Abstract
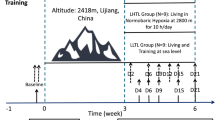
We investigated the impact of 13 days of “living high–training low” (LHTL) on the antioxidant/prooxidant balance in elite endurance swimmers. Eighteen elite swimmers from the French Swimming Federation were submitted to a 13-day endurance training and divided into two groups: one group trained at 1,200 m and lived in hypoxia (2,500–3,000 m simulated altitude) and the second group trained and lived at 1,200 m. The subjects performed an acute hypoxic test (10 min at 4,800 m) before and 1 day after the training period. Plasma levels of advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP), malondialdehydes (MDA), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and lipid-soluble antioxidants were measured before and after the 4,800 m tests. After the training, MDA and AOPP responses to the 4,800 m test were lower than before training for both groups (+10 vs. +2%; P = 0.01 for MDA and +80 vs. +14%; P = 0.01 for AOPP). Thirteen days of LHTL did not modify antioxidant status (FRAP and lipid-soluble antioxidants) despite intakes in vitamins A and E below the recommended daily allowances. The LHTL did not affect the antioxidant status in elite swimmers; however, the normoxic endurance training induced preconditioning mechanisms in response to the 4,800 m test.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASSFA (2003) Compléments et suppléments pour le sportif. In: Apports nutritionnels conseillés pour la population française (3e édition) pp. 380–382 [Tec et Doc eds] Paris
Bailey DM, Davies B, Young IS (2001a) Intermittent hypoxic training: implications for lipid peroxidation induced by acute normoxic exercise in active men. Clin Sci (Lond) 101:465–475. doi:10.1042/CS20010065
Bailey DM, Davies B, Young IS, Hullin DA, Seddon PS (2001b) A potential role for free radical-mediated skeletal muscle soreness in the pathophysiology of acute mountain sickness. Aviat Space Environ Med 72:513–521
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Brugniaux JV, Schmitt L, Robach P, Jeanvoine H, Zimmermann H, Nicolet G, Duvallet A, Fouillot JP, Richalet JP (2006a) Living high–training low: tolerance and acclimatization in elite endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 96:66–77. doi:10.1007/s00421-005-0065-9
Brugniaux JV, Schmitt L, Robach P et al (2006b) Eighteen days of “living high, training low” stimulate erythropoiesis and enhance aerobic performance in elite middle-distance runners. J Appl Physiol 100:203–211. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00808.2005
Chen CF, Tsai SY, Ma MC, Wu MS (2003) Hypoxic preconditioning enhances renal superoxide dismutase levels in rats. J Physiol 552:561–569. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.045559
Clarkson PM, Thompson HS (2000) Antioxidants: what role do they play in physical activity and health? Am J Clin Nutr 72:637S–646S
Das DK, Maulik N (2006) Cardiac genomic response following preconditioning stimulus. Cardiovasc Res 70:254–263. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.02.023
Di MC, Scarpelli P, Penco M, Tozzi-Ciancarelli MG (2004) Possible involvement of plasma antioxidant defences in training-associated decrease of platelet responsiveness in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:406–412. doi:10.1007/s00421-003-0998-9
Gore CJ, Hahn A, Rice A et al (1998) Altitude training at 2690 m does not increase total haemoglobin mass or sea level VO2max in world champion track cyclists. J Sci Med Sport 1:156–170. doi:10.1016/S1440-2440(98)80011-X
Guzy RD, Schumacker PT (2006) Oxygen sensing by mitochondria at complex III: the paradox of increased reactive oxygen species during hypoxia. Exp Physiol 91:807–819. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2006.033506
Jones RD, Hancock JT, Morice AH (2000) NADPH oxidase: a universal oxygen sensor? Free Radic Biol Med 29:416–424. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00320-8
Jordan W, Cohrs S, Degner D, Meier A, Rodenbeck A, Mayer G, Pilz J, Ruther E, Kornhuber J, Bleich S (2006) Evaluation of oxidative stress measurements in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Neural Transm 113:239–254. doi:10.1007/s00702-005-0316-2
Koechlin C, Couillard A, Simar D, Cristol JP, Bellet H, Hayot M, Prefaut C (2004) Does oxidative stress alter quadriceps endurance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:1022–1027. doi:10.1164/rccm.200310-1465OC
Le Moulenc N, Deheeger M, Preziosi P, Monterio P, Valeix P, Rolland-Cachera MF, Potier de Gourcy G, Christides JP, Galan P, Hercberg S (1996) Validation du manuel photo utilisé dans l’enquête alimentaire SU.VI.MAX. Cah Nutr Diet 3:158–164
Lefevre G, Beljean-Leymarie M, Beyerle F, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Cristol JP, Therond P, Torreilles J (1998) Evaluation of lipid peroxidation by measuring thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 56:305–319
Levine BD (2002) Intermittent hypoxic training: fact and fancy. High Alt Med Biol 3:177–193. doi:10.1089/15270290260131911
Levine BD, Stray-Gundersen J (1997) “Living high–training low”: effect of moderate-altitude acclimatization with low-altitude training on performance. J Appl Physiol 83:102–112
Lyan B, Azais-Braesco V, Cardinault N, Tyssandier V, Borel P, Alexandre-Gouabau MC, Grolier P (2001) Simple method for clinical determination of 13 carotenoids in human plasma using an isocratic high-performance liquid chromatographic method. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 751:297–303. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00488-6
Marsh SA, Laursen PB, Coombes JS (2006) Effects of antioxidant supplementation and exercise training on erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 76:324–331. doi:10.1024/0300-9831.76.5.324
Miyazaki H, Oh-ishi S, Ookawara T, Kizaki T, Toshinai K, Ha S, Haga S, Ji LL, Ohno H (2001) Strenuous endurance training in humans reduces oxidative stress following exhausting exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:1–6. doi:10.1007/s004210000342
Neidlinger NA, Hirvela ER, Skinner RA, Larkin SK, Harken AH, Kuypers FA (2005) Postinjury serum secretory phospholipase A2 correlates with hypoxemia and clinical status at 72 hours. J Am Coll Surg 200:173–178. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2004.10.010
Ohno H, Yahata T, Sato Y, Yamamura K, Taniguchi N (1988) Physical training and fasting erythrocyte activities of free radical scavenging enzyme systems in sedentary men. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 57:173–176. doi:10.1007/BF00640658
Palazzetti S, Richard MJ, Favier A, Margaritis I (2003) Overloaded training increases exercise-induced oxidative stress and damage. Can J Appl Physiol 28:588–604
Pialoux V, Mounier R, Ponsot E, Rock E, Mazur A, Dufour S, Richard R, Richalet JP, Coudert J, Fellmann N (2006) Effects of exercise and training in hypoxia on antioxidant/pro-oxidant balance. Eur J Clin Nutr 60:1345–1354. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602462
Pialoux V, Mounier R, Brown AD, Steinback CD, Rawling JM, Poulin MJ (2008a) Relationship between oxidative stress and HIF-1a mRNA during sustained hypoxia in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.10.047
Pialoux V, Mounier R, Rock E, Mazur A, Schmitt L, Richalet JP, Robach P, Brugniaux J, Coudert J, Fellmann N (2008b) Effects of the ‘live high–train low’ method on prooxidant/antioxidant balance on elite athletes. Eur J Clin Nutr. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2008.30
Pialoux V, Mounier R, Rock E, Mazur A, Robach P, Schmitt L, Richalet JP, Coudert J, Fellmann N (2008c) Effects of acute hypoxia on prooxidant/antioxidant balance on elite athletes. Int J Sports Med 29:1–7. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1103284
Reid MB, Moody MR (1994) Dimethyl sulfoxide depresses skeletal muscle contractility. J Appl Physiol 76:2186–2190
Robach P, Schmitt L, Brugniaux JV et al (2006) Living high–training low: effect on erythropoiesis and aerobic performance in highly-trained swimmers. Eur J Appl Physiol 96:423–433. doi:10.1007/s00421-005-0089-1
Robertson JD, Maughan RJ, Duthie GG, Morrice PC (1991) Increased blood antioxidant systems of runners in response to training load. Clin Sci (Lond) 80:611–618
Sen CK (2001) Antioxidants in exercise nutrition. Sports Med 31:891–908. doi:10.2165/00007256-200131130-00001
Sinha R, Patterson BH, Mangels AR, Levander OA, Gibson T, Taylor PR, Block G (1993) Determinants of plasma vitamin E in healthy males. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2:473–479
Sohn HY, Krotz F, Gloe T, Keller M, Theisen K, Klauss V, Pohl U (2003) Differential regulation of xanthine and NAD(P)H oxidase by hypoxia in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Role of nitric oxide and adenosine. Cardiovasc Res 58:638–646. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(03)00262-1
Subudhi AW, Jacobs KA, Hagobian TA, Fattor JA, Fulco CS, Muza SR, Rock PB, Hoffman AR, Cymerman A, Friedlander AL (2004) Antioxidant supplementation does not attenuate oxidative stress at high altitude. Aviat Space Environ Med 75:881–888
Thurnham DI, Davies JA, Crump BJ, Situnayake RD, Davis M (1986) The use of different lipids to express serum tocopherol: lipid ratios for the measurement of vitamin E status. Ann Clin Biochem 23(Pt 5):514–520
Vollaard NB, Shearman JP, Cooper CE (2005) Exercise-induced oxidative stress:myths, realities and physiological relevance. Sports Med 35:1045–1062. doi:10.2165/00007256-200535120-00004
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Capeillere-Blandin C, Nguyen-Khoa T, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J, Jungers P, scamps-Latscha B (1996) Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Int 49:1304–1313. doi:10.1038/ki.1996.186
Acknowledgments
We thank the subjects for their contribution. We also thank Drs. Glen Foster and Andrew Beaudin for reviewing the manuscript. This study was funded by the “International Olympic Committee”, the “Ministère des sports français” and the “Direction Régionale de la Jeunesse et des Sports de la Région Auvergne”.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pialoux, V., Mounier, R., Brugniaux, J.V. et al. Thirteen days of “live high–train low” does not affect prooxidant/antioxidant balance in elite swimmers. Eur J Appl Physiol 106, 517–524 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1046-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1046-1