Abstract
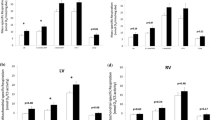
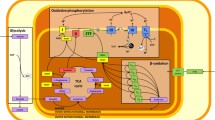
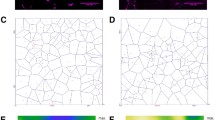
Three groups of sedentary male rats were exposed to intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (IHH) for 22 days (4 h/day, 5 days/week) in a hypobaric chamber at a simulated altitude of 5,000 m. Tibialis anterior (TA) and diaphragm (DG) were removed at the end of the programme (H group), and 20 or 40 days later (P20 and P40 groups). A control group (C) was maintained at sea-level pressure and their TA and DG were compared to those of the experimental rats at the end of the IHH programme, and also 20 and 40 days later. We measured the fibre morphometry and capillaries of each muscle. Our results demonstrate that IHH does not change the fibre type composition (with reference to either their contractile or oxidative properties) for most muscle regions of the muscles analysed analysed. We found few significant differences in muscle capillarity and fibre morphometry for TA after IHH. However, IHH did induce some statistically significant changes in DG: capillary density of the H rats (736 capillaries/mm2) increased compared to C animals (610 capillaries/mm2). Although IHH did not change the fibre capillarization or morphometric parameters of fast fibre types, we observed reductions ranging from 7 to 13% in fibre area, perimeter and diffusion distances between C and H for slow fibres. Moreover, these morphometric changes accounted for increases of 10–20% in capillarization, fibre unit area and fibre unit perimeter. This indicates that SO fibres are more sensitive to IHH than both fast fibre types.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmalki A, Fimbel S, Mayet Sornay MH, Sempore B, Favier R (1996) Aerobic capacity and skeletal muscle properties of normoxic and hypoxic rats in response to training. Pflugers Arch 431:671–679
Ariano MA, Armstrong RB, Edgerton VR (1973) Hindlimb muscle fiber populations of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem 21:51–55
Bender PR, Tucker A, Twietmeyer TA (1984) Skeletal-muscle capillarity during recovery from chronic hypoxic exposure. Microcirc Endothelium Lymphatics 1:71–85
Bigard AX, Brunet A, Guezennec CY, Monod H (1991) Skeletal-muscle changes after endurance training at high-altitude. J Appl Physiol 71:2114–2121
Boyer SJ , Blume FD (1984) Weight loss and changes in body composition at high altitude. J Appl Physiol 57:1580–1585
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol 23:369–379
Casas M, Casas H, Pagés T, Rama R, Ricart A, Ventura JL, Ibañez J, Rodríguez F, Viscor G (2000a) Intermittent hypobaric hypoxia induces altitude acclimation and improves the lactate threshold. Aviat Space Environm Med 71(2):125–130
Casas H, Casas M, Ricart A, Rama R, Ibáñez J, Palacios L, Rodriguez FA, Ventura JL, Viscor G, Pages T (2000b) Effectiveness of three short intermittent hypobaric hypoxia protocols: hematological responses. J Exerc Physiol On line 3:38–45
Cassin S, Gilbert RD, Bunnell CE, Johnson EM (1971) Capillary development during exposure to chronic hypoxia. Am J Physiol 220:448–451
Clanton TL, Klawitter PF (2001) Adaptive responses of skeletal muscle to intermittent hypoxia: the known and the unknown. J Appl Physiol 90:2476–2487
Desplanches D, Hoppeler H, Linossier MT, Denis C, Claassen H, Dormois D, Lacour JR, Geyssant A (1993) Effects of training in normoxia and normobaric hypoxia on human muscle ultrastructure. Pflugers Archiv 425:263–267
De Troyer A, Estenne M (1988) Functional anatomy of the respiratory muscles. Clin Chest Med 9:175–193
Desplanches D, Hoppeler H, Tuscher L, Mayet MH, Spielvogel H, Ferretti G, Kayser B, Leuenberger M, Grunenfelder A, Favier R (1996) Muscle tissue adaptations of high-altitude natives to training in chronic hypoxia or acute normoxia. J Appl Physiol 81:1946–1951
Desplanches D (1997) Structural and functional adaptations of skeletal muscle to weightlessness. Int J Sports Med 18:S259–S264
Deveci D, Marshall JM, Egginton S (2001) Relationship between capillary angiogenesis, fiber type, and fiber size in chronic systemic hypoxia. Am J Physiol 281:H241–H252
Deveci D, Marshall JM, Egginton S (2002) Chronic hypoxia induces prolonged angiogenesis in skeletal muscles of rat. Exp Physiol 87:287–291
Dubowitz V (1985) Muscle Biopsy: a Practical Approach. Bailliere Tindall, London
Eby SH, Banchero N (1976) Capillary density of skeletal muscle in Andean dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 151:795–798
Fouces V, Torrella JR, Palomeque J, Viscor G (1993) A histochemical ATPase method for the demonstration of the muscle capillary network. J Histochem Cytochem 41:283–289
Green HJ, Reichmann H, Pette D (1984) Inter- and intraspecies comparisons of fibre type distribution and succinate dehydrogenase activity in type I, IIA and IIB fibres of mammalian diaphragms. Histochemistry 81:67–73
Greene EC (1959) The Anatomy of the Rat. Trans Am Philosoph Soc 27
Ishihara A, Itoh K, Oishi Y, Itoh M, Hirofuji C, Hayashi H (1995) Effects of hypobaric hypoxia on histochemical fiber-type composition and myosin heavy-chain isoform component in the rat soleus muscle. Pflugers Archiv 429:601–606
Itoh K, Moritani T, Ishida K, Hirofuji C, Taguchi S, Itoh M (1990) Hypoxia-induced fibre type transformation in rat hindlimb muscles. Histochemical and electro-mechanical changes. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 60:331–336
Leon-Velarde F, Sanchez J, Bigard AX, Brunet A, Lesty C, Monge C (1993) High-Altitude tissue adaptation in Andean coots. J Comp Physiol B 163:52–58
Luedeke JD, McCall RD, Dillaman RM, Kinsey ST (2004) Properties of slow- and fast-twitch skeletal muscle from mice with an inherited capacity for hypoxic exercise. Comp Biochem Physiol 138A:373–382
Mantilla CB, Sieck GC (2003) Mechanisms underlying motor unit plasticity in the respiratory system. J Appl Physiol 94:1230–1241
McGuire M, MacDermott M, Bradford A (2003) Effects of chronic intermittent asphyxia on rat diaphragm and limb muscle contractility. Chest 123:875–881
Messonnier L, Freund H, Feasson L, Prieur F, Castells J, Denis C, Linossier MT, Geyssant A, Lacour JR (2001) Blood lactate exchange and removal abilities after relative high-intensity exercise: effects of training in normoxia and hypoxia. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:403–412
Nachlas MM, Tsou KC, De Souza E, Cheng CS, Seligman AM (1957) Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a new p-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole. J Histochem Cytochem 5:420–436
Panisello P, Torrella JR, Pagés T, Viscor G (2007) Capillary supply and fiber morphometry in rat myocardium after intermittent exposure to hypobaric hypoxia. High Altitude Med Biol 8:322–330
Polla B, D’Antona G, Bottinelli R, Reggiani C (2004) Respiratory muscle fibres: specialisation and plasticity. Thorax 59:808–817
Powers SK, Lawler J, Criswell D, Silverman H, Forster HV, Grinton S, Harkins D (1990) Regional metabolic differences in the rat diaphragm. J Appl Physiol 69:648–650
Reid MB, Parsons DB, Giddings CJ, Gonyea WJ, Johnson RL (1992) Capillaries measured in canine diaphragm by 2 methods. Anat Rec 234:49–54
Ricart A, Casas H, Casas M, Pagés T, Palacios L, Rama R, Rodríguez FA, Viscor G, Ventura JL (2000) Acclimatization near home? Early respiratory changes after short-term intermittent exposure to simulated altitude. Wilderness Environm Med 11:84–88
Richalet JP, Bittel J, Herry JP, Savourey G, Le Trong JL, Auvert JF, Janin C (1992) Use of a hypobaric chamber for pre-acclimatization before climbing Mount Everest. Int J Sports Med 13:S216–S220
Rodríguez FA, Casas H, Casas M, Pagés T, Rama R, Ricart A, Ventura JL, Ibáñez J, Viscor G (1999) Intermittent hypobaric hypoxia stimulates erythropoiesis and improves aerobic capacity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:264–268
Rodriguez FA, Ventura JL, Casas M, Casas H, Pagés T, Rama R, Ricart A, Palacios L, Viscor G (2000) Erythropoietin acute reaction and haematological adaptations to short intermittent hypobaric hypoxia. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:170–177
Rose MS, Houston CS, Fulco CS, Coates G, Sutton JR, Cymerman A (1988) Operation Everest. II Nutrition and body composition. J Appl Physiol 65:2545–2551
Sexton WL, Poole DC (1995) Costal diaphragm blood-flow heterogeneity at rest and during exercise. Respir Physiol 101:171–182
Sieck GC, Sacks RD, Blanco CE (1987) Absence of regional differences in the size and oxidative capacity of diaphragm muscle fibers. J Appl Physiol 63:1076–1082
Sieck GC (1988) Diaphragm muscle. Structural and functional organization. Clin Chest Med 9:195–210
Sillau AH, Banchero N (1977) Effects of hypoxia on capillary density and fiber composition in rat skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch 370:227–232
Siqués P, Brito J, León-Velarde F, Barrios L, Cruz JJ, López V, Herruzo R (2006) Time course of cardiovascular and hematological responses in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (4600 m). High Alt Med Biol 7:72–80
Snyder GK, Wilcox EE, Burnham EW (1985) Effects of hypoxia on muscle capillarity in Rats. Respir Physiol 62:135–140
Sutton JR, Reeves JT, Wagner PD, Groves BM, Cyberman A, Malconian MK, Rock PB, Young PM, Walter SD, Houston CS (1988) Operation Everest II: oxygen transport during exercise at extreme simulated altitude. J Appl Physiol 64:1039–1321
Taylor CR, Weibel ER (1981) Design of the mammalian respiratory system. I. Problem and strategy. Respir Physiol 44:1–10
Thomas T, Marshall JM (1997) The roles of adenosine in regulating the respiratory and cardiovascular systems in chronically hypoxic, adult rats. J Physiol 501:439–447
Torrella JR, Whitmore J, Casas M, Fouces V, Viscor G (2000) Capillarity, fibre types and fibre morphometry in different sampling sites across and along the tibialis anterior muscle of the rat. Cells Tissues Organs 167:153–162
Viscor G, Torrella JR, Fouces V, Palomeque J (1992) Skeletal muscle capillarization and fiber types in urban and homing pigeons (Columba livia). Comp Biochem Physiol 101A:751–757
Wagner PD, Sutton JR, Reeves JT, Cymerman A, Groves BM, Malconian MK (1987) Operation Everest II: pulmonary gas exchange during a simulated ascent of Mt Everest. J Appl Physiol 63:2348–2359
Ward MP, Milledge JS, West JB (2000) High Altitude Medicine an Physiology, 3rd edn. Arnold, London
Weibel ER (1984) The Pathway for oxygen: structure and function in the mammalian respiratory system. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
West JB (1993) Acclimatization and tolerance to extreme altitude. J Wild Med 4:17–26
Yamashita H, Nakanishi K, Tajima F, Sato Y, Kizaki T, Ohishi S, Ohno H (1994) Chronic exposure to simulated altitude does not increase angiogenic activity in skeletal-muscle of rats. Tohoku J Exp Med 172:375–379
Zobundzija M, Novak R, Kozaric Z, Mihelic D, Brkic A (1998) The morphohistochemical analysis of the pars costalis and pars lumbalis diaphragmae in lambs. Vet Med Czech 43:357–360
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant BFI2003-03439 as part of the Plan Nacional I+D+I of the Spanish Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia. The authors wish to thank Robin Rycroft and Christopher Evans (UB Language Advisory Service) for their help in editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panisello, P., Torrella, J.R., Esteva, S. et al. Capillary supply, fibre types and fibre morphometry in rat tibialis anterior and diaphragm muscles after intermittent exposure to hypobaric hypoxia. Eur J Appl Physiol 103, 203–213 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0691-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0691-0