Abstract
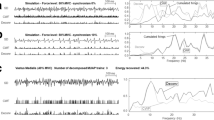
Intramuscular and surface electromyographic (EMG) activities were recorded from the left and right upper trapezius muscle of eight healthy male subjects during 5-min long static contractions at 2% and 5% of the maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) force. Intramuscular signals were detected by wire electrodes while surface EMG signals were recorded with linear adhesive electrode arrays. The surface EMG signals were averaged using the potentials extracted from the intramuscular EMG decomposition as triggers. The conduction velocity of single motor units (MUs) was estimated over time from the averaged surface potentials while average rectified value and mean power spectral frequency were computed over time from 0.5 s epochs of surface EMG signal. It was found that (1) MUs were progressively recruited after the beginning of sustained contractions of the upper trapezius muscle at 2% and 5% MVC, (2) the conduction velocity of the MUs active since the beginning of the contraction significantly decreased over time, and (3) although the CV of single MUs significantly decreased, the mean power spectral frequency of the surface EMG did not show a consistent trend over time. It was concluded that spectral surface EMG analysis, being affected by many physiological mechanisms, may show limitations for the objective assessment of localized muscle fatigue during low force, sustained contractions. On the contrary, single motor unit conduction velocity may provide an early indication of changes in muscle fiber membrane properties with sustained activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendt-Nielsen L, Mills KR (1985) The relationship between mean power frequency of the EMG spectrum and muscle fibre conduction velocity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 60:130–134
Arendt-Nielsen L, Mills KR (1988) Muscle fibre conduction velocity, mean power frequency, mean EMG voltage and force during submaximal fatiguing contractions of human quadriceps. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 58:20–25
Bigland-Ritchie B, Donovan EF, Roussos CS (1981) Conduction velocity and EMG power spectrum changes in fatigue of sustained maximal efforts. J Appl Physiol 51:1300–1305
Dimitrov GV, Dimitrova NA (1998a) Fundamentals of power spectra of extracellular potentials produced by a skeletal muscle fibre of finite length. Part I: effect of fibre anatomy. Med Eng Phys 20:580–587
Dimitrov GV, Dimitrova NA (1998b) Fundamentals of power spectra of extracellular potentials produced by a skeletal muscle fibre of finite length. Part II: effect of parameters altering with functional state. Med Eng Phys 20:702–707
Dimitrova NA, Dimitrov GV (2003) Interpretation of EMG changes with fatigue: facts, pitfalls, and fallacies. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 13:13–36
Fallentin N, Jorgensen K, Simonsen EB (1993) Motor unit recruitment during prolonged isometric contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 67:335–341
Farina D, Muhammad W, Fortunato E, Meste O, Merletti R, Rix H (2001) Estimation of single motor unit conduction velocity from surface electromyogram signals detected with linear electrode arrays. Med Biol Eng Comput 39:225–236
Farina D, Fosci M, Merletti R (2002a) Motor unit recruitment strategies investigated by surface EMG variables. J Appl Physiol 92:235–247
Farina D, Arendt-Nielsen L, Merletti R, Graven-Nielsen T (2002b) Assessment of single motor unit conduction velocity during sustained contractions of the tibialis anterior muscle with advanced spike triggered averaging. J Neurosci Methods 115:1–12
Farina D, Madeleine P, Graven-Nielsen T, Merletti R, Arendt-Nielsen L (2002c) Standardising surface electromyogram recordings for assessment of activity and fatigue in the human upper trapezius muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:469–478
Farina D, Gazzoni M, Merletti R (2003a) Assessment of low back muscle fatigue by surface EMG signal analysis: methodological aspects. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 13:319–332
Farina D, Kallenberg LA, Merletti R, Hermens HJ (2003b) Effect of side dominance on myoelectric manifestations of muscle fatigue in the human upper trapezius muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:480–488
Farina D, Schulte E, Merletti R, Rau G, Disselhorst-Klug C (2003c) Single motor unit analysis from spatially filtered surface EMG signals. Part I: spatial selectivity. Med Biol Eng Comput 41:330–337
Farina D, Merletti R, Enoka RM (2004a) The extraction of neural strategies from surface EMG. J Appl Physiol 96:1486–1495
Farina D, Gazzoni M, Camelia F (2004b) Low threshold motor unit membrane properties vary with contraction intensity during sustained activation with surface EMG visual feedback. J Appl Physiol 96:1505–1515
Garland SJ, Enoka RM, Serrano LP, Robinson GA (1994) Behavior of motor units in human biceps brachii during a submaximal fatiguing contraction. J Appl Physiol 76:2411–2419
Gazzoni M, Farina D, Merletti R (2004) A new method for the extraction and classification of single motor unit action potentials from surface EMG signals. J Neurosci Methods 136:165–177
Hagberg C, Hagberg M (1989) Surface EMG amplitude and frequency dependence on exerted force for the upper trapezius muscle: a comparison between right and left sides. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:641–645
Hansson GA, Nordander C, Asterland P, Ohlsson K, Strömberg U, Skerfving S, Rempel D (2000) Sensitivity of trapezius electromyography to differences between work tasks—influence of gap definition and normalisation methods. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 10:103–115
Jensen C, Nilsen K, Hansen K, Westgaard RH (1993) Trapezius muscle load as a risk indicator for occupational shoulder-neck complaints. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 64:415–423
Kleine BU, Blok JH, Oostenveld R, Praamstra P, Stegeman DF (2000) Magnetic stimulation-induced modulations of motor unit firings extracted from multi-channel surface EMG. Muscle Nerve 23:1005–1015
Lindstrom L, Magnusson R (1977) Interpretation of myoelectric power spectra: a model and its applications. Proc IEEE 65:653–662
Lindstrom L, Magnusson R, Petersen I (1970) Muscular fatigue and action potential conduction velocity changes studied with frequency analysis of EMG signals. Electromyography 10:341–356
Madeleine P, Lundager B, Voigt M, Arendt-Nielsen L (1999) Shoulder muscle coordination under chronic and experimental neck-shoulder pain. An occupational pain study. Eur J Appl Physiol 79:127–140
Madeleine P, Farina D, Merletti R, Arendt-Nielsen L (2002) Upper trapezius muscle mechanomyographic and electromyographic activity in humans during low force fatiguing and non-fatiguing contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol 87:327–336
Merletti R, Knaflitz M, De Luca CJ (1990) Myoelectric manifestations of fatigue in voluntary and electrically elicited contractions. J Appl Physiol 69:1810–1820
Nieminen H, Hameenoja S (1995) Quantification of the static load component in muscle work using nonlinear filtering of surface EMG. Ergonomics 38:1172–1183
Öberg T, Sandsjo L, Kadefors R (1990) Electromyogram mean power frequency in non-fatigued trapezius muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 61:362–369
Öberg T, Sandsjo L, Kadefors R (1994) Subjective and objective evaluation of shoulder muscle fatigue. Ergonomics 37:1323–1333
Pozzo M, Bottin A, Ferrabone R, Merletti R (2004) Sixty-four channel wearable acquisition system for long-term surface EMG recording with electrode arrays. Med Biol Eng Comput 42:455–466
Sjogaard G, Jensen BR, Hargens AR, Sogaard K (2004) Intramuscular pressure and EMG relate during static contractions but dissociate with movement and fatigue. J Appl Physiol 96:1522–1529
Stålberg E (1966) Propagation velocity in human muscle fibers in situ. Acta Physiol Scand 287:1–112
Westgaard RH (1999) Muscle activity as a releasing factor for pain in the shoulder and neck. Cephalalgia 25:1–8
Zennaro D, Läubli T, Wellig P, Krebs D, Schnoz M, Klipstein A, Krueger H (2002) A method to test reliability and accuracy of the decomposition of multi-channel long-term intramuscular EMG signal recordings. Int J Ind Ergonom 30:211–224
Zennaro D, Wellig P, Koch VM, Moschytz GS, Laubli T (2003a) A software package for the decomposition of long-term multichannel EMG signals using wavelet coefficients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50:58–69
Zennaro D, Läubli T, Krueger H (2003b) Accuracy of motor unit identification in two different positions of the human trapezius muscle during prolonged computer work. Eur J Appl Physiol 89:526–535
Zwarts MJ, Van Weerden TW, Haenen HT (1987) Relationship between average muscle fibre conduction velocity and EMG power spectra during isometric contraction, recovery and applied ischemia. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 56:212–216
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Shared Cost Project ‘Neuromuscular assessment in the Elderly Worker’ (NEW) (Contract no. QLRT-2000-00139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farina, D., Zennaro, D., Pozzo, M. et al. Single motor unit and spectral surface EMG analysis during low-force, sustained contractions of the upper trapezius muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 96, 157–164 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1261-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1261-8