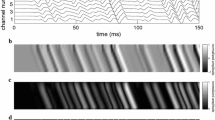
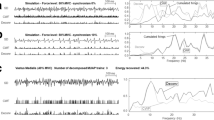
Abstract
This work addresses the problem of estimating the conduction velocity (CV) of single motor unit (MU) action potentials from surface EMG signals detected with linear electrode arrays during voluntary muscle contractions. In ideal conditions, that is without shape or scale changes of the propagating signals and with additive white Gaussian noise, the maximum likelihood (ML) is the optimum estimator of delay. Nevertheless, other methods with computational advantages can be proposed; among them, a modified version of the beamforming algorithm is presented and compared with the ML estimator. In real cases, the resolution in delay estimation in the time domain is limited because of the sampling process. Transformation to the frequency domain allows a continuous estimation. A fast, high-resolution implementation of the presented multichannel techniques in the frequency domain is proposed. This approach is affected by a negligible decrease in performance with respect to ideal interpolation. Application of the ML estimator, based on two-channel information, to ten firings of each of three MUs provides a CV estimate affected by a standard deviation of 0.5 ms−1; the modified beamforming and ML estimators based on five channels provide a CV standard deviation of less than 0.1 ms−1 and allow the detection of statistically significant differences between the CVs of the three MUs. CV can therefore be used for MU classification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergamo, R., Gazzoni, M., Farina, D., Lantermo, A., Merletti, R., Sanfilippo, C., andTitolo, M. (1999): ‘Multichannel surface EMG of muscles of the hand and forearm’. Proc. PROCID Symp. Muscular disorders in computer users, Copenhagen, Denmark, pp. 198–202
Bonato, P., Balestra, G., Knaflitz, M., andMerletti, R. (1990): ‘Comparison between muscle fibre conduction velocity estimation techniques: spectral matching versus crosscorrelation’. Proc. 8th Int. ISEK Congress, pp. 19–22
Brody, L., Pollock, M., Roy, S., De Luca, C. J., andCelli, B. (1991): ‘pH induced effects on median frequency and conduction velocity of the myoelectric signal’,J. Appl. Physiol.,71, pp. 1878–1885
Davies, S., andParker, P. (1987): ‘Estimation of myoelectric conduction velocity distribution’,IEEE Trans.,BME-34, pp. 98–105
Farina, D., Merletti, R., andDimanico, U. (1998): ‘Non-invasive identification of motor units with linear electrode arrays’. Proc. XII ISEK Congress, Montreal, pp. 50–51
Farina, D., andRainoldi, A. (1999): ‘Compensation of the effect of subcutaneous tissue layers on surface EMG: a simulation study’,Med. Eng. Phys.,21, pp. 487–496
Farina, D., Fortunato, E., andMerletti, R. (2000): ‘Non invasive estimation of motor unit conduction velocity distribution using linear electrode arrays’,IEEE Trans.,BME-47, pp. 380–388
Farina, D., andMerletti, R. (2000): ‘Comparison of algorithms for estimation of EMG variables estimation during isometric constant force contractions’,J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol.,10, pp. 337–350
Farina, D., andMerletti, R. (2001): ‘A novel approach for precise simulation of the EMG signal detected by surface electrodes’ to be published inIEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.
Gazzoni, M., Farina, D., Rainoldi, A., andMerletti, R. (2000): ‘Surface EMG signal decomposition’. Proc. XIII ISEK Congress, Sapporo, pp. 403–404
Hakansson, C. H. (1956): ‘Conduction velocity and amplitude of the action potential as related to circumference in the isolated fiber of frog muscle’,Acta Physiol. Scand.,37, pp. 14–22
Johnson, D. H., andDuolgeon, D. E. (1993): ‘Array signal processing-Concepts and techniques’, inOppenheim, A. V. (Ed): (Prentice Hall Signal Processing Series)
Lo Conte, L., andMerletti, R. (1995): ‘Advances in processing of surface myoelectric signals: Part 2’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,33, pp. 362–372
Masuda, T., Miyano, H., andSadoyama, T. (1985a): ‘The position of innervation zones in the biceps brachii investigated by surface electromyography’,IEEE Trans.,BME-32, pp 36–42
Masuda, T., Miyano, H., andSadoyama, T. (1985b): ‘A surface electrode array for detecting action potential trains of single motor units’,Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,60, pp. 435–443
Masuda, T., andSadoyama, T. (1986): ‘The propagation of single motor unit action potentials detected by a surface electrode array’,Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,63, pp. 590–598
McGill, K. C., andDorfman, L. J. (1984): ‘High resolution alignment of sampled waveforms’,IEEE Trans.,BME-31, pp. 462–470
Merletti, R., andDe Luca, C. J. (1989): ‘New techniques in surface electromyography’, inDesmedt, J. E. (Ed.): ‘Computer aided electromyography and expert systems’ (Elsevier Science Publisher)
Merletti, R., Knaflitz, M., andDe Luca, C. J. (1990): ‘Myoelectric manifestations of muscle fatigue during voluntary and electrically elicited contractions’,J. Appl. Physiol.,68, pp. 1657–1667
Merletti, R., andLo Conte, L. (1995): ‘Advances in processing of surface myoelectric signals: Part 1’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,33, pp. 373–384
Merletti, R., Lo Conte, L., Avignone, E., andGuglielminotti, P. (1999a): ‘Modelling of surface EMG signals. Part I: model implementation’,IEEE Trans.,BME-46, pp. 810–820
Merletti, R., Roy, S., Kupa, E., Roatta, S., andGranata, A. (1999b): ‘Modelling of surface EMG signals. Part II: model based interpretation of surface EMG signals’,IEEE Trans.,BME-46, pp. 821–829
Merletti, R., Farina, D., andGranata, A. (1999c): ‘Non-invasive assessment of motor unit properties with linear electrode arrays’ inComi, G.,et al. (Eds): ‘Clinical neurophysiology: from receptors to perception’ (Elsevier Science Publisher)
Merletti, R., Schieroni, M. P., Farina, D., Brero, M., andGazzoni, M. (1999d): ‘Non-invasive assessment of the skeletal musculature in the elderly’. Proc. XI International Congress of EMG and Clinical Neurophysiology, Prague
Morimoto, S., andMasuda, T. (1984): ‘Dependence of conduction velocity on spike interval during voluntary muscular contraction in human motor units’,Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.,53, pp. 191–195
Muhammad, W., Meste, O., andRix, H. (2000): ‘Comparison of single and multiple time delay estimators: application to muscle fiber conduction velocity estimation’. Research report RR-0015, Lab. 135, University of Nice, Sophia Antipolis, France
Nishizono, H., Kurata, H., andMiyashita, M. (1989): ‘Muscle fiber conduction velocity related to stimulation rate’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,72, pp. 529–534
Nishizono, H., Fujimoto, T., Ohtake, H., andMiyashita, M. (1990): ‘Muscle fiber conduction velocity and contractile properties estimated from surface electrode arrays’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,75, pp. 75–81
Press, H., Vetterling, T., Teukolsky, S. A., andFlannery, B. P. (1996): ‘Numerical recipes in C′ (Cambridge University Press)
Rainoldi, A., Galardi, G., Maderna, L., Comi, G., Lo Conte, L., andMerletti, R. (1999): ‘Repeatability of surface EMG variables during voluntary isometric contractions of the biceps brachii muscle’,J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol.,9, pp. 105–119
Rix, H., andMalengé, J. P. (1980): ‘Detecting small variation in shape’,IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern.,10, pp. 90–96
Rix, H., andMeste, O. (1997): ‘Fine structure of ECG signal using wavelet transform’, inD'Attellis, C. E., andFernandez-Berdaguer, E. M. (Eds): ‘Wavelet theory and harmonic analysis in applied sciences’ (Birkhauser Publisher)
Roy, S. H., De Luca, C. J., andSchneider, J. (1986): ‘Effects of electrode location on myoelectric conduction velocity and median frequency estimates’,J. Appl. Physiol.,61, pp. 1510–1517
Sadoyama, T., Masuda, T., andMiyano, T. (1985): ‘Optimal conditions for the measurement of muscle fiber conduction velocity using surface electrode arrays’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,23, pp. 339–342
Schneider, J., Silny, J., andRau, G. (1991): ‘Influence of tissue inhomogeneities on noninvasive muscle fiber conduction velocity measurements investigated by physical and numerical modeling’,IEEE Trans.,BME-38, pp. 851–860
Stalberg, E., Nandekar, S., Sanders, D., andFalck, B. (1996): ‘Quantitative motor unit action potential analysis’,J. Clin. Neurophysiol.,13, pp. 401–422
Theodoridis, S., andKoutroumbas, K. (1999): ‘Pattern recognition’ (Academic Press)
Troni, W., Cantello, R., andRainero, I. (1983): ‘Conduction velocity along human muscle fibersin situ’Neurology,33, pp. 1453–1459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farina, D., Muhammad, W., Fortunato, E. et al. Estimation of single motor unit conduction velocity from surface electromyogram signals detected with linear electrode arrays. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 39, 225–236 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344807
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344807