Abstract
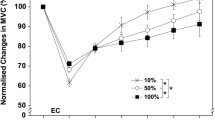
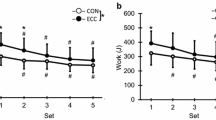
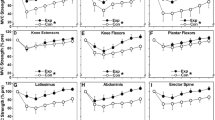
Since little is known about the repeated bout effect of more than two eccentric exercise bouts, this study compared muscle damage responses among four exercise bouts. Fifteen young (21.8 ± 1.9 years) men performed four bouts of 30 maximal isokinetic eccentric contractions of the elbow flexors every 4 weeks. Maximal voluntary elbow flexion isometric and concentric strength, range of motion at the elbow joint (ROM), upper arm circumference, blood markers of muscle damage, and muscle soreness were measured before and up to 120 h following each bout. Changes in all measures following the second to fourth bouts were significantly (P < 0.05) smaller than those after the first bout. The decreases in strength and ROM immediately after the fourth bout were significantly (P < 0.05) smaller than other bouts. It is concluded that the first bout confers the greatest adaptation, but further adaptation is induced when the exercise is repeated more than three times.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen TC (2003) Effects of a second bout of maximal eccentric exercise on muscle damage and EMG activity. Eur J Appl Physiol 89:115–121
Chen TC, Nosaka K (2006) Responses of elbow flexors to two strenuous eccentric exercise bouts separated by 3 days. J Strength Cond Res 28:108–116
Chen TC, Nosaka K, Sacco P (2007) Intensity of eccentric exercise, shift of optimum angle and the magnitude of repeated bout effect. J Appl Physiol 102:992–999
Clarkson PM, Hubal MJ (2002) Exercise-induced muscle damage in humans. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 81:S52–S69
Clarkson PM, Nosaka K, Braun B (1992) Muscle function after exercise-induced muscle damage and rapid adaptation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:512–520
Crameri RM, Aagaard P, Qvortrup K et al (2007) Myofibre damage in human skeletal muscle: effects of electrical stimulation versus voluntary contraction. J Physiol (Lond) 583:365–380
Evans WJ, Meredith CN, Cannon JG et al (1986) Metabolic changes following eccentric exercise in trained and untrained men. J Appl Physiol 61:1864–1868
Fujikake T, Hart R, Nosaka K (2008) Changes in B-mode ultrasound echo intensity following injection of bupivacaine hydrochloride to rat hind limb muscles in relation to histologic changes. Ultrasound Med Biol. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.10.008
Gregory JE, Morgan DL, Allen TJ, Proske U (2007) The shift in muscle’s length-tension relation after exercise attributed to increased series compliance. Eur J Appl Physiol 99:431–441
Ingalls CP, Gorden L, Warren JH et al (1998) E–C coupling failure in mouse EDL muscle after in vivo eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol 85:58–67
Jones C, Allen T, Talbot J, Morgan DL, Proske U (1997) Changes in the mechanical properties of human and amphibian muscle after eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 76:21–31
McHugh MP (2003) Recent advances in the understanding of the repeated bout effect: the protective effect against muscle damage from a single bout of eccentric exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 13:88–97
McHugh MP, Connolly DAJ, Eston RG et al (1999) Exercise-induced muscle damage and potential mechanisms for the repeated bout effect. Sports Med 27:157–170
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Clarkson PM (1987) Repeated high force eccentric exercise: effects on muscle pain and damage. J Appl Physiol 63:1381–1386
Newton MJ, Morgan GT, Sacco P et al (2008) Comparison of responses to strenuous eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors between resistance-trained and untrained men. J Strength Cond Res 22:597–607
Nosaka K, Clarkson PM (1996) Changes in indicators of inflammation after eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:953–961
Nosaka K, Newton M (2002) Concentric or eccentric training effect on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:63–69
Nosaka K, Sakamoto K, Newton M et al (2001) How long does the protective effect on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage last? Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1490–1495
Philippou A, Bogdanis GC, Nevill AM, Maridaki M (2004) Changes in the angle-force curve of human elbow flexors following eccentric and isometric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:237–244
Proske U, Morgan DL (2001) Muscle damage from eccentric exercise: mechanism, mechanical signs, adaptation and clinical applications. J Physiol (Lond) 537:333–345
Warren GL, Hermann KM, Ingalls CP et al (2000) Decreased EMG median frequency during a second bout of eccentric contractions. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:820–829
Whitehead NP, Weerakkody NS, Gregory JE, Morgan DL, Proske U (2001) Changes in passive tension of muscle in humans and animal after eccentric exercise. J Physiol (Lond) 532:593–604
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council of Taiwan for the financial support for this study (Contract #NSC 96-2413-H-415-011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T.C., Chen, HL., Lin, MJ. et al. Muscle damage responses of the elbow flexors to four maximal eccentric exercise bouts performed every 4 weeks. Eur J Appl Physiol 106, 267–275 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1016-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1016-7