Abstract
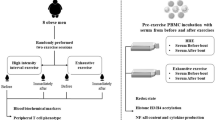
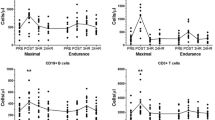
Acute exercise alters the surface expression of toll-like receptors (TLRs) and HLA.DR on blood monocytes, which could transiently compromise immunity. As serum factors might be responsible, we examined the effects of autologous post-exercise serum exposure on TLR2, TLR4 and HLA.DR expression on resting blood monocytes and their subtypes. Eight trained cyclists completed an ergometer 60 km time trial. PBMCs and serum were obtained before, immediately after and 1 h after exercise. TLR2, TLR4 or HLA.DR expression (gMFI) was determined on blood monocyte subtypes expressing combinations of CD14 and CD16 by flow cytometry, and on resting monocytes exposed to 50% autologous serum (pre, immediately after or 1 h after exercise) for 18 h in culture. Immediately after exercise, total monocyte expression of TLR2 and TLR4 increased by 41 and 27%, respectively, while HLA.DR expression was 39% lower than baseline. TLR2 and TLR4 was 53 and 84% greater 1 h after exercise, respectively, while HLA.DR was 48% lower. Changes in TLR2 and TLR4 expression occurred on the CD14++bright/CD16+dim monocyte subtype only, while HLA.DR expression changed on the CD14+dim/CD16++bright subtype. Serum did not affect monocyte TLR2 or TLR4 expression but 1 h post serum increased expression of HLA.DR on total monocytes and the CD14+dim/CD16++bright subtype, which was in contrast to the change observed at this time after exercise. We conclude that a bout of strenuous aerobic exercise alters the surface expression of TLR2, TLR4 and HLA.DR on blood monocytes and some of their subtypes, but these changes appear to be unrelated to blood serum factors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong L, Medford AR, Hunter KJ, Uppington KM, Millar AB (2004) Differential expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-4 on monocytes in human sepsis. Clin Exp Immunol 136:312–319
Ashton T, Young IS, Davison GW, Rowlands CC, McEneny J, Van Blerk C, Jones E, Peters JR, Jackson SK (2003) Exercise-induced endotoxemia: the effect of ascorbic acid supplementation. Free Radic Biol Med 35:284–291
Francaux M (2009) Toll-like receptor signalling induced by endurance exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 34:454–458
Gleeson M, McFarlin B, Flynn M (2006) Exercise and Toll-like receptors. Exerc Immunol Rev 12:34–53
Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K, Wagner H, Takeda K, Akira S (2000) A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 408:740–745
Hilberg T, Glaser D, Koksch M, Schmidt V, Sossdorf M, Gabriel HH (2004) Differentiation of platelet-leukocyte conjugate formation by short term exercise. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 31:217–226
Hong S, Mills PJ (2008) Effects of an exercise challenge on mobilization and surface marker expression of monocyte subsets in individuals with normal vs elevated blood pressure. Brain Behav Immun 22:590–599
Hopkins PA, Pridmore AC, Ellmerich S, Fraser JD, Russell HH, Read RC, Sriskandan S (2008) Increased surface toll-like receptor 2 expression in superantigen shock. Crit Care Med 36:1267–1276
Lancaster GI, Khan Q, Drysdale P, Wallace F, Jeukendrup AE, Drayson MT, Gleeson M (2005) The physiological regulation of toll-like receptor expression and function in humans. J Physiol 563:945–955
Monneret G, Lepape A, Voirin N, Bohe J, Venet F, Debard AL, Thizy H, Bienvenu J, Gueyffier F, Vanhems P (2006) Persisting low monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression predicts mortality in septic shock. Intensive Care Med 32:1175–1183
Ng QY, Lee KW, Byrne C, Ho TF, Lim CL (2008) Plasma endotoxin and immune responses during a 21-km road race under a warm and humid environment. Ann Acad Med Singapore 37:307–314
Nieman DC, Henson DA, Dumke CL, Oley K, McAnulty SR, Davis JM, Murphy EA, Utter AC, Lind RH, McAnulty LS, Morrow JD (2006) Ibuprofen use, endotoxemia, inflammation, and plasma cytokines during ultramarathon competition. Brain Behav Immun 20:578–584
Okutsu M, Suzuki K, Ishijima T, Peake J, Higuchi M (2008) The effects of acute exercise-induced cortisol on CCR2 expression on human monocytes. Brain Behav Immun 22:1066–1071
Oliveira M, Gleeson M (2010) The influence of prolonged cycling on monocyte Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 expression in healthy men. Eur J Appl Physiol 109:251–257
Passlick B, Flieger D, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW (1989) Identification and characterization of a novel monocyte subpopulation in human peripheral blood. Blood 74:2527–2534
Radom-Aizik S, Leu SY, Cooper DM, Zaldivar F Jr (2007) Serum from exercising humans suppresses T-cell cytokine production. Cytokine 40:75–81
Sanchez MD, Garcia Y, Montes C, Paris SC, Rojas M, Barrera LF, Arias MA, Garcia LF (2006) Functional and phenotypic changes in monocytes from patients with tuberculosis are reversed with treatment. Microbes Infect 8:2492–2500
Schaaf B, Luitjens K, Goldmann T, van Bremen T, Sayk F, Dodt C, Dalhoff K, Droemann D (2009) Mortality in human sepsis is associated with downregulation of Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14 expression on blood monocytes. Diagn Pathol 4:12
Selkirk GA, McLellan TM, Wright HE, Rhind SG (2009) Expression of intracellular cytokines, HSP72, and apoptosis in monocyte subsets during exertional heat stress in trained and untrained individuals. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R575–R586
Simpson RJ, McFarlin BK, McSporran C, Spielmann G, o Hartaigh B, Guy K (2009) Toll-like receptor expression on classic and pro-inflammatory blood monocytes after acute exercise in humans. Brain Behav Immun 23:232–239
Skinner NA, MacIsaac CM, Hamilton JA, Visvanathan K (2005) Regulation of Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 on CD14dimCD16+ monocytes in response to sepsis-related antigens. Clin Exp Immunol 141:270–278
Skrzeczynska-Moncznik J, Bzowska M, Loseke S, Grage-Griebenow E, Zembala M, Pryjma J (2008) Peripheral blood CD14 high CD16+ monocytes are main producers of IL-10. Scand J Immunol 67:152–159
Starkie RL, Rolland J, Angus DJ, Anderson MJ, Febbraio MA (2001) Circulating monocytes are not the source of elevations in plasma IL-6 and TNF-alpha levels after prolonged running. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C769–C774
Steppich B, Dayyani F, Gruber R, Lorenz R, Mack M, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW (2000) Selective mobilization of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes by exercise. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C578–C586
Tsujimoto H, Ono S, Majima T, Efron PA, Kinoshita M, Hiraide H, Moldawer LL, Mochizuki H (2006) Differential toll-like receptor expression after ex vivo lipopolysaccharide exposure in patients with sepsis and following surgical stress. Clin Immunol 119:180–187
Xing T, Li L, Cao H, Huang J (2007) Altered immune function of monocytes in different stages of patients with acute or chronic liver failure. Clin Exp Immunol 147:184–188
Ziegler-Heitbrock L (2007) The CD14+ CD16+ blood monocytes: their role in infection and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 81:584–592
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Ward.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Booth, S., Florida-James, G.D., McFarlin, B.K. et al. The impact of acute strenuous exercise on TLR2, TLR4 and HLA.DR expression on human blood monocytes induced by autologous serum. Eur J Appl Physiol 110, 1259–1268 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1616-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1616-2