms of childhood asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema in the Pacific: an ISAAC Phase III study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 12(7):799–806
Gabbay E, Fisher AJ, Small T, Leonard AJ, Corris PA (1998) Exhaled single-breath nitric oxide measurements are reproducible, repeatable and reflect levels of nitric oxide found in the lower airways. Eur Respir J 11(2):467–472
Gallai V, Sarchielli P, Trequattrini A, Franceschini M, Floridi A, Firenze C, Alberti A, Di Benedetto D, Stragliotto E (1995) Cytokine secretion and eicosanoid production in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of MS patients undergoing dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Neuroimmunol 56(2):143–153 (pii: 016557289400140J)
Galland L (2010) Diet and inflammation. Nutr Clin Pract 25(6):634–640 (pii: 25/6/634)
Gibney MJ, Hunter B (1993) The effects of short- and long-term supplementation with fish oil on the incorporation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids into cells of the immune system in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Nutr 47(4):255–259
Hancox RJ, Poulton R, Greene JM, Filsell S, McLachlan CR, Rasmussen F, Taylor DR, Williams MJ, Williamson A, Sears MR (2007) Systemic inflammation and lung function in young adults. Thorax 62(12):1064–1068 (pii: thx.2006.076877)
Harris WS (2004) Fish oil supplementation: evidence for health benefits. Cleve Clin J Med 71(3):208–210, 212, 215–208 passim
Juturu V (2008) Omega-3 fatty acids and the cardiometabolic syndrome. J Cardiometab Syndr 3(4):244–253. doi:10.1111/j.1559-4572.2008.00015.x
Kew S, Mesa MD, Tricon S, Buckley R, Minihane AM, Yaqoob P (2004) Effects of oils rich in eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on immune cell composition and function in healthy humans. Am J Clin Nutr 79(4):674–681
Kinsella JE, Lokesh B, Broughton S, Whelan J (1990) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and eicosanoids: potential effects on the modulation of inflammatory and immune cells: an overview. Nutrition 6(1):24–44 (discussion 59–62)
Laerum BN, Wentzel-Larsen T, Gulsvik A, Omenaas E, Gislason T, Janson C, Svanes C (2007) Relationship of fish and cod oil intake with adult asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 37(11):1616–1623 (pii: CEA2821)
Lee TH, Hoover RL, Williams JD, Sperling RI, Ravalese J 3rd, Spur BW, Robinson DR, Corey EJ, Lewis RA, Austen KF (1985) Effect of dietary enrichment with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on in vitro neutrophil and monocyte leukotriene generation and neutrophil function. N Engl J Med 312(19):1217–1224. doi:10.1056/NEJM198505093121903
Lewis RA, Austen KF, Soberman RJ (1990) Leukotrienes and other products of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Biochemistry and relation to pathobiology in human diseases. N Engl J Med 323(10):645–655. doi:10.1056/NEJM199009063231006
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A (2002) Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105(9):1135–1143
Meydani SN, Lichtenstein AH, Cornwall S, Meydani M, Goldin BR, Rasmussen H, Dinarello CA, Schaefer EJ (1993) Immunologic effects of national cholesterol education panel step-2 diets with and without fish-derived N-3 fatty acid enrichment. J Clin Invest 92(1):105–113. doi:10.1172/JCI116537
Mickleborough TD, Murray RL, Ionescu AA, Lindley MR (2003) Fish oil supplementation reduces severity of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in elite athletes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168(10):1181–1189. doi:10.1164/rccm.200303-373OC
Mickleborough TD, Lindley MR, Ionescu AA, Fly AD (2006) Protective effect of fish oil supplementation on exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in asthma. Chest 129(1):39–49 (pii: 129/1/39)
Miyamoto S, Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Ohya Y, Matsunaga I, Yoshida T, Oda H, Ishiko O, Hirota Y (2007) Fat and fish intake and asthma in Japanese women: baseline data from the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 11(1):103–109
Nagel G, Linseisen J (2005) Dietary intake of fatty acids, antioxidants and selected food groups and asthma in adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 59(1):8–15. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602025
Nicholls SJ, Lundman P, Harmer JA, Cutri B, Griffiths KA, Rye KA, Barter PJ, Celermajer DS (2006) Consumption of saturated fat impairs the anti-inflammatory properties of high-density lipoproteins and endothelial function. J Am Coll Cardiol 48(4):715–720 (pii: S0735-1097(06)01338-6)
Obata T, Nagakura T, Masaki T, Maekawa K, Yamashita K (1999) Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits prostaglandin D2 generation by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase-2 in cultured human mast cells. Clin Exp Allergy 29(8):1129–1135 (pii: cea604)
Patel S, Puranik R, Nakhla S, Lundman P, Stocker R, Wang XS, Lambert G, Rye KA, Barter PJ, Nicholls SJ, Celermajer DS (2009) Acute hypertriglyceridaemia in humans increases the triglyceride content and decreases the anti-inflammatory capacity of high density lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis 204(2):424–428 (pii: S0021-9150(08)00750-8)
Porsbjerg C, Lund TK, Pedersen L, Backer V (2009) Inflammatory subtypes in asthma are related to airway hyperresponsiveness to mannitol and exhaled NO. J Asthma 46(6):606–612 (pii: 913557390)
Rasmussen F, Mikkelsen D, Hancox RJ, Lambrechtsen J, Nybo M, Hansen HS, Siersted HC (2009) High-sensitive C-reactive protein is associated with reduced lung function in young adults. Eur Respir J 33(2):382–388 (pii: 09031936.00040708)
Rosenkranz SK, Townsend DK, Steffens SE, Harms CA (2010) Effects of a high-fat meal on pulmonary function in healthy subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 109(3):499–506. doi:10.1007/s00421-010-1390-1
Sadeghi S, Wallace FA, Calder PC (1999) Dietary lipids modify the cytokine response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide in mice. Immunology 96(3):404–410 (pii: imm701)
Schwartz J, Weiss ST (1994) The relationship of dietary fish intake to level of pulmonary function in the first National Health and Nutrition Survey (NHANES I). Eur Respir J 7(10):1821–1824
Sherwood L (2001) Human physiology: from cells to systems, 4th edn. Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove
Simopoulos AP (2002) Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. J Am Coll Nutr 21(6):495–505
Simopoulos AP (2008) The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233(6):674–688 (pii: 0711-MR-311)
Sperling RI, Benincaso AI, Knoell CT, Larkin JK, Austen KF, Robinson DR (1993) Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit phosphoinositide formation and chemotaxis in neutrophils. J Clin Invest 91(2):651–660. doi:10.1172/JCI116245
Tecklenburg-Lund S, Mickleborough TD, Turner LA, Fly AD, Stager JM, Montgomery GS (2010) Randomized controlled trial of fish oil and montelukast and their combination on airway inflammation and hyperpnea-induced bronchoconstriction. PLoS ONE 5(10):e13487. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013487
van Oostrom AJ, Sijmonsma TP, Verseyden C, Jansen EH, de Koning EJ, Rabelink TJ, Castro Cabezas M (2003) Postprandial recruitment of neutrophils may contribute to endothelial dysfunction. J Lipid Res 44(3):576–583. doi:10.1194/jlr.M200419-JLR200
van Oostrom AJ, Rabelink TJ, Verseyden C, Sijmonsma TP, Plokker HW, De Jaegere PP, Cabezas MC (2004) Activation of leukocytes by postprandial lipemia in healthy volunteers. Atherosclerosis 177(1):175–182 (pii: S0021-9150(04)00374-0)
Whelan J, Rust C (2006) Innovative dietary sources of n-3 fatty acids. Annu Rev Nutr 26:75–103. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.25.050304.092605
Conflict of interest
There is no financial or other relationship that influenced the outcome of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Fabio Fischetti.
This manuscript represents original work without fabrication, fraud or plagiarism and has been read and approved by all authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ade, C.J., Rosenkranz, S.K. & Harms, C.A. The effects of short-term fish oil supplementation on pulmonary function and airway inflammation following a high-fat meal. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 675–682 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2792-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2792-7